From DNA to Proteins
... It is caused by point mutations in the CFTR gene, which codes for a transmembrane protein that acts as an ion pump. The CFTR gene is found on chromosome 7. It codes for 1480 amino acids. There are over 1000 known mutations, which can affect the function of the CFTR gene in different ways. In around ...
... It is caused by point mutations in the CFTR gene, which codes for a transmembrane protein that acts as an ion pump. The CFTR gene is found on chromosome 7. It codes for 1480 amino acids. There are over 1000 known mutations, which can affect the function of the CFTR gene in different ways. In around ...
The origin of genetic variation
... II. What is a mutation??? -new variant of DNA that is different from both parents -deleterious alleles in population are often referred to as mutations Variation at third position is much greater than at other two Transitions are more common than transversions because DNA DNA repair enzymes can reco ...
... II. What is a mutation??? -new variant of DNA that is different from both parents -deleterious alleles in population are often referred to as mutations Variation at third position is much greater than at other two Transitions are more common than transversions because DNA DNA repair enzymes can reco ...
jeopardy honors DNA
... Mutations are the ultimate source of genetic variation. If something is a beneficial mutation, it may increase over time in the population (change over time). ...
... Mutations are the ultimate source of genetic variation. If something is a beneficial mutation, it may increase over time in the population (change over time). ...
Mutations and Metabolic Pathways
... In the above diagram, the enzymes are shown in red. Discuss why patients with Porphyria may have different causes of the disorder, and how two parents with Porphyria could give birth to children who do not have it. In your answer you should consider: ...
... In the above diagram, the enzymes are shown in red. Discuss why patients with Porphyria may have different causes of the disorder, and how two parents with Porphyria could give birth to children who do not have it. In your answer you should consider: ...
File - Mrs. Badger`s Honors Biology Class
... a. carry a message that, when translated, forms proteins. b. form a portion of ribosomes, a cell’s protein factories. c. string together complementary RNA and DNA strands. d. bring amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. _____ 3. What is the term for a three-nucleotide sequence that codes f ...
... a. carry a message that, when translated, forms proteins. b. form a portion of ribosomes, a cell’s protein factories. c. string together complementary RNA and DNA strands. d. bring amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. _____ 3. What is the term for a three-nucleotide sequence that codes f ...
flyer
... When time is of the utmost importance. GenomeScan knows that in genetic testing, sometimes every day counts. With Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) we find the mutations that cause the patients’ clinical features. From DNA to report letter in 12 to 14 days! ...
... When time is of the utmost importance. GenomeScan knows that in genetic testing, sometimes every day counts. With Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) we find the mutations that cause the patients’ clinical features. From DNA to report letter in 12 to 14 days! ...
2. The histogram below shows the total estimated new breast cancer
... Mutations happen when your genetic code gets altered or modified as an example if a mother is addicted to smoking while pregnancy then her offspring will likely be born with birth defects which are mutations which will lead to genetic variations. 2. Which appears to be more dangerous: the BRC1 or BR ...
... Mutations happen when your genetic code gets altered or modified as an example if a mother is addicted to smoking while pregnancy then her offspring will likely be born with birth defects which are mutations which will lead to genetic variations. 2. Which appears to be more dangerous: the BRC1 or BR ...
Unit 4 Review Sheet Genetics and Biotechnology Vocabulary
... - Do you know how to use the codon chart? - Why is the sequence of amino acids important to the shape and function of a protein? *You do NOT need to know the names of the enzymes involved in this process. Mutations - What is a mutation? - What kind of mutations can happen to DNA (i.e. a nucleotide i ...
... - Do you know how to use the codon chart? - Why is the sequence of amino acids important to the shape and function of a protein? *You do NOT need to know the names of the enzymes involved in this process. Mutations - What is a mutation? - What kind of mutations can happen to DNA (i.e. a nucleotide i ...
File
... • Give rise to new alleles • Causes: – Random – Environmental factors (increase chances) • Ionizing radiation • UV Radiation • Chemicals ...
... • Give rise to new alleles • Causes: – Random – Environmental factors (increase chances) • Ionizing radiation • UV Radiation • Chemicals ...
Basics in Genetics
... Thus most mutations recessive!! Null mutation= makes no protein or totally non-functional protein. Weak or Hypomorphic mutation= makes protein that retains some but not all function. Loss of function mutation vs. Gain of function mutation c. One gene has different alleles. Normal allele = wild type. ...
... Thus most mutations recessive!! Null mutation= makes no protein or totally non-functional protein. Weak or Hypomorphic mutation= makes protein that retains some but not all function. Loss of function mutation vs. Gain of function mutation c. One gene has different alleles. Normal allele = wild type. ...
genetics 2-2
... Law of Dominance and Recessiveness: one gene in a pair may mask or prevent the expression of the other. GENETIC DISORDERS PKU: A genetic disease due to a lack of an enzyme. Klinefelter’s Syndrome- Results of non-disjunction when an abnormal sperm containing both the X and Y chromosomes, fertilizes a ...
... Law of Dominance and Recessiveness: one gene in a pair may mask or prevent the expression of the other. GENETIC DISORDERS PKU: A genetic disease due to a lack of an enzyme. Klinefelter’s Syndrome- Results of non-disjunction when an abnormal sperm containing both the X and Y chromosomes, fertilizes a ...
Ch. 5_Study_Guide
... □ I can explain the fundamental principles of taxonomy ie: domains, kingdoms, and binomial nomenclature (5.1) ...
... □ I can explain the fundamental principles of taxonomy ie: domains, kingdoms, and binomial nomenclature (5.1) ...
Mutations
... 5. Translocation = occurs when part of one chromosome breaks off and is added to a different chromosome. ...
... 5. Translocation = occurs when part of one chromosome breaks off and is added to a different chromosome. ...
MUTATIONS
... DNA just happen. Our DNA can change without warning, which changes the genes and how they behave. Factors that cause changes in our DNA: Errors when DNA is copied for new cells Environmental factors change DNA (nicotine, sunlight, x-rays, chemicals Mutations are inherited from the parents ...
... DNA just happen. Our DNA can change without warning, which changes the genes and how they behave. Factors that cause changes in our DNA: Errors when DNA is copied for new cells Environmental factors change DNA (nicotine, sunlight, x-rays, chemicals Mutations are inherited from the parents ...
DNA Connection (pgs.101-106)
... Human Genetic Disorders A genetic disorder is Abnormal condition that a ...
... Human Genetic Disorders A genetic disorder is Abnormal condition that a ...
Gene Section P53 (protein 53 kDa) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... P53 is mutated in about 50% of human cancers, and the non-mutated allele is generally lost; the frequency and the type of mutation may vary from one tumor type to another; in general, mutations are found in the central part (exons 4-8) of the p53 gene; these mutations are missense, non-sense, deleti ...
... P53 is mutated in about 50% of human cancers, and the non-mutated allele is generally lost; the frequency and the type of mutation may vary from one tumor type to another; in general, mutations are found in the central part (exons 4-8) of the p53 gene; these mutations are missense, non-sense, deleti ...
The Sound of a Silent Mutation - ScienceNOW
... versions with either of two other mutations known to occur sometimes along with C3435T (one of them silent as well, the other nonsilent but without an effect on protein function), and versions with various combinations of two or three of the mutations. They found that the mutations individually appe ...
... versions with either of two other mutations known to occur sometimes along with C3435T (one of them silent as well, the other nonsilent but without an effect on protein function), and versions with various combinations of two or three of the mutations. They found that the mutations individually appe ...
Protein Synth Notes GO New
... A protein and its function is determined by: What’s another word for phenotype? Which macromolecule does the phenotype describe? Which macromolecule does the genotype describe? Which macromolecule does variation describe? ...
... A protein and its function is determined by: What’s another word for phenotype? Which macromolecule does the phenotype describe? Which macromolecule does the genotype describe? Which macromolecule does variation describe? ...
Mutations
... – Causes a change in a single amino acid in the protein for which the gene codes Example: ...
... – Causes a change in a single amino acid in the protein for which the gene codes Example: ...
Chapter 12 SWBAT`s and Standards
... Genes are a set of instructions encoded in the DNA sequence of each organism that specify the sequence of amino acids in proteins characteristic of that organism. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. ...
... Genes are a set of instructions encoded in the DNA sequence of each organism that specify the sequence of amino acids in proteins characteristic of that organism. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. ...
Biology Chapter 12 Review 5-6
... 8. Explain how the information Watson and Crick acquired from Rosalind Franklin and Chargaff was used to determine the structure of DNA. 9. Explain complementary base pairing and the bases involved. 10. What hold base pairs together and how many? 11. Explain the steps involved in replication. 12. Wh ...
... 8. Explain how the information Watson and Crick acquired from Rosalind Franklin and Chargaff was used to determine the structure of DNA. 9. Explain complementary base pairing and the bases involved. 10. What hold base pairs together and how many? 11. Explain the steps involved in replication. 12. Wh ...
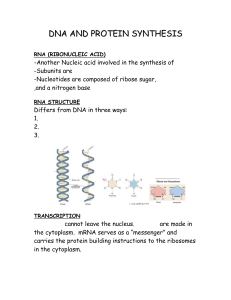
DNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... the cytoplasm. mRNA serves as a “messenger” and carries the protein building instructions to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. ...
... the cytoplasm. mRNA serves as a “messenger” and carries the protein building instructions to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.