Components of the Climate System
... (99.9% of the atmosphere’s mass is below the mesosphere) Exposure to solar radiation would severely burn our bodies! The transition region to the next layer is the “mesopause” ...
... (99.9% of the atmosphere’s mass is below the mesosphere) Exposure to solar radiation would severely burn our bodies! The transition region to the next layer is the “mesopause” ...
File - Mr. Dudek`s Science
... • The solar system also contains a sizable collection of meteors, comets, and belts of rocky materials that also orbit the Sun. • The solar system is thought to have formed from a condensing cloud of gas and dust known as a nebula. As the ...
... • The solar system also contains a sizable collection of meteors, comets, and belts of rocky materials that also orbit the Sun. • The solar system is thought to have formed from a condensing cloud of gas and dust known as a nebula. As the ...
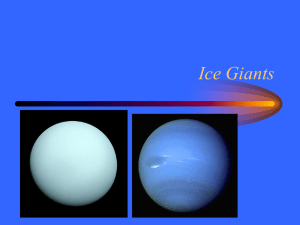
Ice Giants
... • The colliding object must have been huge to deflect a planet the size of Uranus (14 times the mass of Earth). ...
... • The colliding object must have been huge to deflect a planet the size of Uranus (14 times the mass of Earth). ...
Properties of Earth`s Atmosphere
... Properties of Earth’s Atmosphere Purpose: The purpose of this activity is to identify relationships that exist between the elevation above sea level versus air density and temperature. Procedure: ____ 1. Enter the web address below: http://www.glencoe.com/sites/common_assets/science/virtual_labs/ES1 ...
... Properties of Earth’s Atmosphere Purpose: The purpose of this activity is to identify relationships that exist between the elevation above sea level versus air density and temperature. Procedure: ____ 1. Enter the web address below: http://www.glencoe.com/sites/common_assets/science/virtual_labs/ES1 ...
Inner Planets - Spokane Public Schools
... demon of the Solar System, however, because it takes only 88 days to orbit around the Sun. ...
... demon of the Solar System, however, because it takes only 88 days to orbit around the Sun. ...
Our Solar System
... Our solar system is made up of: Sun – Star in the center of a solar system. Nine planets Their moons – a natural satellite that orbits a primary planet. Asteroids ...
... Our solar system is made up of: Sun – Star in the center of a solar system. Nine planets Their moons – a natural satellite that orbits a primary planet. Asteroids ...
Astrobiology notes for October 18th - 22nd
... a forming star, the amount of volatiles available increase with distance from the star, because closer they vaporize. Atmospheric pressure and distance decides the form that water stays in (gas, liquid, ice). In an atmosphere, molecules break apart and reassemble constantly. Atoms leak off of the to ...
... a forming star, the amount of volatiles available increase with distance from the star, because closer they vaporize. Atmospheric pressure and distance decides the form that water stays in (gas, liquid, ice). In an atmosphere, molecules break apart and reassemble constantly. Atoms leak off of the to ...
Earths_atmosphere
... Atmospheric effects • Reflection – albedo (percent reflected) • Scattering • Absorption ...
... Atmospheric effects • Reflection – albedo (percent reflected) • Scattering • Absorption ...
abundance of elements pie graph activity
... 1. Convert each percentage into degrees by multiplying it by 3.6, which is the number you arrive at when you divide 360 (degrees in a circle) by 100 (total amount in percentages). 2. Add the total of all the items to make certain that the total is equal to 360˚. If not, recalculate the degrees for e ...
... 1. Convert each percentage into degrees by multiplying it by 3.6, which is the number you arrive at when you divide 360 (degrees in a circle) by 100 (total amount in percentages). 2. Add the total of all the items to make certain that the total is equal to 360˚. If not, recalculate the degrees for e ...
The Sun and Planets Homework Solutions 4.
... Calculate the following quantities for the orbits below: periastron and apoastron distances, minimum and maximum orbital speeds, and orbital period. Report your distances in AU, speeds in km/s, and periods in days. a) Earth orbits the Sun at a cozy average distance of 1 AU with a relatively small ec ...
... Calculate the following quantities for the orbits below: periastron and apoastron distances, minimum and maximum orbital speeds, and orbital period. Report your distances in AU, speeds in km/s, and periods in days. a) Earth orbits the Sun at a cozy average distance of 1 AU with a relatively small ec ...
The Atmospheres of Different Planets
... atmosphere freezes and solidifies back down on the surface of Pluto. It’s not confirmed yet but it seems from its dual orbit with its moon Charon that Pluto may have a magnetic field. ...
... atmosphere freezes and solidifies back down on the surface of Pluto. It’s not confirmed yet but it seems from its dual orbit with its moon Charon that Pluto may have a magnetic field. ...
SPACE By: Hailey Merrill and Katie Whatley Earth
... Jupiter is a bid ball of mostly gasses and helium. Three interesting facts about Jupiter Jupiter has a red spot that is a storm that storm has been going on science Jupiter was first observed. Jupiter is the largest planet. Jupiter produces it’s own energy. Jupiter is a gas planet ...
... Jupiter is a bid ball of mostly gasses and helium. Three interesting facts about Jupiter Jupiter has a red spot that is a storm that storm has been going on science Jupiter was first observed. Jupiter is the largest planet. Jupiter produces it’s own energy. Jupiter is a gas planet ...
Chapter 11 Case Studies and Study Guide: The Atmosphere
... the same time, oceans acidify which may have a negative impact on marine life. Earth’s atmosphere is mainly composed of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%) with other components present only in trace amounts (such as argon and greenhouse gases). Water vapor is the most dominant greenhouse gas in Earth’s ...
... the same time, oceans acidify which may have a negative impact on marine life. Earth’s atmosphere is mainly composed of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%) with other components present only in trace amounts (such as argon and greenhouse gases). Water vapor is the most dominant greenhouse gas in Earth’s ...
a naturally occuring object in space such as a star, planet, moon
... object in space such as a star, planet, moon, asteroid, galaxy, or a comet corona - the outermost layer of the Sun. It stretches far into space, appears very thin and faint and can only be seen from Earth during a total solar eclipse. ...
... object in space such as a star, planet, moon, asteroid, galaxy, or a comet corona - the outermost layer of the Sun. It stretches far into space, appears very thin and faint and can only be seen from Earth during a total solar eclipse. ...
Layers of the Atmosphere - ms. Clayton`s 7th grade Science
... chlorine and fluorine, float around the stratosphere, breaking up ozone molecules. • One molecule of CFC can destroy more than 100,000 molecules of stratospheric ozone. • Today, no spray cans contain CFCs. Other chemicals are gradually replacing the CFCs in air conditioners. ...
... chlorine and fluorine, float around the stratosphere, breaking up ozone molecules. • One molecule of CFC can destroy more than 100,000 molecules of stratospheric ozone. • Today, no spray cans contain CFCs. Other chemicals are gradually replacing the CFCs in air conditioners. ...
File - Global Scholars
... increased burning of fossil fuels. Most atmospheric scientists believe this warming of the lower layers of the atmosphere are leading to unpredictable global climate changes. Ozone is another minor gas in the atmosphere. It’s a molecule made up of three oxygen atoms (O₃), instead of the common two o ...
... increased burning of fossil fuels. Most atmospheric scientists believe this warming of the lower layers of the atmosphere are leading to unpredictable global climate changes. Ozone is another minor gas in the atmosphere. It’s a molecule made up of three oxygen atoms (O₃), instead of the common two o ...
EPO4 Atmosphere, weather, and climate
... 5. Answer the questions. What’s the name of the noise made by lightning? ___________________ What’s the rainbow? ____________________ What’s the name of the water condensed in the clouds? ______________________ Precipitation can be… ____________ , _____________ or _____________ . What do we use to m ...
... 5. Answer the questions. What’s the name of the noise made by lightning? ___________________ What’s the rainbow? ____________________ What’s the name of the water condensed in the clouds? ______________________ Precipitation can be… ____________ , _____________ or _____________ . What do we use to m ...
1. How did the size of the Neanderthal brain compare to that of
... a random, one-time event that will never repeat, so we can’t learn any more about the planet by further observation. 9. Many extra-solar planets (exoplanets) have been discovered. About how many are known at present? Name two features of these planets and/or their orbits were not at all expected by ...
... a random, one-time event that will never repeat, so we can’t learn any more about the planet by further observation. 9. Many extra-solar planets (exoplanets) have been discovered. About how many are known at present? Name two features of these planets and/or their orbits were not at all expected by ...
Presentación de PowerPoint
... together, and its volume is one thousand times the volume of Earth. It has many satellites, and four of them (Io, Callisto, Europa and Ganymede) were discovered by Galilei in 1610. Its thick atmosphere is complex, and it is made up of hydrogen (90%) and helium (10%). It has clouds and storms, so it ...
... together, and its volume is one thousand times the volume of Earth. It has many satellites, and four of them (Io, Callisto, Europa and Ganymede) were discovered by Galilei in 1610. Its thick atmosphere is complex, and it is made up of hydrogen (90%) and helium (10%). It has clouds and storms, so it ...
Our Solar System
... Beautiful set of rings 31 moons Largest moon, Titan, Easily visible in the night sky Voyager explored Saturn and its rings. ...
... Beautiful set of rings 31 moons Largest moon, Titan, Easily visible in the night sky Voyager explored Saturn and its rings. ...
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres:
... • Why did Mars change? – Its atmosphere must have once been much thicker for its greenhouse effect to allow liquid water on the surface – Somehow Mars lost most of its atmosphere, perhaps because of declining magnetic field ...
... • Why did Mars change? – Its atmosphere must have once been much thicker for its greenhouse effect to allow liquid water on the surface – Somehow Mars lost most of its atmosphere, perhaps because of declining magnetic field ...
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: What is an atmosphere? Earth`s
... – Mars is cold, dry, and frozen – Strong seasonal changes cause CO2 to move from pole to pole, leading to dust storms ...
... – Mars is cold, dry, and frozen – Strong seasonal changes cause CO2 to move from pole to pole, leading to dust storms ...
Lesson Presentation
... to space. They also heat up at different rates. For example, dry land heats up rapidly and gives most of that heat back into the atmosphere. Water temperature changes slowly and stores heat, releasing it over time. This uneven pattern of surface heating cause changes in pressure and creates wi ...
... to space. They also heat up at different rates. For example, dry land heats up rapidly and gives most of that heat back into the atmosphere. Water temperature changes slowly and stores heat, releasing it over time. This uneven pattern of surface heating cause changes in pressure and creates wi ...