Consciousness, Literature and the Arts
... 'becoming-imperceptible') as a way of encountering life philosophically not by describing it as a standoff between adversaries, but as something mobile, crossing borders rather than encountering boundaries, and always open to the intensity of life. But it isn't necessary to invoke only French abstru ...
... 'becoming-imperceptible') as a way of encountering life philosophically not by describing it as a standoff between adversaries, but as something mobile, crossing borders rather than encountering boundaries, and always open to the intensity of life. But it isn't necessary to invoke only French abstru ...
Functions of the Nervous System Functions of the
... 2. CSF flows through the ventricles and into the subarachnoid space via the median and lateral apertures. Some CSF flows through the central canal of the spinal cord. 3. CSF flows through the subarachnoid space. 4. CSF is absorbed into the dural venous sinuses via the arachnoid villi. ...
... 2. CSF flows through the ventricles and into the subarachnoid space via the median and lateral apertures. Some CSF flows through the central canal of the spinal cord. 3. CSF flows through the subarachnoid space. 4. CSF is absorbed into the dural venous sinuses via the arachnoid villi. ...
Structural Classification of the Nervous System
... 2. CSF flows through the ventricles and into the subarachnoid space via the median and lateral apertures. Some CSF flows through the central canal of the spinal cord. 3. CSF flows through the subarachnoid space. 4. CSF is absorbed into the dural venous sinuses via the arachnoid villi. ...
... 2. CSF flows through the ventricles and into the subarachnoid space via the median and lateral apertures. Some CSF flows through the central canal of the spinal cord. 3. CSF flows through the subarachnoid space. 4. CSF is absorbed into the dural venous sinuses via the arachnoid villi. ...
Chapter 4
... through a surgical procedure in order to wipe out the specific part of the brain they are interested in - see BIO1 overhead for a depiction of the stereotopic apparatus used to do this The “destruction” of brain tissue is usually done by touching a small wire to the brain site of interest, then pass ...
... through a surgical procedure in order to wipe out the specific part of the brain they are interested in - see BIO1 overhead for a depiction of the stereotopic apparatus used to do this The “destruction” of brain tissue is usually done by touching a small wire to the brain site of interest, then pass ...
The Essential Role of Enriched Stable Nuclides in Positron Emission
... Other enriched compounds include enriched molecular oxygen and nitrogen enriched in nitrogen-13 and are also used as target materials to produce PET radiopharmaceuticals. Oxygen gas is used in several centers to produce another radioactive drug, fluorine-18-labeled dopamine, used to study brain func ...
... Other enriched compounds include enriched molecular oxygen and nitrogen enriched in nitrogen-13 and are also used as target materials to produce PET radiopharmaceuticals. Oxygen gas is used in several centers to produce another radioactive drug, fluorine-18-labeled dopamine, used to study brain func ...
Parts of the Brain - University of Peradeniya
... Nervous system and Brain Few facts from your A/Levels or high school biology • In a Fresh brain or Spinal cord., – White is due to myelinated (protein +l ipid); nerve fibers or Axons – Gay is due to cells; neurons & glia But in imaging techniques gray and white may look different ...
... Nervous system and Brain Few facts from your A/Levels or high school biology • In a Fresh brain or Spinal cord., – White is due to myelinated (protein +l ipid); nerve fibers or Axons – Gay is due to cells; neurons & glia But in imaging techniques gray and white may look different ...
Document
... participate in the immune response of the brain scar tissue formation following neuronal loss storage of glycogen as an energy reserve in the brain uptake and release of neuroactive compounds buffering of the extracellular ion homeostasis (spatial buffering of K+ ions) participate in the formation o ...
... participate in the immune response of the brain scar tissue formation following neuronal loss storage of glycogen as an energy reserve in the brain uptake and release of neuroactive compounds buffering of the extracellular ion homeostasis (spatial buffering of K+ ions) participate in the formation o ...
animal nervous system - mf011
... The motor system carries signals to skeletal muscles and is voluntary The autonomic nervous system regulates the internal environment in an involuntary manner ...
... The motor system carries signals to skeletal muscles and is voluntary The autonomic nervous system regulates the internal environment in an involuntary manner ...
A Glossary
... MRI, that gathers information relating to short-term changes in oxygen uptake by neurons. It typically uses this information to depict the brain areas that become more active or less active—and presumably more or less involved—while a subject in the fMRI scanner performs a cognitive task. ...
... MRI, that gathers information relating to short-term changes in oxygen uptake by neurons. It typically uses this information to depict the brain areas that become more active or less active—and presumably more or less involved—while a subject in the fMRI scanner performs a cognitive task. ...
MF011_fhs_lnt_008a_Jan11
... The motor system carries signals to skeletal muscles and is voluntary The autonomic nervous system regulates the internal environment in an involuntary manner ...
... The motor system carries signals to skeletal muscles and is voluntary The autonomic nervous system regulates the internal environment in an involuntary manner ...
The Discovery of the Endocannabinoid System
... looking in many brain areas, and reveals the endocannabinoids as an innate defense mechanism of the brain. It also helps explain how cannabinoids could help lessen the damaging effects of stroke, epilepsy and perhaps other brain traumas. D) When endocannabinoids target certain strategically located ...
... looking in many brain areas, and reveals the endocannabinoids as an innate defense mechanism of the brain. It also helps explain how cannabinoids could help lessen the damaging effects of stroke, epilepsy and perhaps other brain traumas. D) When endocannabinoids target certain strategically located ...
Computational Intelligence in a Human Brain Model
... process, a new contribution from the point of view of comparison with other similar works. This new proposal captures most of the brain's cognitive capabilities, but does not show very detailed how the parts of the brain work together to produce cognition. In this new conception, the presented solut ...
... process, a new contribution from the point of view of comparison with other similar works. This new proposal captures most of the brain's cognitive capabilities, but does not show very detailed how the parts of the brain work together to produce cognition. In this new conception, the presented solut ...
Drug-Induced Psychosis and Schizophrenia
... addiction and detoxification. These are often interlinked, in which case we generally term clients with “co-occurring disorders” or “dual-diagnoses”. This is a fairly recent way of defining persons living with mental illness as well as substance abuse, and is a very grey area within the world of beh ...
... addiction and detoxification. These are often interlinked, in which case we generally term clients with “co-occurring disorders” or “dual-diagnoses”. This is a fairly recent way of defining persons living with mental illness as well as substance abuse, and is a very grey area within the world of beh ...
LESSON 1.2 WORKBOOK How does brain structure impact its function?
... efficiently. Because of this white appearance, this area of the spinal cord is referred to as white matter. The area where connections between the peripheral and central nervous system neurons are made is in the middle of the spinal cord, and lacks myelin. Because of this it appears grey in comparis ...
... efficiently. Because of this white appearance, this area of the spinal cord is referred to as white matter. The area where connections between the peripheral and central nervous system neurons are made is in the middle of the spinal cord, and lacks myelin. Because of this it appears grey in comparis ...
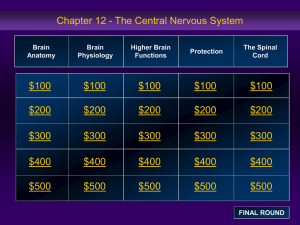
Jeopardy
... seen on the external surfaces of the brain? a. pineal and hypothalamus b. thalamus and hypothalamus c. pineal and corpora quadrigemini d. pons and medulla BACK TO GAME ...
... seen on the external surfaces of the brain? a. pineal and hypothalamus b. thalamus and hypothalamus c. pineal and corpora quadrigemini d. pons and medulla BACK TO GAME ...
What Brain Research Says About Learning
... The connections made are like_________________________ in that they_____________________________ Learning is like_________________________ in that it_____________________________ Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. ...
... The connections made are like_________________________ in that they_____________________________ Learning is like_________________________ in that it_____________________________ Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. ...
Slide () - Anesthesiology - American Society of Anesthesiologists
... Myelinating oligodendrocytes at a midrostrocaudal level: All panels are stained immunochemically with antibodies to myelin basic protein (MBP). A presents an overview showing different stages of myelination at a midrostrocaudal level of a control brain. In the cerebrocortical mantel, and in the tran ...
... Myelinating oligodendrocytes at a midrostrocaudal level: All panels are stained immunochemically with antibodies to myelin basic protein (MBP). A presents an overview showing different stages of myelination at a midrostrocaudal level of a control brain. In the cerebrocortical mantel, and in the tran ...
The Evolution of Reentrance in the Vertebrate Brain
... brain. In general, the cell bodies of most neurons are located near the ventricles, while the tissue near the pial (superficial) surface is composed largely of fibers, both dendrites and axons. Both local and long-range axonal projections are intermingled in a dense neuropil. Within this synaptic fi ...
... brain. In general, the cell bodies of most neurons are located near the ventricles, while the tissue near the pial (superficial) surface is composed largely of fibers, both dendrites and axons. Both local and long-range axonal projections are intermingled in a dense neuropil. Within this synaptic fi ...
MODULE J – CONTROL OF VENTILATION
... A. The function of the medulla oblongata is necessary for regulation of blood pressure, heart rate, and ventilation (i.e. life). B. When increased intracranial pressure is present as a result of cerebral trauma and edema or other intracerebral abnormality (tumor), the ability of the brain to move to ...
... A. The function of the medulla oblongata is necessary for regulation of blood pressure, heart rate, and ventilation (i.e. life). B. When increased intracranial pressure is present as a result of cerebral trauma and edema or other intracerebral abnormality (tumor), the ability of the brain to move to ...
TRUTH Read
... much smaller. It is involved in balance and coordi rianon. A person whose cerebellum is injured may have trouble with coordination. [he person may walk unevenly and even occasionally fail doivn. [he midbrain is located between the hindbrain and the forebrain Areas within the midbrain are involi ed i ...
... much smaller. It is involved in balance and coordi rianon. A person whose cerebellum is injured may have trouble with coordination. [he person may walk unevenly and even occasionally fail doivn. [he midbrain is located between the hindbrain and the forebrain Areas within the midbrain are involi ed i ...
Nervous System Game Show
... occurs in the spinal cord or brain will determine the extent of this ...
... occurs in the spinal cord or brain will determine the extent of this ...
FUNCTIONAL ORGANIZATION OF THE HUMAN BODY
... absorbed form, they may be transported to the liver where their chemical composition is changed so they are in more useable forms. The Digestive Process: The Mouth (the start of the process): The digestive process begins in the mouth. Food is partly broken down by the process of chewing and by the ...
... absorbed form, they may be transported to the liver where their chemical composition is changed so they are in more useable forms. The Digestive Process: The Mouth (the start of the process): The digestive process begins in the mouth. Food is partly broken down by the process of chewing and by the ...
From blood–brain barrier to blood–brain interface: new
... oligonucleotide analogues10. Phosphorothioate oligonucleotides are rapidly sequestered by and transported across the BBB. The transporter seems promiscuous towards phosphorothioate oligonucleotides, as it has been shown to transport into the brain every phosphorothioate oligonucleotide tested so far ...
... oligonucleotide analogues10. Phosphorothioate oligonucleotides are rapidly sequestered by and transported across the BBB. The transporter seems promiscuous towards phosphorothioate oligonucleotides, as it has been shown to transport into the brain every phosphorothioate oligonucleotide tested so far ...
Ch 2 The Biological Basis of Behavior
... List and describe how the nervous and endocrine systems use chemicals to direct everything our bodies do? Describe the two major subdivisions of the peripheral nervous system and how they initiate bodily activity and ...
... List and describe how the nervous and endocrine systems use chemicals to direct everything our bodies do? Describe the two major subdivisions of the peripheral nervous system and how they initiate bodily activity and ...
Medicines stimulants
... • Caffeine is a psychoactive stimulant (=acts on CNS). When consumed in large amounts it can cause anxiety, irritability and sleeplessness. It is a weak diuretic i.e. causes the body to lose more water than it takes in. • Its structure is similar to ...
... • Caffeine is a psychoactive stimulant (=acts on CNS). When consumed in large amounts it can cause anxiety, irritability and sleeplessness. It is a weak diuretic i.e. causes the body to lose more water than it takes in. • Its structure is similar to ...
Blood–brain barrier

The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective permeability barrier that separates the circulating blood from the brain extracellular fluid (BECF) in the central nervous system (CNS). The blood–brain barrier is formed by brain endothelial cells, which are connected by tight junctions with an extremely high electrical resistivity of at least 0.1 Ω⋅m. The blood–brain barrier allows the passage of water, some gases, and lipid-soluble molecules by passive diffusion, as well as the selective transport of molecules such as glucose and amino acids that are crucial to neural function. On the other hand, the blood–brain barrier may prevent the entry of lipophilic, potential neurotoxins by way of an active transport mechanism mediated by P-glycoprotein. Astrocytes are necessary to create the blood–brain barrier. A small number of regions in the brain, including the circumventricular organs (CVOs), do not have a blood–brain barrier.The blood–brain barrier occurs along all capillaries and consists of tight junctions around the capillaries that do not exist in normal circulation. Endothelial cells restrict the diffusion of microscopic objects (e.g., bacteria) and large or hydrophilic molecules into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), while allowing the diffusion of small hydrophobic molecules (O2, CO2, hormones). Cells of the barrier actively transport metabolic products such as glucose across the barrier with specific proteins. This barrier also includes a thick basement membrane and astrocytic endfeet.