Motor Pathways
... Voluntary movements are organized by motor programs • Translate goal into action – Formation of a movement representation, or motor program ...
... Voluntary movements are organized by motor programs • Translate goal into action – Formation of a movement representation, or motor program ...
The Muscular System - Catherine Huff`s Site
... • Muscle fibers may store glucose and oxygen in glycogen or myoglobin (oxygen attached to a protein) • Myoglobin can release oxygen during strenuous exercise (process is called aerobic metabolism) • Anaerobic metabolism occurs when not enough oxygen is stored. By product is lactic acid, a by-product ...
... • Muscle fibers may store glucose and oxygen in glycogen or myoglobin (oxygen attached to a protein) • Myoglobin can release oxygen during strenuous exercise (process is called aerobic metabolism) • Anaerobic metabolism occurs when not enough oxygen is stored. By product is lactic acid, a by-product ...
The Muscular System
... • Muscle fibers may store glucose and oxygen in glycogen or myoglobin (oxygen attached to a protein) • Myoglobin can release oxygen during strenuous exercise (process is called aerobic metabolism) • Anaerobic metabolism occurs when not enough oxygen is stored. By product is lactic acid, a by-product ...
... • Muscle fibers may store glucose and oxygen in glycogen or myoglobin (oxygen attached to a protein) • Myoglobin can release oxygen during strenuous exercise (process is called aerobic metabolism) • Anaerobic metabolism occurs when not enough oxygen is stored. By product is lactic acid, a by-product ...
sample - Testbankonline.Com
... What are the different ways in which there is plasticity in the brain? ▪ Plasticity in the brain is due to a number of different factors. These can include neuronal growth (neurogenesis), changes in dendritic connections among neurons, and changes in chemicals bonds. In addition to alcohol, name oth ...
... What are the different ways in which there is plasticity in the brain? ▪ Plasticity in the brain is due to a number of different factors. These can include neuronal growth (neurogenesis), changes in dendritic connections among neurons, and changes in chemicals bonds. In addition to alcohol, name oth ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... turned off leading to a small depolarization • If stimulation is repated, repetitive spikes appear • Muscarinic receptors modulates the repetitive firing properties and enhance the ability of ANS to control visceral activity ...
... turned off leading to a small depolarization • If stimulation is repated, repetitive spikes appear • Muscarinic receptors modulates the repetitive firing properties and enhance the ability of ANS to control visceral activity ...
No Slide Title
... PERIPHERAL CHEMORECEPTORS CENTRAL CHEMORECEPTORS PULMONARY RECEPTORS CHEST WALL AND MUSCLE RECEPTORS ...
... PERIPHERAL CHEMORECEPTORS CENTRAL CHEMORECEPTORS PULMONARY RECEPTORS CHEST WALL AND MUSCLE RECEPTORS ...
Transcript
... properties of individual nerve cells or neurons within those circuits. So we're going to focus now on one individual nerve cell which is shown in the left in brown, and look at this in slightly higher magnification. So you can see that the nerve cell is a highly specialized cell type. It's not like ...
... properties of individual nerve cells or neurons within those circuits. So we're going to focus now on one individual nerve cell which is shown in the left in brown, and look at this in slightly higher magnification. So you can see that the nerve cell is a highly specialized cell type. It's not like ...
Functional features of the rat subicular microcircuits studied in vitro
... EPSPs evoked in subicular cells by CA1 and entorhinal cortex stimulation are also glutamatergic, with different AMPA and NMDA components [6,78]. Nevertheless, these two subicular inputs are differentially modulated. The CA1-activated EPSPs are the main targets of a dopaminergic control that depresse ...
... EPSPs evoked in subicular cells by CA1 and entorhinal cortex stimulation are also glutamatergic, with different AMPA and NMDA components [6,78]. Nevertheless, these two subicular inputs are differentially modulated. The CA1-activated EPSPs are the main targets of a dopaminergic control that depresse ...
BRS Physiology
... depends on the size of the inward current during the upstroke of the action potential. The larger the inward current, the higher the conduction velocity. is fastest in the Purkinje system. is slowest in the AV node (seen as the PR interval on the ECG), allowing time for ventricular filling before ve ...
... depends on the size of the inward current during the upstroke of the action potential. The larger the inward current, the higher the conduction velocity. is fastest in the Purkinje system. is slowest in the AV node (seen as the PR interval on the ECG), allowing time for ventricular filling before ve ...
Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 3: Structure of the
... This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: •any public performance or display, including transmission of any image over a network; •preparation of any derivative work, including extraction, in whole or in part, of any images; •any ...
... This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: •any public performance or display, including transmission of any image over a network; •preparation of any derivative work, including extraction, in whole or in part, of any images; •any ...
Chapter 14: Brain Control of Movement
... Represent highest levels of motor control Decisions made about actions and their outcome Area 5: Inputs from areas 3, 1, and 2 Area 7: Inputs from higher-order visual cortical areas such as MT ...
... Represent highest levels of motor control Decisions made about actions and their outcome Area 5: Inputs from areas 3, 1, and 2 Area 7: Inputs from higher-order visual cortical areas such as MT ...
Portfolio - TRG Communications, LLC Specializing in the Pharmabio
... Human emotion involves the entire nervous system, but there are two parts of the CNS that are especially important: the limbic system and the autonomic nervous system. The limbic system is a complex set of structures that lies on both sides of the thalamus, just under the cerebrum. It includes the d ...
... Human emotion involves the entire nervous system, but there are two parts of the CNS that are especially important: the limbic system and the autonomic nervous system. The limbic system is a complex set of structures that lies on both sides of the thalamus, just under the cerebrum. It includes the d ...
Brain Evolution Relevant to Language
... requires that cortical areas somehow communicate with these lower motor nuclei. In humans, these nuclei receive both direct (straight from the cortex) and indirect (routed through intermediate brain nuclei) connections from the cortex (Butler et al. 2001, Striedter 2005). The indirect connections fo ...
... requires that cortical areas somehow communicate with these lower motor nuclei. In humans, these nuclei receive both direct (straight from the cortex) and indirect (routed through intermediate brain nuclei) connections from the cortex (Butler et al. 2001, Striedter 2005). The indirect connections fo ...
Prefrontal abilities
... picture provided of earlier cultures may be similarly inadequate. A second approach is the study of primitive cultures, the lost tribes of jungle recesses, discovered and investigated by explorers. While these studies provide valuable insights, they focus on the basic life patterns developed to main ...
... picture provided of earlier cultures may be similarly inadequate. A second approach is the study of primitive cultures, the lost tribes of jungle recesses, discovered and investigated by explorers. While these studies provide valuable insights, they focus on the basic life patterns developed to main ...
PDF
... is a discrete computational (in the broad sense of having rulebased input–output relations) unit, conforming to biophysical laws. The timing of firing of a neuron is determined by chemical and electrical interactions between the cell and its immediate environment. All cause and effect relations occu ...
... is a discrete computational (in the broad sense of having rulebased input–output relations) unit, conforming to biophysical laws. The timing of firing of a neuron is determined by chemical and electrical interactions between the cell and its immediate environment. All cause and effect relations occu ...
Freud Returns - Socialscientist.us
... The seeking system, regulated by the neurotransmitter dopamine, bears a remarkable resemblance to the Freudian “libido.” According to Freud, the libidinal or sexual drive is a pleasure-seeking system that energizes most of our goaldirected interactions with the world. Modern research shows that its ...
... The seeking system, regulated by the neurotransmitter dopamine, bears a remarkable resemblance to the Freudian “libido.” According to Freud, the libidinal or sexual drive is a pleasure-seeking system that energizes most of our goaldirected interactions with the world. Modern research shows that its ...
Neuroscientists are finding that their biological
... The seeking system, regulated by the neurotransmitter dopamine, bears a remarkable resemblance to the Freudian “libido.” According to Freud, the libidinal or sexual drive is a pleasure-seeking system that energizes most of our goaldirected interactions with the world. Modern research shows that its ...
... The seeking system, regulated by the neurotransmitter dopamine, bears a remarkable resemblance to the Freudian “libido.” According to Freud, the libidinal or sexual drive is a pleasure-seeking system that energizes most of our goaldirected interactions with the world. Modern research shows that its ...
Astrocyte-Neuron Interactions during Learning May Occur by Lactate
... experimental evidence indicates that cerebral lactate has signaling functions that are independent of its role as energy source (Bergersen and Gjedde, 2012). In particular, the brain expresses Gi -protein coupled hydroxycarboxylic acid (HCA) receptors, the activation of which inhibits adenylate cycl ...
... experimental evidence indicates that cerebral lactate has signaling functions that are independent of its role as energy source (Bergersen and Gjedde, 2012). In particular, the brain expresses Gi -protein coupled hydroxycarboxylic acid (HCA) receptors, the activation of which inhibits adenylate cycl ...
Neuroanatomical correlates of intelligence
... 2005) and in the (anterior) cingulate (Frangou et al., 2004; Haier et al., 2004; Wilke et al., 2003). However, less significant positive correlations also seem to exist in other medial and lateral temporal, parietal, and occipital sections, as well as subcortically and in the cerebellum. Voxel-wise p ...
... 2005) and in the (anterior) cingulate (Frangou et al., 2004; Haier et al., 2004; Wilke et al., 2003). However, less significant positive correlations also seem to exist in other medial and lateral temporal, parietal, and occipital sections, as well as subcortically and in the cerebellum. Voxel-wise p ...
Pausing to Regroup: Thalamic Gating of Cortico
... The key, they believe, lies in the projections of the intralaminar thalamic neurons to the striatum, especially to the cholinergic interneurons of the striatum, which release acetylcholine (ACh) on being stimulated. These interneurons fire tonically and are thought to correspond to the ‘‘tonically a ...
... The key, they believe, lies in the projections of the intralaminar thalamic neurons to the striatum, especially to the cholinergic interneurons of the striatum, which release acetylcholine (ACh) on being stimulated. These interneurons fire tonically and are thought to correspond to the ‘‘tonically a ...
מצגת של PowerPoint
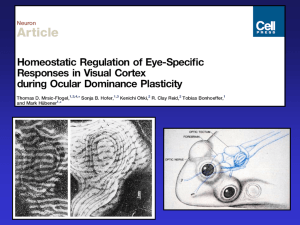
... neurons was full after 2-3 days of MD. - The increase in the response to the closed eye in monocular neurons was only full after 4-7 days of MD, just like the general increase in binocular neurons (supporting prediction ‘c’). binocular ...
... neurons was full after 2-3 days of MD. - The increase in the response to the closed eye in monocular neurons was only full after 4-7 days of MD, just like the general increase in binocular neurons (supporting prediction ‘c’). binocular ...
Preview Sample 1
... E. Tools for Studying the Brain (Lecture/Discussion Suggestion: Psychophysiological Measurement) i. Four basic techniques used by neuroscientists for studying the brain 1. Microelectrode Techniques: used to study the functions of individual neurons. 2. Macroelectrode Techniques: used to obtain a pic ...
... E. Tools for Studying the Brain (Lecture/Discussion Suggestion: Psychophysiological Measurement) i. Four basic techniques used by neuroscientists for studying the brain 1. Microelectrode Techniques: used to study the functions of individual neurons. 2. Macroelectrode Techniques: used to obtain a pic ...
Physiology # 2 Dr. Ahmad Dwari Qaisar A. Maaya`h
... Factors that affect GFR 1- Decrease (↓) in the Glomerular capillary filtration coefficient (↓) GFR. (e.g.: chronic uncontrolled hypertension, DM, or chronic kidney disease). So, the filtration membranes are of no efficient filtration of the plasma. 2- Increase (↑) in the Bowman's capsule hydro ...
... Factors that affect GFR 1- Decrease (↓) in the Glomerular capillary filtration coefficient (↓) GFR. (e.g.: chronic uncontrolled hypertension, DM, or chronic kidney disease). So, the filtration membranes are of no efficient filtration of the plasma. 2- Increase (↑) in the Bowman's capsule hydro ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.