Chapter 27 – The Planets and the Solar System
... The Inner Planets A. Two Planetary Neighborhoods 1. Inner Planets – Mercury, Venus, _______, Mars a. All have _____________ crust b. Dense mantle layers and ____________ c. Because of their Earth like appearance they are also known as ___________________ planets 2. Outer Planets – Jupiter, Saturn, U ...
... The Inner Planets A. Two Planetary Neighborhoods 1. Inner Planets – Mercury, Venus, _______, Mars a. All have _____________ crust b. Dense mantle layers and ____________ c. Because of their Earth like appearance they are also known as ___________________ planets 2. Outer Planets – Jupiter, Saturn, U ...
Earth - Capital High School
... • objects are so far away, we are seeing what they looked like millions of years ago – it takes one year for light to travel 5+ trillion miles (a light year) ...
... • objects are so far away, we are seeing what they looked like millions of years ago – it takes one year for light to travel 5+ trillion miles (a light year) ...
Semester #1 – GeoScience Review Guide – Final Exam Scale
... 67. On the moon, you'd be able to lift ________ times as much as you can on Earth, and it would feel exactly the same. 68. When a planet is closer to the Sun, it moves (faster / slower) in its orbit. 69. Almost all of the mass of our solar system is located within what object? 70. Which planet has ...
... 67. On the moon, you'd be able to lift ________ times as much as you can on Earth, and it would feel exactly the same. 68. When a planet is closer to the Sun, it moves (faster / slower) in its orbit. 69. Almost all of the mass of our solar system is located within what object? 70. Which planet has ...
The solar system
... wander among the stars at night. • They called these objects planets, from the Greek word meaning “wandering star,” and named them Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn. ...
... wander among the stars at night. • They called these objects planets, from the Greek word meaning “wandering star,” and named them Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn. ...
File
... sun is the source of light that lights the moon. Changes in the length and direction of an object’s shadow show the changing position of the Sun during the day although the patterns of the stars in the sky, to include the Sun, stay the same. Orbit- The path an object takes as it moves around another ...
... sun is the source of light that lights the moon. Changes in the length and direction of an object’s shadow show the changing position of the Sun during the day although the patterns of the stars in the sky, to include the Sun, stay the same. Orbit- The path an object takes as it moves around another ...
Document
... • No actual motion of the viewed object • Difference in angle between line of sight from the Earth and from the Sun (half the diameter or the radius of the Earth’s orbit, ...
... • No actual motion of the viewed object • Difference in angle between line of sight from the Earth and from the Sun (half the diameter or the radius of the Earth’s orbit, ...
Earth`s Movements The moon revolves around the Earth
... It follows the same path around the sun called its orbit. Why are there 365 days in a year? o The Earth spins 365 times as we revolve around the sun. How long does it take Earth to revolve once? o One year or 365 days What an axis? An axis is an imaginary line through the Earth. Imagine a ...
... It follows the same path around the sun called its orbit. Why are there 365 days in a year? o The Earth spins 365 times as we revolve around the sun. How long does it take Earth to revolve once? o One year or 365 days What an axis? An axis is an imaginary line through the Earth. Imagine a ...
Today`s Powerpoint - Physics and Astronomy
... Dipper will appear to have moved in roughly what direction? a) east (to your right) a) west (to your left) c) up (away from the horizon) c) down (closer to the horizon) ...
... Dipper will appear to have moved in roughly what direction? a) east (to your right) a) west (to your left) c) up (away from the horizon) c) down (closer to the horizon) ...
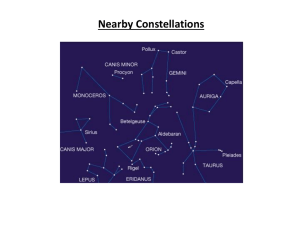
Nearby Constellations
... Half-hour time exposure facing north & west. The stars are tracing counter-clockwise circles, centered on a point near the prominent North Star (Polaris). Notice the Big Dipper at the lower-left. ...
... Half-hour time exposure facing north & west. The stars are tracing counter-clockwise circles, centered on a point near the prominent North Star (Polaris). Notice the Big Dipper at the lower-left. ...
The Sky and Its Motion - west
... • Celestial Sphere – an imaginary sphere of very large radius surrounding Earth, to which the planets, stars, sun, and moon seem to be attached. • Scientific Model – a concept that helps you think about some aspects of nature without necessarily being true. ...
... • Celestial Sphere – an imaginary sphere of very large radius surrounding Earth, to which the planets, stars, sun, and moon seem to be attached. • Scientific Model – a concept that helps you think about some aspects of nature without necessarily being true. ...
Revision on Universe 1-The nearest planet to the sun is Mercury
... 2-A phenomenon of day and nightsequence results from the rotation of the Earth around its axis ,while the four seasons sequence results from the revolution of Earth around the sun 3-Revolution of Earth around the sun once every 365 1\4 ,while rotation of Earth around its axis once every 24 hours 4-T ...
... 2-A phenomenon of day and nightsequence results from the rotation of the Earth around its axis ,while the four seasons sequence results from the revolution of Earth around the sun 3-Revolution of Earth around the sun once every 365 1\4 ,while rotation of Earth around its axis once every 24 hours 4-T ...
Physical Geography Exam Review Part 2
... ѺEarths Age and Uniqueness ѺThe Earth in Motion (Seasons) ...
... ѺEarths Age and Uniqueness ѺThe Earth in Motion (Seasons) ...
5a: So, what was wrong with Ptolemy`s model to a contemporary
... Ptolemy’s model. He showed that in his new heliocentric model one can compute the radii of the orbits of the other planets in terms of the radius of the earth’s orbit, and that their orbital periods fall into a very regular progression with increasing orbital radius. ...
... Ptolemy’s model. He showed that in his new heliocentric model one can compute the radii of the orbits of the other planets in terms of the radius of the earth’s orbit, and that their orbital periods fall into a very regular progression with increasing orbital radius. ...
Outline of Lecture on Copernican Revolution: 5b: So, what was
... invention of the telescope, which showed that the nearest star is too distant to have its parallax observable with the naked eye.) Copernicus was able to remove much of the unappealing arbitrariness of Ptolemy’s model. He showed that in his new heliocentric model one can compute the radii of the orb ...
... invention of the telescope, which showed that the nearest star is too distant to have its parallax observable with the naked eye.) Copernicus was able to remove much of the unappealing arbitrariness of Ptolemy’s model. He showed that in his new heliocentric model one can compute the radii of the orb ...
Astronomy Humble ISD Curriculum Year-At-A
... • Research and describe the use of astronomy in ancient civilizations. • Research and describe the contributions of scientists to our changing understanding of astronomy. • Describe and explain the historical origins of the perceived patterns of constellations and the role of constellations in ancie ...
... • Research and describe the use of astronomy in ancient civilizations. • Research and describe the contributions of scientists to our changing understanding of astronomy. • Describe and explain the historical origins of the perceived patterns of constellations and the role of constellations in ancie ...
Destination Antarctica Study Buddy
... I can explain why the positions of the Earth, moon, sun and stars change over time. Because the Earth orbits the sun and the moon orbits the Earth, our views of the night sky change in their positions change over time. Stars also change in position over time because the Milky Way galaxy is also rota ...
... I can explain why the positions of the Earth, moon, sun and stars change over time. Because the Earth orbits the sun and the moon orbits the Earth, our views of the night sky change in their positions change over time. Stars also change in position over time because the Milky Way galaxy is also rota ...
1 History of Astronomy - Journigan-wiki
... heavens is not like a divine animal but like a clock (and anyone who believes a clock has a soul gives the work the honor due to its maker) and that in it almost all the variety of motions is from one very simple magnetic force acting on bodies, as in the clock all motions are from a ...
... heavens is not like a divine animal but like a clock (and anyone who believes a clock has a soul gives the work the honor due to its maker) and that in it almost all the variety of motions is from one very simple magnetic force acting on bodies, as in the clock all motions are from a ...
Solar system
... SATELLITE- An object that moves or revolves around a planet SUNSPOT- A part of the sun that is very magnetic and is not as hot as other parts ...
... SATELLITE- An object that moves or revolves around a planet SUNSPOT- A part of the sun that is very magnetic and is not as hot as other parts ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • Often one is interested in how quantities change when an object or a system is enlarged or shortened • Different quantities will change by different factors! • Typical example: how does the circumference, surface, volume of a sphere change when its radius changes? ...
... • Often one is interested in how quantities change when an object or a system is enlarged or shortened • Different quantities will change by different factors! • Typical example: how does the circumference, surface, volume of a sphere change when its radius changes? ...
Science Standards - Explore-It
... 3.3.2 Demonstrate how the Earth rotates on its axis every 24 hours, producing the night-and-day cycle 5.3.3 Demonstrate how the Earth orbits the sun in a year’s time, and Earth rotates on its axis about once every 24 hours 5.3.4 Explain that the alternation between day and night and the apparent mov ...
... 3.3.2 Demonstrate how the Earth rotates on its axis every 24 hours, producing the night-and-day cycle 5.3.3 Demonstrate how the Earth orbits the sun in a year’s time, and Earth rotates on its axis about once every 24 hours 5.3.4 Explain that the alternation between day and night and the apparent mov ...
Document
... Jupiter is named after the Roman king of the Gods. It would take 11 earths lined up next to each other to get from one side of Jupiter to the other, it would also take 317 earths to equal Jupiter's mass. Jupiter's red spot is a gigantic storm that has been there for over 300 years! If Jupiter had 80 ...
... Jupiter is named after the Roman king of the Gods. It would take 11 earths lined up next to each other to get from one side of Jupiter to the other, it would also take 317 earths to equal Jupiter's mass. Jupiter's red spot is a gigantic storm that has been there for over 300 years! If Jupiter had 80 ...
Earth Science SOL Review Sheet #1
... asteroids. The sun is made of mostly hydrogen gas and its energy comes from nuclear fusion reactions. Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars are terrestrial planets. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune are gas giants. The asteroid belt is located between Mars and Jupiter. Made of ice and frozen gases, ...
... asteroids. The sun is made of mostly hydrogen gas and its energy comes from nuclear fusion reactions. Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars are terrestrial planets. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune are gas giants. The asteroid belt is located between Mars and Jupiter. Made of ice and frozen gases, ...
Asteroids PP - MR D`S ICT CORNER
... • Comets are balls of ice and dust that orbit the Sun in an elliptical orbit, that takes it very close to the Sun, then far away, beyond the planets. • The time to complete an orbit can take a few years, or millions of years. • The speed of a comet increases as it approaches the Sun, because the str ...
... • Comets are balls of ice and dust that orbit the Sun in an elliptical orbit, that takes it very close to the Sun, then far away, beyond the planets. • The time to complete an orbit can take a few years, or millions of years. • The speed of a comet increases as it approaches the Sun, because the str ...
Coursework 2 File
... In 1786 James Bradley, the 3rd Astronomer Royal, noticed that the apparent positions of stars on the night sky shift slightly relative to their real positions as the Earth orbits the Sun. This effect is due to the combined effect of the finite speed of light and the motion of the Earth around its or ...
... In 1786 James Bradley, the 3rd Astronomer Royal, noticed that the apparent positions of stars on the night sky shift slightly relative to their real positions as the Earth orbits the Sun. This effect is due to the combined effect of the finite speed of light and the motion of the Earth around its or ...
Geocentric model

In astronomy, the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, or the Ptolemaic system) is a description of the cosmos where Earth is at the orbital center of all celestial bodies. This model served as the predominant cosmological system in many ancient civilizations such as ancient Greece including the noteworthy systems of Aristotle (see Aristotelian physics) and Ptolemy. As such, they believed that the Sun, Moon, stars, and naked eye planets circled Earth.Two commonly made observations supported the idea that Earth was the center of the Universe. The stars, the sun, and planets appear to revolve around Earth each day, making Earth the center of that system. The stars were thought to be on a celestial sphere, with the earth at its center, that rotated each day, using a line through the north and south pole as an axis. The stars closest to the equator appeared to rise and fall the greatest distance, but each star circled back to its rising point each day. The second observation supporting the geocentric model was that the Earth does not seem to move from the perspective of an Earth-bound observer, and that it is solid, stable, and unmoving.Ancient Roman and medieval philosophers usually combined the geocentric model with a spherical Earth. It is not the same as the older flat Earth model implied in some mythology, as was the case with the biblical and postbiblical Latin cosmology. The ancient Jewish Babylonian uranography pictured a flat Earth with a dome-shaped rigid canopy named firmament placed over it. (רקיע- rāqîa').However, the ancient Greeks believed that the motions of the planets were circular and not elliptical, a view that was not challenged in Western culture until the 17th century through the synthesis of theories by Copernicus and Kepler.The astronomical predictions of Ptolemy's geocentric model were used to prepare astrological and astronomical charts for over 1500 years. The geocentric model held sway into the early modern age, but from the late 16th century onward was gradually superseded by the heliocentric model of Copernicus, Galileo and Kepler. There was much resistance to the transition between these two theories. Christian theologians were reluctant to reject a theory that agreed with Bible passages (e.g. ""Sun, stand you still upon Gibeon"", Joshua 10:12 – King James 2000 Bible). Others felt a new, unknown theory could not subvert an accepted consensus for geocentrism.