Calculating Consequences - Human Reward and Decision Making lab
... lowest objective contingency measure for each subject and compared their associated causality judgments (the specific schedules assigned to each condition for each subject are listed in supplemental Table 1, available at www.jneurosci.org as supplemental material). The high-contingency schedules (65 ...
... lowest objective contingency measure for each subject and compared their associated causality judgments (the specific schedules assigned to each condition for each subject are listed in supplemental Table 1, available at www.jneurosci.org as supplemental material). The high-contingency schedules (65 ...
Seizure, neurotransmitter release, and gene expression are closely
... The present experiments aimed to compare the length of seizure activity with the time-related increase of transmitter release and the induction of c-fos gene expression in the striatum of the rat. Anesthetized Wistar rats were intraperitoneally treated with 7 mg/kg 4-aminopyridine, and the transmitt ...
... The present experiments aimed to compare the length of seizure activity with the time-related increase of transmitter release and the induction of c-fos gene expression in the striatum of the rat. Anesthetized Wistar rats were intraperitoneally treated with 7 mg/kg 4-aminopyridine, and the transmitt ...
S - 7473-2390-3942 Accountability in United States
... Studies have revealed that prenatal stress has significant impact on placental roles. In this light, constant exposure to stress during gestation alters the functions of the placental some of which relates to fetal brain development. Among the major functions of the placenta is the transfer of impor ...
... Studies have revealed that prenatal stress has significant impact on placental roles. In this light, constant exposure to stress during gestation alters the functions of the placental some of which relates to fetal brain development. Among the major functions of the placenta is the transfer of impor ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... Cholinergic Synaptic Transmission • Acetylcholine (ACh) is the neurotransmitter used by all preganglionic neurons. – It is also the neurotransmitter released from most parasympathetic postganglionic neurons. – Some sympathetic postganglionic neurons (those that innervate sweat glands and skeletal m ...
... Cholinergic Synaptic Transmission • Acetylcholine (ACh) is the neurotransmitter used by all preganglionic neurons. – It is also the neurotransmitter released from most parasympathetic postganglionic neurons. – Some sympathetic postganglionic neurons (those that innervate sweat glands and skeletal m ...
Chapter 7 | Pigments and Minerals
... kidneys, a condition known as gout. Larger accumulations of the crystals in soft tissues, especially near joints, are known as tophi. ...
... kidneys, a condition known as gout. Larger accumulations of the crystals in soft tissues, especially near joints, are known as tophi. ...
Dopamine control of pyramidal neuron activity in the primary motor
... cortex (Cg), or in the deep layers of M1, by using 3H-DA labelling. More recently, Hosp et al. (2011) described in rats direct projections from the Ventral Tegmental Area (VTA) to M1. Although detectable dopaminergic tissue levels can be measured in the motor cortex, this DA innervation remains weak ...
... cortex (Cg), or in the deep layers of M1, by using 3H-DA labelling. More recently, Hosp et al. (2011) described in rats direct projections from the Ventral Tegmental Area (VTA) to M1. Although detectable dopaminergic tissue levels can be measured in the motor cortex, this DA innervation remains weak ...
Dysregulating Factors
... genetic linkage has been established, it has also been hypothesised that mutations in genes encoding sodium channels SCN1A and SCN2A, and those encoding potassium channels, such as CASPR2, may play a role [12610651, 10673544]. On the other hand, physical disruption in the gene KCNMA1 encoding BKCa c ...
... genetic linkage has been established, it has also been hypothesised that mutations in genes encoding sodium channels SCN1A and SCN2A, and those encoding potassium channels, such as CASPR2, may play a role [12610651, 10673544]. On the other hand, physical disruption in the gene KCNMA1 encoding BKCa c ...
A Mindful Vixen: Degradation Due to Methamphetamine
... mesocorticolimbic-dopamine system in the small town of Ventral Tegmentum, Midbrain USA; home of the famous reward circuit of Stewart Evans. Stewart Evans exists because I allow him to think and function and he loves activating his reward circuit and every neuron knows it. This is why me and my conne ...
... mesocorticolimbic-dopamine system in the small town of Ventral Tegmentum, Midbrain USA; home of the famous reward circuit of Stewart Evans. Stewart Evans exists because I allow him to think and function and he loves activating his reward circuit and every neuron knows it. This is why me and my conne ...
PHYSIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY B.Sc. Counselling Psychology
... In the same way that having two eyes allows for greater visual abilities through stereoscopic vision, so having two ears affords a greater skill in hearing. The use of two ears is called binaural detection. Without two ears, our ability to locate a sound source is diminished, although, as we shall s ...
... In the same way that having two eyes allows for greater visual abilities through stereoscopic vision, so having two ears affords a greater skill in hearing. The use of two ears is called binaural detection. Without two ears, our ability to locate a sound source is diminished, although, as we shall s ...
Tuesday, January 06, 1998: (Day 1) Syllabus and course policy. No
... Talk about macro and micro features of the kidney Renin angiotensin sytem is an important function of kidney. It is extremely self serving process of the kidney. Its job is to maintain flow rates of glomerulus. It is very potent and important. Produces hemopoietin to maintain the red cell mass ...
... Talk about macro and micro features of the kidney Renin angiotensin sytem is an important function of kidney. It is extremely self serving process of the kidney. Its job is to maintain flow rates of glomerulus. It is very potent and important. Produces hemopoietin to maintain the red cell mass ...
The neurophysiological correlates of motor tics following focal
... inhibited during tics, although tics were only manifested in a small confined muscle group. This suggests that rather than representing a specific action within the basal ganglia itself, these nuclei provide a temporally exact but spatially distributed release signal. The tics induced by striatal di ...
... inhibited during tics, although tics were only manifested in a small confined muscle group. This suggests that rather than representing a specific action within the basal ganglia itself, these nuclei provide a temporally exact but spatially distributed release signal. The tics induced by striatal di ...
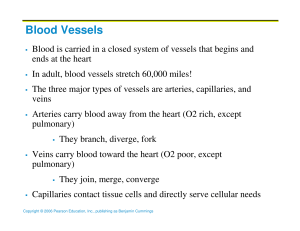
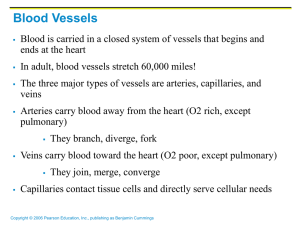
Blood Vessels
... Cardiovascular center – vasomotor center plus the cardiac centers that integrate blood pressure control by altering cardiac output and blood vessel diameter ...
... Cardiovascular center – vasomotor center plus the cardiac centers that integrate blood pressure control by altering cardiac output and blood vessel diameter ...
Chapter 19
... during breathing suck blood toward the heart by squeezing local veins Muscular “pump” – contraction of skeletal muscles surrounding deep veins “pump” blood toward the heart with valves prevent backflow during venous ...
... during breathing suck blood toward the heart by squeezing local veins Muscular “pump” – contraction of skeletal muscles surrounding deep veins “pump” blood toward the heart with valves prevent backflow during venous ...
EN Sokolov`s Neural Model of Stimuli as Neuro
... maintenance level of protein synthesis, governing receptors involved neurotransmitter active synapses (Fig . 6). By this scheme, the transition from addiction to the development of the memory trace occurs on pre-and postsynaptic mechanism (Fig. 5). In case of developing a new skill, reflex should st ...
... maintenance level of protein synthesis, governing receptors involved neurotransmitter active synapses (Fig . 6). By this scheme, the transition from addiction to the development of the memory trace occurs on pre-and postsynaptic mechanism (Fig. 5). In case of developing a new skill, reflex should st ...
Connectivity and circuitry in a dish versus in a brain
... membrane time constant (τ) as well as the resting membrane potential (RMP). With progressive neuronal development, Rin and τ values have been found to decrease whereas Cm values increase and the RMP shows a negative shift [4, 5]. These passive membrane properties render immature neurons highly excit ...
... membrane time constant (τ) as well as the resting membrane potential (RMP). With progressive neuronal development, Rin and τ values have been found to decrease whereas Cm values increase and the RMP shows a negative shift [4, 5]. These passive membrane properties render immature neurons highly excit ...
Large-Scale Fluorescence Calcium-Imaging
... recordings show the reliability of the optical response to each action potential. Asterisks below the electrical traces (lower traces in each pair) mark occurrences of individual action potentials; numerals mark action potential bursts and report the number of spikes in each burst. (Inset) Two-photo ...
... recordings show the reliability of the optical response to each action potential. Asterisks below the electrical traces (lower traces in each pair) mark occurrences of individual action potentials; numerals mark action potential bursts and report the number of spikes in each burst. (Inset) Two-photo ...
Review Historical aspects of the anatomy of the reticular formation
... in these nuclei. According to Bechterew, the most important rostral connections in the ascending fibres of the RF were with the inferior colliculi, with the areas adjacent to the third ventricle, and probably also with the thalamus. The RF was regarded as a structure which carried sensory stimuli fr ...
... in these nuclei. According to Bechterew, the most important rostral connections in the ascending fibres of the RF were with the inferior colliculi, with the areas adjacent to the third ventricle, and probably also with the thalamus. The RF was regarded as a structure which carried sensory stimuli fr ...
Sensory system evolution at the origin of craniates
... line, neural crest, placodal and brain precursors were in place. With the evolutionary stage thus fully set, can we now reconstruct the sequence of the play? 5. CONCURRENT GAIN AND SERIAL TRANSFORMATION HYPOTHESES ...
... line, neural crest, placodal and brain precursors were in place. With the evolutionary stage thus fully set, can we now reconstruct the sequence of the play? 5. CONCURRENT GAIN AND SERIAL TRANSFORMATION HYPOTHESES ...
Nervous System I - Union County College
... • Resting or Membrane Potential: a small difference in voltage across the cell membrane; the cell is normally negatively charged. – This allows the neuron to be ready to respond more quickly than it could if it were electrically neutral. – Think about a car battery. It retains a charge so that the c ...
... • Resting or Membrane Potential: a small difference in voltage across the cell membrane; the cell is normally negatively charged. – This allows the neuron to be ready to respond more quickly than it could if it were electrically neutral. – Think about a car battery. It retains a charge so that the c ...
The Interacting Neuroendocrine Network in Stress
... into the blood stream. This functional imbalance of this neuroendocrine system has been shown to promote longlasting changes in neuron morphology (e.g., neuronal atrophy in hippocampal regions) associated with altered changes in cognitive functions, (e.g., impairment of hippocampal-dependent learnin ...
... into the blood stream. This functional imbalance of this neuroendocrine system has been shown to promote longlasting changes in neuron morphology (e.g., neuronal atrophy in hippocampal regions) associated with altered changes in cognitive functions, (e.g., impairment of hippocampal-dependent learnin ...
Proceedings - Neuroscience Meetings
... 2 - Medical University Nizhny Novgorod Medical Academy, Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, 603950, Nizhny Novgorod, Gagarin ave., 70 ...
... 2 - Medical University Nizhny Novgorod Medical Academy, Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, 603950, Nizhny Novgorod, Gagarin ave., 70 ...
Origins of Behavioral Neuroscience 1.1 Multiple Choice 1) The mind
... 16) The scent of a flower sniffed through the right nostril in a "split-brain" person would be expected to A) generate a sensory message in the left hemisphere of the brain. B) generate a sensory message in both hemispheres of the brain. C) lead that person to report the smell of a flower. D) allow ...
... 16) The scent of a flower sniffed through the right nostril in a "split-brain" person would be expected to A) generate a sensory message in the left hemisphere of the brain. B) generate a sensory message in both hemispheres of the brain. C) lead that person to report the smell of a flower. D) allow ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.