Chapter 9 answers
... manage to hold together until cell division and mitosis occurred, the two daughter cells would have two different copies of the DNA; one would have the old version, with cytosine, the second would have the new version with adenine. Second, if it were to be read by an mRNA molecule, one of the codons ...
... manage to hold together until cell division and mitosis occurred, the two daughter cells would have two different copies of the DNA; one would have the old version, with cytosine, the second would have the new version with adenine. Second, if it were to be read by an mRNA molecule, one of the codons ...
what is mutation?
... INSERTION: when genetic material is put into another region of DNA. This may be the insertion of 1 or more bases, or it can be part of one chromosome being inserted into another, non-homologous chromosome MISSENSE: a change in DNA sequence that changes the codon to be different amino acid. Not all m ...
... INSERTION: when genetic material is put into another region of DNA. This may be the insertion of 1 or more bases, or it can be part of one chromosome being inserted into another, non-homologous chromosome MISSENSE: a change in DNA sequence that changes the codon to be different amino acid. Not all m ...
Mutations - Fort Bend ISD
... coded proteins in the ribosomes. • tRNA is the go-for that brings the amino acids to the ribosomes to make the protein). ...
... coded proteins in the ribosomes. • tRNA is the go-for that brings the amino acids to the ribosomes to make the protein). ...
Gene Regulation and Mutation Notes and Questions
... in which one nucleotide base replaces another • Point mutations affect only one codon, so they affect only one amino acid in a peptide chain • It may or may not have serious effects on an organism. It depends on where the mutation occurs and how it affects the protein for which it codes • It can be ...
... in which one nucleotide base replaces another • Point mutations affect only one codon, so they affect only one amino acid in a peptide chain • It may or may not have serious effects on an organism. It depends on where the mutation occurs and how it affects the protein for which it codes • It can be ...
Mutations
... These are the sickle-shaped blood cells of someone with sickle cell anemia. Sickle cell anemia is the result of a point mutation, a change in just one nucleotide in the gene for hemoglobin. This mutation causes the hemoglobin in red blood cells to distort to a sickle shape when deoxygenated. The sic ...
... These are the sickle-shaped blood cells of someone with sickle cell anemia. Sickle cell anemia is the result of a point mutation, a change in just one nucleotide in the gene for hemoglobin. This mutation causes the hemoglobin in red blood cells to distort to a sickle shape when deoxygenated. The sic ...
Mutations
... A change in the DNA sequence that is present in <1% of the population Mutations can happen at the DNA level or at the chromosome level Can affect any part of the genome (introns, exons, etc.) A polymorphism is also a change in a single nucleotide but occurs in >1% of the population Change in DNA Al ...
... A change in the DNA sequence that is present in <1% of the population Mutations can happen at the DNA level or at the chromosome level Can affect any part of the genome (introns, exons, etc.) A polymorphism is also a change in a single nucleotide but occurs in >1% of the population Change in DNA Al ...
Mutations Learning goals Mutation Where Mutations Occur
... Where Mutations Occur – Mutations occur in regular body cells • 1. Occurs during mitosis (cell division) • 2. Affects the person, not the offspring • 3. Affects the function of the cell – This may cause cancer ...
... Where Mutations Occur – Mutations occur in regular body cells • 1. Occurs during mitosis (cell division) • 2. Affects the person, not the offspring • 3. Affects the function of the cell – This may cause cancer ...
• •
... Point Mutations : Changes in single DNA nucleotides. o A missense mutation substitutes a different amino acid for the original one. Example: Sickle cell disease results from a single base change Remember! In RNA, the nucleotide base uracil replaces thymine. TEMPLATE DNA code CTC (Glutamine - glu) -m ...
... Point Mutations : Changes in single DNA nucleotides. o A missense mutation substitutes a different amino acid for the original one. Example: Sickle cell disease results from a single base change Remember! In RNA, the nucleotide base uracil replaces thymine. TEMPLATE DNA code CTC (Glutamine - glu) -m ...
Biology Name____________________ 10.2 wks Period ______ De
... _______________2. Some of these may play a role in causing the different types of cancer. _______________3. A substitution occurs and one nucleotide is substituted for another. _______________4. In this type of gene mutation, a nucleotide is left out. _______________5. This causes such a small chang ...
... _______________2. Some of these may play a role in causing the different types of cancer. _______________3. A substitution occurs and one nucleotide is substituted for another. _______________4. In this type of gene mutation, a nucleotide is left out. _______________5. This causes such a small chang ...
Slide 1
... homologous chromosomes breaks and binds to the other. Usually this sort of mutation is lethal ...
... homologous chromosomes breaks and binds to the other. Usually this sort of mutation is lethal ...
D5 Phylogeny and systematics – summary of mark
... more similar the amino acid sequence, the more closely related the species are; eg cytochrome C / hemoglobin / chlorophyll / other valid example; DNA / mitochondrial DNA / gene nucleic acid sequence analysed; differences due to mutations at a certain rate / the number of differences is proportional ...
... more similar the amino acid sequence, the more closely related the species are; eg cytochrome C / hemoglobin / chlorophyll / other valid example; DNA / mitochondrial DNA / gene nucleic acid sequence analysed; differences due to mutations at a certain rate / the number of differences is proportional ...
Chapter 3 Section 4
... The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins. Proteins help determine the size, shape and other traits of organisms. Nitrogen bases form “rungs” of DNA ladder. The order of the nitrogen bases along a gene form a genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be pr ...
... The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins. Proteins help determine the size, shape and other traits of organisms. Nitrogen bases form “rungs” of DNA ladder. The order of the nitrogen bases along a gene form a genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be pr ...
Unit2Day2
... cave fish populations is caused by independently derived mutations that prevents the Oca2 gene from producing a functional protein (LOF mutations) ...
... cave fish populations is caused by independently derived mutations that prevents the Oca2 gene from producing a functional protein (LOF mutations) ...
Ch. 8 Mutations
... What is a mutation? A mutation is any change in an organism’s DNA There are two types of mutations a) Gene mutation. Influences usually only one gene b) Chromosomal mutations. Changes in the structure of a chromosomes or the number of chromosomes ...
... What is a mutation? A mutation is any change in an organism’s DNA There are two types of mutations a) Gene mutation. Influences usually only one gene b) Chromosomal mutations. Changes in the structure of a chromosomes or the number of chromosomes ...
Genetic Mutations
... change in the polypeptide chain. It is caused by errors that occur during DNA replication. ...
... change in the polypeptide chain. It is caused by errors that occur during DNA replication. ...
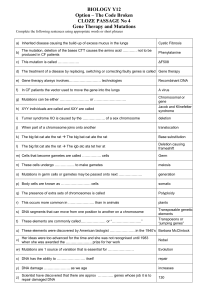
Cloze passage 4
... Gene Therapy and Mutations Complete the following sentences using appropriate words or short phrases a) Inherited disease causing the build-up of excess mucus in the lungs ...
... Gene Therapy and Mutations Complete the following sentences using appropriate words or short phrases a) Inherited disease causing the build-up of excess mucus in the lungs ...
Mutations Notes - Mr. Coleman`s Biology
... Factors that cause mutations. Mutagens can be chemical, radiation, high temperature, X-Rays, or UV light. ...
... Factors that cause mutations. Mutagens can be chemical, radiation, high temperature, X-Rays, or UV light. ...
What are mutations and how do they affect the production
... Aim 25: What are mutations and how do they affect the production of proteins? What is a Mutation? ...
... Aim 25: What are mutations and how do they affect the production of proteins? What is a Mutation? ...
Unit 8 Molecular Genetics: Chp 12 Mutations Notes PPT
... mRNA is transcribed from DNA. • What might happen if one base is deleted from the DNA? • The transcribed mRNA would also be affected. ...
... mRNA is transcribed from DNA. • What might happen if one base is deleted from the DNA? • The transcribed mRNA would also be affected. ...
12.4 Mutations
... • Insertions and deletions • They shift the reading frame of the genetic message… remember bases are read in groups of three • Entire protein can be ruined ...
... • Insertions and deletions • They shift the reading frame of the genetic message… remember bases are read in groups of three • Entire protein can be ruined ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.