Glycolytic enzymes localize to ribonucleoprotein
... However, the union of egg and sperm gives rise to a zygote, which is capable of producing all cell lineages in the organism of the next generation [6,7]. Germ cells in many organisms have distinct cytoplasmic structures referred to as germ granules, which contain RNAs and proteins required for germl ...
... However, the union of egg and sperm gives rise to a zygote, which is capable of producing all cell lineages in the organism of the next generation [6,7]. Germ cells in many organisms have distinct cytoplasmic structures referred to as germ granules, which contain RNAs and proteins required for germl ...
Activity 2.2.3 The Biochemistry of Food
... The foods we eat contain the nutrients and molecules we need to survive. Some of these molecules are used to build our body parts, some are used to drive chemical reactions necessary for life, and others are used as sources of energy. Many of the molecules in our bodies are very large and are made b ...
... The foods we eat contain the nutrients and molecules we need to survive. Some of these molecules are used to build our body parts, some are used to drive chemical reactions necessary for life, and others are used as sources of energy. Many of the molecules in our bodies are very large and are made b ...
A Survey of Left-handed Helices in Protein Structures
... All naturally occurring amino acids with the exception of glycine contain one or more chiral carbon atoms and can therefore occur in two different configurations, L (levo, left-handed) and D (dextro, right-handed). Proteins are almost exclusively built from L-amino acids. The stereochemical bias of ...
... All naturally occurring amino acids with the exception of glycine contain one or more chiral carbon atoms and can therefore occur in two different configurations, L (levo, left-handed) and D (dextro, right-handed). Proteins are almost exclusively built from L-amino acids. The stereochemical bias of ...
figure 18.2
... signaling. Noncanonical Wnt signaling triggers its effects through alternative pathways including Wnt/Ca2+, Wnt/PCP, Wnt/Rho-Rac, Wnt/G-protein coupled receptors, Wnt/Ror, Wnt-aPKC, Wnt-RYK, and Wnt-mTOR pathways. In these pathways, Wnt proteins signal through the Fzd receptors and activate Dvl lead ...
... signaling. Noncanonical Wnt signaling triggers its effects through alternative pathways including Wnt/Ca2+, Wnt/PCP, Wnt/Rho-Rac, Wnt/G-protein coupled receptors, Wnt/Ror, Wnt-aPKC, Wnt-RYK, and Wnt-mTOR pathways. In these pathways, Wnt proteins signal through the Fzd receptors and activate Dvl lead ...
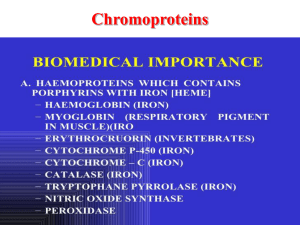
38_Chromoproteins. Pathological and physiological forms of h
... Carboxyhemoglobin • The binding of oxygen is affected by molecules such as carbon monoxide (CO) (for example from tobacco smoking, car exhaust and incomplete combustion in furnaces). CO competes with oxygen at the heme binding site. • Hemoglobin binding affinity for CO is 200 times greater than its ...
... Carboxyhemoglobin • The binding of oxygen is affected by molecules such as carbon monoxide (CO) (for example from tobacco smoking, car exhaust and incomplete combustion in furnaces). CO competes with oxygen at the heme binding site. • Hemoglobin binding affinity for CO is 200 times greater than its ...
... ii) What is the distribution of polar and non-polar residues along the polypeptide sequence and how does this distribution relate to the interaction of the protein with the membrane? iii) Residues that contact the lipid are generally large and nonpolar. Why are small non-polar seldom found? The diag ...
... Choice A: Describe the basic reaction mechanism for a typical DNA polymerase. Discuss why the Gibbs energy for the overall reaction is negative and also comment on the fidelity of the reaction, or why the polymerase is more likely to incorporate the correct base (Note: do not discuss removal of an i ...
AMINO ACID METABOLISM
... environment alters the conformation of pepsinogen so that it can cleave itself to yield pepsin. • Pepsin acts as an endopeptidase to cleave dietary proteins with a broad spectrum of specificity, although it prefers to cleave peptide bonds in which the carboxyl group is provided by aromatic or acidic ...
... environment alters the conformation of pepsinogen so that it can cleave itself to yield pepsin. • Pepsin acts as an endopeptidase to cleave dietary proteins with a broad spectrum of specificity, although it prefers to cleave peptide bonds in which the carboxyl group is provided by aromatic or acidic ...
Datasheet - BosterBio
... detection. Tested with WB, IHC-P in Human;Mouse;Rat. No cross reactivity with other proteins IHC-P, WB Human, Mouse, Rat A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence at the C-terminus of human ABCB11(1299-1313aa THEELMAQKGAYYKL), different from the related rat sequence by one amino acid, and from ...
... detection. Tested with WB, IHC-P in Human;Mouse;Rat. No cross reactivity with other proteins IHC-P, WB Human, Mouse, Rat A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence at the C-terminus of human ABCB11(1299-1313aa THEELMAQKGAYYKL), different from the related rat sequence by one amino acid, and from ...
Adrenergic Transmission
... The terminals of cholinergic neurons contain large numbers of small membrane-bound vesicles concentrated near the synaptic portion of the cell membrane as well as a smaller number of large dense-cored vesicles located farther from the synaptic membrane. The large vesicles contain a high concentratio ...
... The terminals of cholinergic neurons contain large numbers of small membrane-bound vesicles concentrated near the synaptic portion of the cell membrane as well as a smaller number of large dense-cored vesicles located farther from the synaptic membrane. The large vesicles contain a high concentratio ...
Lec 12: Fatty acid biosynthesis
... Acetyl‐CoA carboxylase Carboxylation of acetyl‐CoA by Acetyl‐CoA carboxylase (ACCase) is the committed step for fatty acid biosynthesis. This is often believed to be the limiting step of fatty acid biosynthesis ACCase is a multifunctional enzyme with 3 enzymatic activities: • Bacterial ACCase is ...
... Acetyl‐CoA carboxylase Carboxylation of acetyl‐CoA by Acetyl‐CoA carboxylase (ACCase) is the committed step for fatty acid biosynthesis. This is often believed to be the limiting step of fatty acid biosynthesis ACCase is a multifunctional enzyme with 3 enzymatic activities: • Bacterial ACCase is ...
Nutrition to Support Recovery from Endurance Exercise: Optimal
... summarized in the Table but can be consulted in their entirety in the International Olympic Committee Consensus Conference on Nutrition for Sport review (10). Protein Amino acids represent a relatively minor energy substrate during normal exercise (approximately 2% to 5% of total adenosine triphosph ...
... summarized in the Table but can be consulted in their entirety in the International Olympic Committee Consensus Conference on Nutrition for Sport review (10). Protein Amino acids represent a relatively minor energy substrate during normal exercise (approximately 2% to 5% of total adenosine triphosph ...
Contributions of direct incorporation from diet and microbial amino
... & Martinez del Rio 2010). While these experiments demonstrate that routing produces results that deviate from expectations based on mixing models, they were not able to characterize the isotopic patterns among specific amino acids that contribute to routing because they were conducted at the bulk ti ...
... & Martinez del Rio 2010). While these experiments demonstrate that routing produces results that deviate from expectations based on mixing models, they were not able to characterize the isotopic patterns among specific amino acids that contribute to routing because they were conducted at the bulk ti ...
PPT
... • Assign all of the residues in the peptide the appropriate set of parameters. • Scan through the peptide and identify regions where 4 out of 6 contiguous residues have P(a-helix) > 100. • That region is declared an alpha-helix. Extend the helix in both directions until a set of four contiguous resi ...
... • Assign all of the residues in the peptide the appropriate set of parameters. • Scan through the peptide and identify regions where 4 out of 6 contiguous residues have P(a-helix) > 100. • That region is declared an alpha-helix. Extend the helix in both directions until a set of four contiguous resi ...
Expanding the Genetic Code
... with an N-terminal Cys residue through a transthioesterification reaction. The thioester-linked intermediate then undergoes an irreversible S!N acyl rearrangement to form a native peptide bond at the ligation site. This method typically requires an N-terminal Cys residue at the ligation site, but re ...
... with an N-terminal Cys residue through a transthioesterification reaction. The thioester-linked intermediate then undergoes an irreversible S!N acyl rearrangement to form a native peptide bond at the ligation site. This method typically requires an N-terminal Cys residue at the ligation site, but re ...
poster - Computer Science and Engineering
... Yasser EL-Manzalawy, Cornelia Caragea, Drena Dobbs, and Vasant Honavar Profile-Based Approaches ...
... Yasser EL-Manzalawy, Cornelia Caragea, Drena Dobbs, and Vasant Honavar Profile-Based Approaches ...
Diversity of heterotrimeric G-protein γ subunits in plants | SpringerLink
... Representatives of type A were found in gymnosperms and flowering plants. Notably, in rosid species there are at least two variants of this type related to the Arabidopsis AGG1 and AGG2 proteins. At the same time most asterid species have only one Gγ subunit of this type. The second Gγ subunit type, ...
... Representatives of type A were found in gymnosperms and flowering plants. Notably, in rosid species there are at least two variants of this type related to the Arabidopsis AGG1 and AGG2 proteins. At the same time most asterid species have only one Gγ subunit of this type. The second Gγ subunit type, ...
Beer
... • Mashing begins at ~ 38°C • Temperature is gradually raised to 77°C • Heating is done in steps with rest periods of ~30 min (Allows enzymes to work before they are heat inactivated) ...
... • Mashing begins at ~ 38°C • Temperature is gradually raised to 77°C • Heating is done in steps with rest periods of ~30 min (Allows enzymes to work before they are heat inactivated) ...
PPT4 - Ycmou
... Catabolism of proteins contribute only 10% to 15% of total energy. Amino acids produced after the breaking down of proteins enter the catabolic pathways . The alpha amino group of 20 amino acids is removed during the first stage of degradation of amino acids by enzyme, aminotransferase. ...
... Catabolism of proteins contribute only 10% to 15% of total energy. Amino acids produced after the breaking down of proteins enter the catabolic pathways . The alpha amino group of 20 amino acids is removed during the first stage of degradation of amino acids by enzyme, aminotransferase. ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.