Our Solar System
... distances and sizes compared to a scale model. The distances to the planets and the sizes of the planets are shown on the same scale, which is 1 inch = 12,000 miles. At this scale, Jupiter is 1,111 yards from the Sun and is represented by a soccer ball of diameter about 7.33 inches. Pluto is 4.73 mi ...
... distances and sizes compared to a scale model. The distances to the planets and the sizes of the planets are shown on the same scale, which is 1 inch = 12,000 miles. At this scale, Jupiter is 1,111 yards from the Sun and is represented by a soccer ball of diameter about 7.33 inches. Pluto is 4.73 mi ...
originofsolarsystem
... As planets moved through their orbits, they swept up any material in their paths. Gravitational effects due to massive planets ejected particles out of the solar system. ...
... As planets moved through their orbits, they swept up any material in their paths. Gravitational effects due to massive planets ejected particles out of the solar system. ...
Level 2 Earth and Space Science (91192) 2015
... the early morning sky marks the dawn of the Māori New Year. In this cluster there is a star named HD 23514, which has been observed with dust particles around it that are thought to be the beginning of a solar system that will eventually orbit this star. Explain in detail how a solar system could fo ...
... the early morning sky marks the dawn of the Māori New Year. In this cluster there is a star named HD 23514, which has been observed with dust particles around it that are thought to be the beginning of a solar system that will eventually orbit this star. Explain in detail how a solar system could fo ...
evidence found of solar system around nearby star
... They say that at least one and probably three or more planets are orbiting the star Epsilon Eridani, 10.5 light-years — about 63 trillion miles — from Earth. Only eight stars are closer. The host star, slightly smaller and cooler than our sun, is in the constellation Eridanus — the name of a mytholo ...
... They say that at least one and probably three or more planets are orbiting the star Epsilon Eridani, 10.5 light-years — about 63 trillion miles — from Earth. Only eight stars are closer. The host star, slightly smaller and cooler than our sun, is in the constellation Eridanus — the name of a mytholo ...
Habitibility of Earth, in our Solar System, and Beyond
... Hot, large stars (O, B, some A) explode too soon. Hot stars (O, B) make too much deadly ultraviolet radiation. Variable stars, flare stars don’t provide stable environments Giants, supergiants ...
... Hot, large stars (O, B, some A) explode too soon. Hot stars (O, B) make too much deadly ultraviolet radiation. Variable stars, flare stars don’t provide stable environments Giants, supergiants ...
tata - surya
... How did the Solar System form? Any theory of the solar system formation must account for the obvious features we see, such as 1) the fact that solar system is a fairly flat place, with all the planets within a few degrees of the ecliptic and revolving in roughly circular oribts that are all goin ...
... How did the Solar System form? Any theory of the solar system formation must account for the obvious features we see, such as 1) the fact that solar system is a fairly flat place, with all the planets within a few degrees of the ecliptic and revolving in roughly circular oribts that are all goin ...
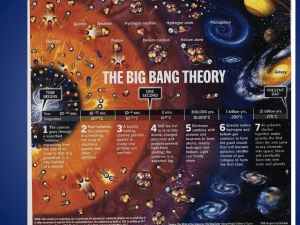
The Big Bang Theory
... evenly spread across space b) The amount of radiation matched predictions c) C.O.B.E satellite confirmed for the entire universe that noise radiation (static) is evenly spread d) Law of conservation of energy (energy can neither be created or destroyed) – energy remains constant over time ...
... evenly spread across space b) The amount of radiation matched predictions c) C.O.B.E satellite confirmed for the entire universe that noise radiation (static) is evenly spread d) Law of conservation of energy (energy can neither be created or destroyed) – energy remains constant over time ...
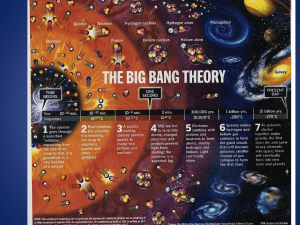
The Big Bang Theory
... evenly spread across space b) The amount of radiation matched predictions c) C.O.B.E satellite confirmed for the entire universe that noise radiation (static) is evenly spread d) Law of conservation of energy (energy can neither be created or destroyed) – energy remains constant over time ...
... evenly spread across space b) The amount of radiation matched predictions c) C.O.B.E satellite confirmed for the entire universe that noise radiation (static) is evenly spread d) Law of conservation of energy (energy can neither be created or destroyed) – energy remains constant over time ...
Meteors - Little Worksheets
... There are lots of objects that we see in the sky. During the day we see the sun. After the sun sets in the evening we see mostly the stars. Not all the lights in the sky that we see are really stars. Of course, we see the moon. Some of the other lights in the sky are planets. Planets revolve around ...
... There are lots of objects that we see in the sky. During the day we see the sun. After the sun sets in the evening we see mostly the stars. Not all the lights in the sky that we see are really stars. Of course, we see the moon. Some of the other lights in the sky are planets. Planets revolve around ...
Models of the Solar System
... Components of the Solar System The ancients knew of six planets. Three more planets were discovered with the aid of telescopes: • Uranus in 1781 • Neptune in 1846 • Pluto in 1930 (Pluto was later reclassified as a dwarf ...
... Components of the Solar System The ancients knew of six planets. Three more planets were discovered with the aid of telescopes: • Uranus in 1781 • Neptune in 1846 • Pluto in 1930 (Pluto was later reclassified as a dwarf ...
Chapter 16: The Origin of the Solar System RQ 16
... and more and more pieces could stick together. Therefore, the Jovian planets started to form from these icy grains consisting mostly of light elements. The Jovians contain both heavy and light elements due to cooler temperatures of the outer solar system during its formation but a much higher fracti ...
... and more and more pieces could stick together. Therefore, the Jovian planets started to form from these icy grains consisting mostly of light elements. The Jovians contain both heavy and light elements due to cooler temperatures of the outer solar system during its formation but a much higher fracti ...
Middle School - Starry Night Software
... 2. Describe how the planets move around the Sun in elliptical orbits; and the nearcoplanetarity of the orbits, along with the principle of conservation of momentum, is evidence essential to our understanding of how the Solar System was originally formed. ...
... 2. Describe how the planets move around the Sun in elliptical orbits; and the nearcoplanetarity of the orbits, along with the principle of conservation of momentum, is evidence essential to our understanding of how the Solar System was originally formed. ...
tail can extend millions of kilometers into space
... shooting star Meteor showers are large numbers of small meteors usually caused by Earth passing by dusty debris left by a comet ...
... shooting star Meteor showers are large numbers of small meteors usually caused by Earth passing by dusty debris left by a comet ...
PHYS 200 - Understanding the Universe
... • Report on: what makes up the solar system, what is the physical difference between planets and stars, whether stars live forever, and what makes up our Milky Way Galaxy. • Comprehend that cosmic bodies are always in motion relative to each other. That for example the relative motion of the Earth, ...
... • Report on: what makes up the solar system, what is the physical difference between planets and stars, whether stars live forever, and what makes up our Milky Way Galaxy. • Comprehend that cosmic bodies are always in motion relative to each other. That for example the relative motion of the Earth, ...
lesson 1 Solar system - science
... of ice and dust a few kilometres across. The tail only appears when the comet is near the Sun. It consist of gas and dust which are released by the heat of the Sun. ...
... of ice and dust a few kilometres across. The tail only appears when the comet is near the Sun. It consist of gas and dust which are released by the heat of the Sun. ...
Origin of the Universe and of the Solar System
... 1º At the outset, the matter and the space were concentrated in a same point (primigenius atom), with a density and temperature that had of being very high. 2º Suddenly, the atom primigenius expanded abruptly in a great explosion that initiated the expansion of the universe. The energy moved away in ...
... 1º At the outset, the matter and the space were concentrated in a same point (primigenius atom), with a density and temperature that had of being very high. 2º Suddenly, the atom primigenius expanded abruptly in a great explosion that initiated the expansion of the universe. The energy moved away in ...
ASTRO OTTER JUNIOR
... about the US vs. Soviet Space Race, Shuttle missions to the International Space Station, unmanned missions throughout the solar system, and information about ...
... about the US vs. Soviet Space Race, Shuttle missions to the International Space Station, unmanned missions throughout the solar system, and information about ...
NEBULAR HYPOTHESIS
... inward due to gravitational forces ⦿ At the beginning of this collapse we form a SOLAR NEBULA. ...
... inward due to gravitational forces ⦿ At the beginning of this collapse we form a SOLAR NEBULA. ...
PPT - ILWS
... • Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO), in Earth orbit, to be launched in 2008, life time more than 4 years • But: no in-situ instruments, no coronagraph • Solar Orbiter, in near-Sun execliptic orbit, launch 2015 (?) But: not much context with Earth • Sentinels 2013 ?? • Solar Probe ??? ...
... • Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO), in Earth orbit, to be launched in 2008, life time more than 4 years • But: no in-situ instruments, no coronagraph • Solar Orbiter, in near-Sun execliptic orbit, launch 2015 (?) But: not much context with Earth • Sentinels 2013 ?? • Solar Probe ??? ...
Uninhabitableearth
... Form into small groups of four of five and discuss the following questions: What are the necessary conditions for a planet to support life as we know it? Are any of these factors more important than the others? Are there any other planets in our solar system other than Earth that are in the habi ...
... Form into small groups of four of five and discuss the following questions: What are the necessary conditions for a planet to support life as we know it? Are any of these factors more important than the others? Are there any other planets in our solar system other than Earth that are in the habi ...
Knows that Earth is the only body in our solar system that
... Definition: A celestial body that consists of a fuzzy-appearing head usually surrounding a bright nucleus, usually with a highly eccentric orbit, and that often, when in the part of its orbit near the sun, develops a long tail that points away from the sun. Context: The massive gravitational pull o ...
... Definition: A celestial body that consists of a fuzzy-appearing head usually surrounding a bright nucleus, usually with a highly eccentric orbit, and that often, when in the part of its orbit near the sun, develops a long tail that points away from the sun. Context: The massive gravitational pull o ...
Unit 8 Chapter 26 Studying Space
... As new things are discovered in space like Black Holes, new planets, stars and nebula, scientists can use that information to learn about Earth. Scientists have been able to piece together the processes that involve the formation of our planet, the solar system and the universe. ...
... As new things are discovered in space like Black Holes, new planets, stars and nebula, scientists can use that information to learn about Earth. Scientists have been able to piece together the processes that involve the formation of our planet, the solar system and the universe. ...
Midterm Review -- Astronomy Unit
... What shape is the Milky Way galaxy? a. Irregular b. Elliptical c. Spiral ...
... What shape is the Milky Way galaxy? a. Irregular b. Elliptical c. Spiral ...
how do the planets affeCt earth?
... Learning from the planets Scientists have learned a lot from studying the planets. Venus and Mars are planets that are a lot like Earth. If Earth’s atmosphere becomes too polluted, our planet could become like Venus, which is too harsh and hot for life. Space probes have gathered information about a ...
... Learning from the planets Scientists have learned a lot from studying the planets. Venus and Mars are planets that are a lot like Earth. If Earth’s atmosphere becomes too polluted, our planet could become like Venus, which is too harsh and hot for life. Space probes have gathered information about a ...
Panspermia
Panspermia (from Greek πᾶν (pan), meaning ""all"", and σπέρμα (sperma), meaning ""seed"") is the hypothesis that life exists throughout the Universe, distributed by meteoroids, asteroids, comets, planetoids and, also, by spacecraft in the form of unintended contamination by microorganisms.Panspermia is a hypothesis proposing that microscopic life forms that can survive the effects of space, such as extremophiles, become trapped in debris that is ejected into space after collisions between planets and small Solar System bodies that harbor life. Some organisms may travel dormant for an extended amount of time before colliding randomly with other planets or intermingling with protoplanetary disks. If met with ideal conditions on a new planet's surfaces, the organisms become active and the process of evolution begins. Panspermia is not meant to address how life began, just the method that may cause its distribution in the Universe.Pseudo-panspermia (sometimes called ""soft panspermia"" or ""molecular panspermia"") argues that the pre-biotic organic building blocks of life originated in space and were incorporated in the solar nebula from which the planets condensed and were further —and continuously— distributed to planetary surfaces where life then emerged (abiogenesis). From the early 1970s it was becoming evident that interstellar dust consisted of a large component of organic molecules. Interstellar molecules are formed by chemical reactions within very sparse interstellar or circumstellar clouds of dust and gas. The dust plays a critical role of shielding the molecules from the ionizing effect of ultraviolet radiation emitted by stars.Several simulations in laboratories and in low Earth orbit suggest that ejection, entry and impact is survivable for some simple organisms.