TGFBR2 - Loeys-Dietz syndrome Testing Indication
... are inherited in an autosomal dominant manner with a variable clinical expression. Approximately 75% of individuals with LDS have an affected parent, and 25% have a de novo mutation. TGFBR2 and TGFBR1 are the only two genes known to cause LDS. Mutations in TGFBR2 have also been identified in patient ...
... are inherited in an autosomal dominant manner with a variable clinical expression. Approximately 75% of individuals with LDS have an affected parent, and 25% have a de novo mutation. TGFBR2 and TGFBR1 are the only two genes known to cause LDS. Mutations in TGFBR2 have also been identified in patient ...
2.5.4. DNA Revision Qs
... 4 Heredity is the passing on of features from one generation to another by means of ________________________________________. ...
... 4 Heredity is the passing on of features from one generation to another by means of ________________________________________. ...
Genetic Mutation - Raymond Williams Foundation
... ‘ mutation – the raw material of evolution… fuel for the Darwinian factory’; ‘What is Life? – unlike, say a pebble, living beings store information and also develop it over time…’; attempted explanations of ‘enzymes, DNA, ‘the gene pool’, ‘randomness, and genetic drift…’ , ‘induced mutations’ , ‘dis ...
... ‘ mutation – the raw material of evolution… fuel for the Darwinian factory’; ‘What is Life? – unlike, say a pebble, living beings store information and also develop it over time…’; attempted explanations of ‘enzymes, DNA, ‘the gene pool’, ‘randomness, and genetic drift…’ , ‘induced mutations’ , ‘dis ...
Mutations Notes - Oakman School News
... May occur in somatic cells (aren’t passed to offspring) ...
... May occur in somatic cells (aren’t passed to offspring) ...
BIOLOGY CONTENT STANDARDS REVIEW
... 2. How do diploid and haploid cells differ? 3. Explain crossing over in terms of its process and its value. Only certain cells in a multi-cellular organism undergo meiosis. 4. Identify cells in the human body that are haploid. How many chromosomes are present? 5. Identify cells in the body that are ...
... 2. How do diploid and haploid cells differ? 3. Explain crossing over in terms of its process and its value. Only certain cells in a multi-cellular organism undergo meiosis. 4. Identify cells in the human body that are haploid. How many chromosomes are present? 5. Identify cells in the body that are ...
DNA mutations power point
... Sickle cell disease •Haemoglobin is made up of 4 polypeptide chains (2 alpha & 2 beta chains). •Gene for beta chain is found on chromosome 11 and consists of 438 bases. •A mutation occurs in the gene coding for the beta chain. •The mutation is a substitution where adenine replace thymine on the DNA ...
... Sickle cell disease •Haemoglobin is made up of 4 polypeptide chains (2 alpha & 2 beta chains). •Gene for beta chain is found on chromosome 11 and consists of 438 bases. •A mutation occurs in the gene coding for the beta chain. •The mutation is a substitution where adenine replace thymine on the DNA ...
chapter 4.4 review
... When a plant reproduces vegetatively, are the offspring genetically different from or genetically identical to the parent? ...
... When a plant reproduces vegetatively, are the offspring genetically different from or genetically identical to the parent? ...
Changes in DNA
... TAT changed to TAC—both still code from Tyrosine CTC changed to CTA—both still code for Leucine ...
... TAT changed to TAC—both still code from Tyrosine CTC changed to CTA—both still code for Leucine ...
Changes in DNA
... TAT changed to TAC—both still code from Tyrosine CTC changed to CTA—both still code for Leucine ...
... TAT changed to TAC—both still code from Tyrosine CTC changed to CTA—both still code for Leucine ...
Gene Mutations
... cystic fibrosis have been found in almost 1000 combinations. Each of these mutations occurs in a huge gene that encodes a protein (of 1480 amino acids) called the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR). Unlike a missence mutation in sickle cell anemia, it can be various mutations ...
... cystic fibrosis have been found in almost 1000 combinations. Each of these mutations occurs in a huge gene that encodes a protein (of 1480 amino acids) called the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR). Unlike a missence mutation in sickle cell anemia, it can be various mutations ...
DNA - SchoolRack
... • A point mutation is a change in a single base pair (A-T, G-C). • A point mutation causes an incorrect amino acid to be inserted into the growing amino acid chain during translation; this results in a protein that does not function properly. ...
... • A point mutation is a change in a single base pair (A-T, G-C). • A point mutation causes an incorrect amino acid to be inserted into the growing amino acid chain during translation; this results in a protein that does not function properly. ...
how mutations affect gene function
... Missense mutation: changes an amino acid to another amino acid. This may or may not affect protein function, depending on whether the change is “conservative” or “nonconservative,” and what the amino acid actually does. Nonsense mutation: changes an amino acid to a STOP codon, resulting in prematur ...
... Missense mutation: changes an amino acid to another amino acid. This may or may not affect protein function, depending on whether the change is “conservative” or “nonconservative,” and what the amino acid actually does. Nonsense mutation: changes an amino acid to a STOP codon, resulting in prematur ...
Document
... Use one of the above terms to best complete each sentence #1-15 below. (2 pts. each) 1. _____cDNA_______ is a DNA copy of an RNA molecule. 2. ___reverse transcriptase__ is an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase. 3. Knockout mice are created by replacing a normal gene segment with a modified segment within ...
... Use one of the above terms to best complete each sentence #1-15 below. (2 pts. each) 1. _____cDNA_______ is a DNA copy of an RNA molecule. 2. ___reverse transcriptase__ is an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase. 3. Knockout mice are created by replacing a normal gene segment with a modified segment within ...
Gene mutations
... Chemicals and radiation also can damage DNA. High-energy forms of radiation, such as X rays and gamma rays, are highly mutagenic. ...
... Chemicals and radiation also can damage DNA. High-energy forms of radiation, such as X rays and gamma rays, are highly mutagenic. ...
Chapter 8 DNA: the universal molecule of life All living things share
... the gene are cut out, some introns may be retained, some exons removed. This could result in different proteins being produced from the same gene in different conditions. Text questions – 13, 14, Variation – new combinations of alleles, DNA mutations, multiple alleles, polygenes, environment Chromos ...
... the gene are cut out, some introns may be retained, some exons removed. This could result in different proteins being produced from the same gene in different conditions. Text questions – 13, 14, Variation – new combinations of alleles, DNA mutations, multiple alleles, polygenes, environment Chromos ...
Point Mutation
... Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome The disease is caused by a small point mutation on a single gene known as LMNA. Almost all cases are caused by the substitution of only one base pair out of the approximate 25 000 DNA base pairs that compose the LMNA gene. This gene codes for the protein lamin A ...
... Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome The disease is caused by a small point mutation on a single gene known as LMNA. Almost all cases are caused by the substitution of only one base pair out of the approximate 25 000 DNA base pairs that compose the LMNA gene. This gene codes for the protein lamin A ...
Mutation - La Salle University
... • ALL genes can mutate • Observed levels are usually low • Some genes have very high rates of mutation (Mutable Genes) • Some genes seem to increase the rate of mutation in adjacent genes (Mutator Genes) ...
... • ALL genes can mutate • Observed levels are usually low • Some genes have very high rates of mutation (Mutable Genes) • Some genes seem to increase the rate of mutation in adjacent genes (Mutator Genes) ...
S3. Effects of Mutations on Proteins – Formative
... d. All three comparisons are likely to show the same degree of sequence similarity 6) The coding DNA sequence (CDS) of a protein is given below. The nucleotides are numbered as shown. What would be the effect on the protein produces by translation of this CDS if a mutation inserted two nucleotides ( ...
... d. All three comparisons are likely to show the same degree of sequence similarity 6) The coding DNA sequence (CDS) of a protein is given below. The nucleotides are numbered as shown. What would be the effect on the protein produces by translation of this CDS if a mutation inserted two nucleotides ( ...
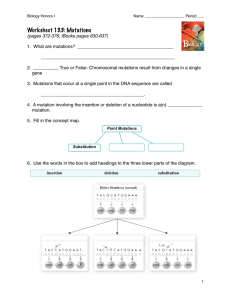
Worksheet 13.3
... 2. __________ True or False: Chromosomal mutations result from changes in a single gene 3. Mutations that occur at a single point in the DNA sequence are called ...
... 2. __________ True or False: Chromosomal mutations result from changes in a single gene 3. Mutations that occur at a single point in the DNA sequence are called ...
DNA Mutations
... • A substitution will cause either a single amino acid change or no change at all. – Remember that many different ___________________________________ ...
... • A substitution will cause either a single amino acid change or no change at all. – Remember that many different ___________________________________ ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.