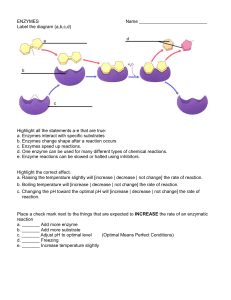
4 - Ms McRae`s Science
... a)yes bec an increase in the temperature of the HCl will increase the velocity of the reactant particles which will increase the number of collisions AND increase the number of effective collisions i.e. ones that have sufficient energy (activation energy) to react b) skipping this one for now until ...
... a)yes bec an increase in the temperature of the HCl will increase the velocity of the reactant particles which will increase the number of collisions AND increase the number of effective collisions i.e. ones that have sufficient energy (activation energy) to react b) skipping this one for now until ...
Faculty of Science Department of chemistry Physical Chemistry (2)
... 1. Develop a comprehensive understanding of the fundamental principles of physical chemistry. 2. Explain the fundamental principles of physical chemistry and their applications in chemical kinetics, molecular reaction dynamics, surface chemistry, catalysis, and colloid fields. 3. Promote problem-sol ...
... 1. Develop a comprehensive understanding of the fundamental principles of physical chemistry. 2. Explain the fundamental principles of physical chemistry and their applications in chemical kinetics, molecular reaction dynamics, surface chemistry, catalysis, and colloid fields. 3. Promote problem-sol ...
Equilibrium 4 Noteform - IndustrialProcesses
... 2. How can the rate be maximized? (Think about the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction.) ...
... 2. How can the rate be maximized? (Think about the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction.) ...
Equilibrium and Kinetics
... reaction which exhibits zero order kinetics. How can this expression be used graphically to evaluate the rate constant? 11. Sketch and label the phase diagram of Sulphur system. 12. Differentiate between the terms triple point and eutectic point. . 13. What is Joule Thomson Inversion Temperature? 14 ...
... reaction which exhibits zero order kinetics. How can this expression be used graphically to evaluate the rate constant? 11. Sketch and label the phase diagram of Sulphur system. 12. Differentiate between the terms triple point and eutectic point. . 13. What is Joule Thomson Inversion Temperature? 14 ...
CHEM_2nd_Semester_Final_R eview
... 44. Are the following changes of state exothermic or endothermic: a. An ice cube melting c. Water vapor condensing on a mirror b. Dry ice subliming to carbon dioxide d. Water freezing into an ice cube 45. How many calories are needed to raise 450. grams of water from 21.0 oC to 85.5oC? 46. How many ...
... 44. Are the following changes of state exothermic or endothermic: a. An ice cube melting c. Water vapor condensing on a mirror b. Dry ice subliming to carbon dioxide d. Water freezing into an ice cube 45. How many calories are needed to raise 450. grams of water from 21.0 oC to 85.5oC? 46. How many ...
2nd Semester Final Review
... 44. Are the following changes of state exothermic or endothermic: a. An ice cube melting c. Water vapor condensing on a mirror b. Dry ice subliming to carbon dioxide d. Water freezing into an ice cube 45. How many calories are needed to raise 450. grams of water from 21.0 oC to 85.5oC? 46. How many ...
... 44. Are the following changes of state exothermic or endothermic: a. An ice cube melting c. Water vapor condensing on a mirror b. Dry ice subliming to carbon dioxide d. Water freezing into an ice cube 45. How many calories are needed to raise 450. grams of water from 21.0 oC to 85.5oC? 46. How many ...
Syllabus
... Grading Policy: There will be 12 homework assignments, a midterm and a final. All are given on a take-home basis. If you have any question about a problem before starting to work, you are strongly encouraged to discuss the matter with the professor or fellow students. That is, students are encourage ...
... Grading Policy: There will be 12 homework assignments, a midterm and a final. All are given on a take-home basis. If you have any question about a problem before starting to work, you are strongly encouraged to discuss the matter with the professor or fellow students. That is, students are encourage ...
RTF
... Would you expect the combustion of methane, CH4 with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water, to be a reversible reaction? Hint: Methane, or natural gas, is an important energy source. Considering this, what did you learn in the last unit that will help you predict whether or not the reverse reactio ...
... Would you expect the combustion of methane, CH4 with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water, to be a reversible reaction? Hint: Methane, or natural gas, is an important energy source. Considering this, what did you learn in the last unit that will help you predict whether or not the reverse reactio ...