CHM 111: General Physical Chemistry 3 Units
... Clausius-Clapeyron equation, freezing point, melting point and phase diagrams of simple systems; solids types of solids and their properties, ionic solids and lattice energy, crystalline solids. Chemical Energetic: definition of some thermodynamic terms, heat, work, internal energy, enthalpy, pressu ...
... Clausius-Clapeyron equation, freezing point, melting point and phase diagrams of simple systems; solids types of solids and their properties, ionic solids and lattice energy, crystalline solids. Chemical Energetic: definition of some thermodynamic terms, heat, work, internal energy, enthalpy, pressu ...
one way
... Summary The velocity v of a given chemical reaction generally depends on: - the concentration of the educts: according to v = k caA cbB ccC ... - the temperature: according to k = A exp(-Ea/RT) - the presence or the absence of a catalyst: a catalyst lowers the activation energy Ea The chemical equi ...
... Summary The velocity v of a given chemical reaction generally depends on: - the concentration of the educts: according to v = k caA cbB ccC ... - the temperature: according to k = A exp(-Ea/RT) - the presence or the absence of a catalyst: a catalyst lowers the activation energy Ea The chemical equi ...
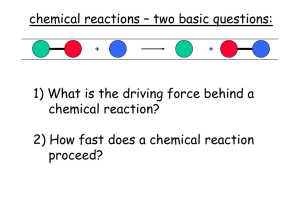
A Guide to Rate of Reactions
... Chemical equilibrium is based on thermodynamics and answers the question: ‘How far does the reaction go?’ Learners are inclined to confuse the two concepts. In this series we explain what we mean by the rate of a reaction and the factors that determine this rate. Whereas this can be very theoretical ...
... Chemical equilibrium is based on thermodynamics and answers the question: ‘How far does the reaction go?’ Learners are inclined to confuse the two concepts. In this series we explain what we mean by the rate of a reaction and the factors that determine this rate. Whereas this can be very theoretical ...
Determination of the reaction order Determination of the reaction
... experiments required much more sophisticated approach. These old methods are also very useful for analysis of kinetic data (small data sets) in text problem solving exercises. Hence, their application is essential for chemists. It is always useful to inspect the data carefully if any regularities di ...
... experiments required much more sophisticated approach. These old methods are also very useful for analysis of kinetic data (small data sets) in text problem solving exercises. Hence, their application is essential for chemists. It is always useful to inspect the data carefully if any regularities di ...
Rate of Reaction
... Rate of Reaction Rates of reactions are usually expressed in units of moles per liter per unit time. If we know the chemical equation for a reaction, its rate can be determined by following the change in concentration of any product or reactant that can be detected quantitatively. r = ∆ concentratio ...
... Rate of Reaction Rates of reactions are usually expressed in units of moles per liter per unit time. If we know the chemical equation for a reaction, its rate can be determined by following the change in concentration of any product or reactant that can be detected quantitatively. r = ∆ concentratio ...
Chemistry 116: General Chemistry
... As a gas molecule, N2 does not often collide with other reactants. The lone pairs on N do react but only reversibly. Reactions with N2 are indeed thermodynamically favorable, but they are just slow. ...
... As a gas molecule, N2 does not often collide with other reactants. The lone pairs on N do react but only reversibly. Reactions with N2 are indeed thermodynamically favorable, but they are just slow. ...
Annexure `CD-01` L T P/S SW/FW TOTAL CREDIT UNITS 3 1 2 0 5
... Classification, Lyophobic and lyophilic sols, electrical double layer, Zeta potential, Electrophoresis, origin of charge on colloidal particles, protective colloids, gold number, applications. Module III Adsorption Heat of adsorption, Freundlich adsorption isotherm, physisorption and chemisorp ...
... Classification, Lyophobic and lyophilic sols, electrical double layer, Zeta potential, Electrophoresis, origin of charge on colloidal particles, protective colloids, gold number, applications. Module III Adsorption Heat of adsorption, Freundlich adsorption isotherm, physisorption and chemisorp ...
N H CCl3 C O N CCl3 C Cl (ii) SOCl2 7.55 g 7.78 g CCl C N NH N H
... Covers Chapter 6 of Sorrell, “Organic Chemistry” ...
... Covers Chapter 6 of Sorrell, “Organic Chemistry” ...