Comets
... core of a comet. The coma is a fuzzy outer layer made up of clouds of gas and dust. • A small glowing nucleus with a diameter of only a few kilometers can sometimes be detected within a coma. As comets approach the sun, some, but not all, develop a tail that extends for millions of kilometers. ...
... core of a comet. The coma is a fuzzy outer layer made up of clouds of gas and dust. • A small glowing nucleus with a diameter of only a few kilometers can sometimes be detected within a coma. As comets approach the sun, some, but not all, develop a tail that extends for millions of kilometers. ...
1st Semester Earth Science Review 2014-15
... b. the composition and temperature of a star. c. the size and weight of a star. d. the galaxy that the star belongs to. ____ 51. Circumpolar stars in the Northern Hemisphere appear to circle a. the moon. c. Proxima Centauri. b. the sun. d. Polaris. ____ 52. Objects, such a stars, moving toward an ob ...
... b. the composition and temperature of a star. c. the size and weight of a star. d. the galaxy that the star belongs to. ____ 51. Circumpolar stars in the Northern Hemisphere appear to circle a. the moon. c. Proxima Centauri. b. the sun. d. Polaris. ____ 52. Objects, such a stars, moving toward an ob ...
(AU): Average distance from Earth to Sun
... Parts of Solar System 1. Planet • Celestial body in orbit around the Sun. • 8 in our solar system: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune • Distance from the sun determines characteristics (ESRT) • Density generally decreases with distance from the sun ...
... Parts of Solar System 1. Planet • Celestial body in orbit around the Sun. • 8 in our solar system: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune • Distance from the sun determines characteristics (ESRT) • Density generally decreases with distance from the sun ...
(Part I) 1. Practice Quiz 2. Introduction 3. Earth Spins Around Its Axis
... towards Polaris, otherwise known as the ...
... towards Polaris, otherwise known as the ...
THE COLORADO MODEL SOLAR SYSTEM
... The Colorado Scale Model Solar System is on a scale of 1 to 10 billion (1010 )!!! That is, for every meter (or foot) in the scale model, there are 10 billion meters (or feet) in the real solar system. Note: A review of scientific notation can be found on page 15 of this manual. All of the sizes of t ...
... The Colorado Scale Model Solar System is on a scale of 1 to 10 billion (1010 )!!! That is, for every meter (or foot) in the scale model, there are 10 billion meters (or feet) in the real solar system. Note: A review of scientific notation can be found on page 15 of this manual. All of the sizes of t ...
Jeopardy
... This planet has more water on the surface than any other planet (there are moons with more). ...
... This planet has more water on the surface than any other planet (there are moons with more). ...
Astronomy - Learn Earth Science
... Use the Luminosity & Temperature of Stars diagram on the ESRTs to identify the characteristics of specific stars in relation to Earth’s sun. ...
... Use the Luminosity & Temperature of Stars diagram on the ESRTs to identify the characteristics of specific stars in relation to Earth’s sun. ...
Earth in the Universe Grade One
... What are the predictable patterns caused by Earth’s movement in the solar system? The solar system consists of the sun and a collection of objects of varying sizes and conditions—including planets and their moons—that are held in orbit around the sun by its gravitational pull on them. This system ap ...
... What are the predictable patterns caused by Earth’s movement in the solar system? The solar system consists of the sun and a collection of objects of varying sizes and conditions—including planets and their moons—that are held in orbit around the sun by its gravitational pull on them. This system ap ...
Lecture 3
... • Sun plus 8 (or 9 with Pluto) planets many of which have moons • plus “debris”: comets, asteroids, meteors, etc • We’ll go over historical understanding of motion (which is “complicated” when viewed from the Earth) and later look at Solar System formation, planetary atmospheres, and planets discove ...
... • Sun plus 8 (or 9 with Pluto) planets many of which have moons • plus “debris”: comets, asteroids, meteors, etc • We’ll go over historical understanding of motion (which is “complicated” when viewed from the Earth) and later look at Solar System formation, planetary atmospheres, and planets discove ...
Unit 1 Test Review Answers - School District of La Crosse
... 23.Extensions of the earth's poles onto the celestial sphere are called: CELESTRIAL POLES 24. In the horizon coordinate system, the amount of the celestial sphere which is observable is; 50% 25,Right ascension is measured in which direction along the celestial equator? EASTWARD 26.An asterism is: SM ...
... 23.Extensions of the earth's poles onto the celestial sphere are called: CELESTRIAL POLES 24. In the horizon coordinate system, the amount of the celestial sphere which is observable is; 50% 25,Right ascension is measured in which direction along the celestial equator? EASTWARD 26.An asterism is: SM ...
Astronomy - Core Knowledge UK
... Children to create script to TeacherTube video about why we have seasons. Inves?gate phases of the moon. Create a lunar diary Create eclipses in the classroom Explore shadows on Earth Watch video of ...
... Children to create script to TeacherTube video about why we have seasons. Inves?gate phases of the moon. Create a lunar diary Create eclipses in the classroom Explore shadows on Earth Watch video of ...
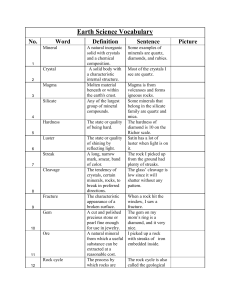
Earth Science Vocabulary No. Word Definition Sentence Picture 1
... The heating of two substances in ...
... The heating of two substances in ...
Mountain Skies March 7 2016
... Mercury in the evening sky, Jupiter is rising right about sunset. Look for it low in the east as the sun sets in the west. Until a waxing crescent moon enters the evening sky later this week, Jupiter is the brightest object in the evening sky. In fact, tonight Jupiter is at opposition which means it ...
... Mercury in the evening sky, Jupiter is rising right about sunset. Look for it low in the east as the sun sets in the west. Until a waxing crescent moon enters the evening sky later this week, Jupiter is the brightest object in the evening sky. In fact, tonight Jupiter is at opposition which means it ...
May 13, 2014 - In the News Story 1
... for Saturn to its upper right. Once the Moon is well up after dark, look for Antares and the other stars of upper Scorpius below it. Thursday, May 15 Jupiter's moon Io crosses the face of the planet from 9:41 to 11:57 p.m. Eastern Daylight Time. Io's tiny but more visible shadow follows it across fr ...
... for Saturn to its upper right. Once the Moon is well up after dark, look for Antares and the other stars of upper Scorpius below it. Thursday, May 15 Jupiter's moon Io crosses the face of the planet from 9:41 to 11:57 p.m. Eastern Daylight Time. Io's tiny but more visible shadow follows it across fr ...
Universal Gravitation
... determine that a presumed “star” was actually an additional planet The new planet was Uranus ...
... determine that a presumed “star” was actually an additional planet The new planet was Uranus ...
Comets and Mass Extinction
... •A comet has approximately 100 times more kinetic energy per gram than 420J/g of TNT! Jupiter—the trashcan • As large as 2.5 times all of the other planets in the solar system combined, known as a “Gas Giant,” 318 times as massive as the earth and therefore has a much greater gravitational pull, hol ...
... •A comet has approximately 100 times more kinetic energy per gram than 420J/g of TNT! Jupiter—the trashcan • As large as 2.5 times all of the other planets in the solar system combined, known as a “Gas Giant,” 318 times as massive as the earth and therefore has a much greater gravitational pull, hol ...
Planets or other objects orbiting a star are accelerating
... To observe Kepler’s and Newton's laws INTRODUCTION Planets or other objects orbiting a star are accelerating -- they are continually changing direction. The force that produces this acceleration is the gravitational attraction to the star. PROCEDURE Go to http://phet.colorado.edu, click on “play w ...
... To observe Kepler’s and Newton's laws INTRODUCTION Planets or other objects orbiting a star are accelerating -- they are continually changing direction. The force that produces this acceleration is the gravitational attraction to the star. PROCEDURE Go to http://phet.colorado.edu, click on “play w ...
Astronomy Terms
... Comet = large frozen mass of gas and dust that has a regular orbit around the sun; an icy body that orbits the sun in an elliptical orbit Nucleus = solid part of a comet made mainly of ice; tiny solid part of a comet made up of bits of rock and dust frozen in ice Tail = gaseous part of a comet that ...
... Comet = large frozen mass of gas and dust that has a regular orbit around the sun; an icy body that orbits the sun in an elliptical orbit Nucleus = solid part of a comet made mainly of ice; tiny solid part of a comet made up of bits of rock and dust frozen in ice Tail = gaseous part of a comet that ...
Our Solar System
... • Jupiter (5th planet from the Sun) – Largest planet in our solar system. – Its outer layer are made up of swirling gases. – Jupiter’s atmosphere is very colorful and it has an are called the Great Red Spot. • This spot is a storm that has been raging from hundreds of years and is three times larger ...
... • Jupiter (5th planet from the Sun) – Largest planet in our solar system. – Its outer layer are made up of swirling gases. – Jupiter’s atmosphere is very colorful and it has an are called the Great Red Spot. • This spot is a storm that has been raging from hundreds of years and is three times larger ...
Astrophysics 2012_2013 Grade 10 April 29, 2013
... 26. A meteoroid is a chunk of rock or dust in space. A meteor (shooting star) is a meteoroid that has been captured by the gravity of a planet, moon or other asteroid. What is the name of a meteor that has made impact with the surface of another place? 27. What do you call the place around a star i ...
... 26. A meteoroid is a chunk of rock or dust in space. A meteor (shooting star) is a meteoroid that has been captured by the gravity of a planet, moon or other asteroid. What is the name of a meteor that has made impact with the surface of another place? 27. What do you call the place around a star i ...
The most important questions to study for the exam
... • The stars in the sky are at very large distances from us, and their nightly motions relative to one another are not easily detected. • The stars we see are all moving directly away from us; from our viewpoint, they do not appear to be moving. 2. Stars on the celestial equator appear to move throug ...
... • The stars in the sky are at very large distances from us, and their nightly motions relative to one another are not easily detected. • The stars we see are all moving directly away from us; from our viewpoint, they do not appear to be moving. 2. Stars on the celestial equator appear to move throug ...
Chapter 1 - Colorado Mesa University
... • In our solar system the planets are • Terrestial Mercury(.4 AU), Venus(.7 AU), Earth, Mars(1.5 AU) • Gas: Jupiter(5 AU), Saturn(10 AU), Uranus(20 AU), Neptune(30 AU) • NOTICE A TREND? ROCKY CLOSE IN/GAS FAR OUT • WHY? • To date we have found over 1000 planets around other stars, they do not follow ...
... • In our solar system the planets are • Terrestial Mercury(.4 AU), Venus(.7 AU), Earth, Mars(1.5 AU) • Gas: Jupiter(5 AU), Saturn(10 AU), Uranus(20 AU), Neptune(30 AU) • NOTICE A TREND? ROCKY CLOSE IN/GAS FAR OUT • WHY? • To date we have found over 1000 planets around other stars, they do not follow ...
DaysSeasnsYears
... • “The time it takes for the Earth (or any planet/moon) to make one complete rotation.” • 24 hours • Part of each 24-hour day is lighted (daytime), part is dark (night). • The length of daytime and nighttime varies depending on how the Earth is tilted. ...
... • “The time it takes for the Earth (or any planet/moon) to make one complete rotation.” • 24 hours • Part of each 24-hour day is lighted (daytime), part is dark (night). • The length of daytime and nighttime varies depending on how the Earth is tilted. ...
Beyond our Sol. System
... After most of the planet’s surface was solid rock, the inner Earth was still outgassing (giving off water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen etc..) There was virtually no oxygen. The atmosphere was mostly Methane. Steam from the cooling planet eventually condensed to form the primitive oceans. ...
... After most of the planet’s surface was solid rock, the inner Earth was still outgassing (giving off water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen etc..) There was virtually no oxygen. The atmosphere was mostly Methane. Steam from the cooling planet eventually condensed to form the primitive oceans. ...