Name
... (d) b and c, but not a 2. A nonsense mutation: (a) causes one amino acid to be substituted for another in a protein chain. (b) results from the deletion of one or more bases, leading to a shift in the reading frame. (c) results from the insertion of one of more bases, leading to a shift in the readi ...
... (d) b and c, but not a 2. A nonsense mutation: (a) causes one amino acid to be substituted for another in a protein chain. (b) results from the deletion of one or more bases, leading to a shift in the reading frame. (c) results from the insertion of one of more bases, leading to a shift in the readi ...
4-14
... Subject: Gene mutation. Reading in ‘An introduction to genetic analysis’ (Griffiths et al., 7th edition) Chapter 15: Gene mutation ________________________________________________________________________ Key concepts: How DNA changes affect phenotype (15-1, 15-2) ...
... Subject: Gene mutation. Reading in ‘An introduction to genetic analysis’ (Griffiths et al., 7th edition) Chapter 15: Gene mutation ________________________________________________________________________ Key concepts: How DNA changes affect phenotype (15-1, 15-2) ...
DNA, Mutations, Chromosomes, and Reproduction Review
... • Any change in a gene or chromosome – Can cause a cell to produce an incorrect protein during protein synthesis – The trait or phenotype may be different ...
... • Any change in a gene or chromosome – Can cause a cell to produce an incorrect protein during protein synthesis – The trait or phenotype may be different ...
Protein Synthesis Review Concepts • Protein synthesis occurs in two
... Protein Synthesis Review Concepts • Protein synthesis occurs in two stages: transcription and translation • Transcription is the process in which information is copied from DNA to RNA • Translation is the process in which information from RNA codes for amino acids • Cells with the same DNA can speci ...
... Protein Synthesis Review Concepts • Protein synthesis occurs in two stages: transcription and translation • Transcription is the process in which information is copied from DNA to RNA • Translation is the process in which information from RNA codes for amino acids • Cells with the same DNA can speci ...
DNA Replication, Transcription, and Translation STUDY GUIDE
... What are the main functions of DNA polymerase? The main function of tRNA is to: What is the term for a three-nucleotide sequence that codes for an amino acid? How many amino acids are used to make up the all of the proteins in the human body? A tRNA that carries the amino acid methionine pairs with ...
... What are the main functions of DNA polymerase? The main function of tRNA is to: What is the term for a three-nucleotide sequence that codes for an amino acid? How many amino acids are used to make up the all of the proteins in the human body? A tRNA that carries the amino acid methionine pairs with ...
Mutations - nimitz163
... • When a part of a chromosome is left out, a deletion occurs. • When part of a chromatid breaks off and attaches to its sister chromatid, an insertion occurs. • The result is a duplication of genes on the same chromosome. • When part of a chromosome breaks off and reattaches backwards, an inversion ...
... • When a part of a chromosome is left out, a deletion occurs. • When part of a chromatid breaks off and attaches to its sister chromatid, an insertion occurs. • The result is a duplication of genes on the same chromosome. • When part of a chromosome breaks off and reattaches backwards, an inversion ...
Higher Biology: Genome - Gene Mutation
... After a deletion or insertion the open reading frame is moved one base pair forward or backward. ...
... After a deletion or insertion the open reading frame is moved one base pair forward or backward. ...
DNA Structure and Function
... D. This mutation causes a change in the protein that forms during translation. 4. What is the purpose of replication? P152 A. to make an RNA template from DNA B. to produce copies of a DNA molecule C. to move mRNA through the ribosome D. to change the number, type, or order of bases in DNA ...
... D. This mutation causes a change in the protein that forms during translation. 4. What is the purpose of replication? P152 A. to make an RNA template from DNA B. to produce copies of a DNA molecule C. to move mRNA through the ribosome D. to change the number, type, or order of bases in DNA ...
Mutations & Genetic Engineering
... • A change in the reading pattern of the DNA • Causes: – Deletions • Sections of DNA are missing • Example: Williams Syndrome ...
... • A change in the reading pattern of the DNA • Causes: – Deletions • Sections of DNA are missing • Example: Williams Syndrome ...
Guided Notes - Boone County Schools
... ● The big thing to remember: The only way a mutation can be passed onto the next generation is if: ...
... ● The big thing to remember: The only way a mutation can be passed onto the next generation is if: ...
Slide 1
... Mutation: is a change in the genetic material Mutations can be neutral, beneficial, or harmful Mutagen: Agent that causes mutations Spontaneous mutations: Occur in the absence of a mutagen ...
... Mutation: is a change in the genetic material Mutations can be neutral, beneficial, or harmful Mutagen: Agent that causes mutations Spontaneous mutations: Occur in the absence of a mutagen ...
MUTATIONS
... Defined: A change in an organism’s DNA. • Many kinds of mutations can occur, especially during replication. ...
... Defined: A change in an organism’s DNA. • Many kinds of mutations can occur, especially during replication. ...
MUTATIONS CAN OCCUR IN SOMATIC OR IN REPRODUCTIVE
... Caused by various damages to the structure of a chromosome; often caused by a toxic chemical or radiation particle ...
... Caused by various damages to the structure of a chromosome; often caused by a toxic chemical or radiation particle ...
How many phosphate bonds are required to build a protein with 50
... How many phosphate bonds are required to build a protein with 50 amino acids? What kind of cancer causing allele is the result of a loss of function mutation? What initiates transcription from the early promoter of the Sxl gene? is the function of amino acyl RNA synthetase? What In recombinant DNA t ...
... How many phosphate bonds are required to build a protein with 50 amino acids? What kind of cancer causing allele is the result of a loss of function mutation? What initiates transcription from the early promoter of the Sxl gene? is the function of amino acyl RNA synthetase? What In recombinant DNA t ...
Mutations - Warren County Schools
... • Mutations happen regularly • Almost all mutations are neutral • Chemicals & UV radiation cause mutations • Many mutations are repaired by enzymes ...
... • Mutations happen regularly • Almost all mutations are neutral • Chemicals & UV radiation cause mutations • Many mutations are repaired by enzymes ...
Chapter 9 answers
... manage to hold together until cell division and mitosis occurred, the two daughter cells would have two different copies of the DNA; one would have the old version, with cytosine, the second would have the new version with adenine. Second, if it were to be read by an mRNA molecule, one of the codons ...
... manage to hold together until cell division and mitosis occurred, the two daughter cells would have two different copies of the DNA; one would have the old version, with cytosine, the second would have the new version with adenine. Second, if it were to be read by an mRNA molecule, one of the codons ...
Name Unit 6 DNA Test (Chapters 8) Study Guide
... Fruit flies with the curly-wing trait will develop straight wings if kept at a temperature of 16°C during development and curly wings if kept at 25°C. The best explanation for this change in the shape of wings is that the a. genes for curly wings and genes for straight wings are found on different c ...
... Fruit flies with the curly-wing trait will develop straight wings if kept at a temperature of 16°C during development and curly wings if kept at 25°C. The best explanation for this change in the shape of wings is that the a. genes for curly wings and genes for straight wings are found on different c ...
Research Questions
... methionine (Met), and tryptophan (Trp).Hydrophobic amino have side-chains that do not like to reside in an aqueous environment. For this reason, one generally finds these amino acids buried within the hydrophobic core of the protein, or within the lipid portion of the membrane. Hydrophilic amino aci ...
... methionine (Met), and tryptophan (Trp).Hydrophobic amino have side-chains that do not like to reside in an aqueous environment. For this reason, one generally finds these amino acids buried within the hydrophobic core of the protein, or within the lipid portion of the membrane. Hydrophilic amino aci ...
Mutations - The Super Heroes of Biology
... • One nucleotide is replaced by another but it still codes for the same amino acid ...
... • One nucleotide is replaced by another but it still codes for the same amino acid ...
chromosomal
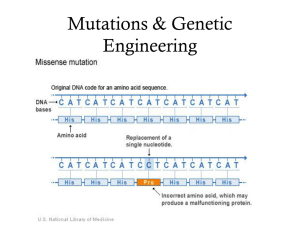
... Silent and nonsense mutations • Silent: an alteration in a DNA sequence that does not result in an amino acid change because many codons code for the same amino acid. For instance: GAA and GAG both code for amino acid GLU • Nonsense mutation: replacement of one base in the DNA code results in a “st ...
... Silent and nonsense mutations • Silent: an alteration in a DNA sequence that does not result in an amino acid change because many codons code for the same amino acid. For instance: GAA and GAG both code for amino acid GLU • Nonsense mutation: replacement of one base in the DNA code results in a “st ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.