Division of Brain Sciences Department of Medicine PhD studentship
... the most part unknown and current therapeutic approaches fail to halt this process. Mitochondrial dysfunction, including changes in the structural integrity of mitochondria, disruption of energy metabolism and abnormal calcium (Ca2+) buffering, has been extensively implicated in neurodegenerative di ...
... the most part unknown and current therapeutic approaches fail to halt this process. Mitochondrial dysfunction, including changes in the structural integrity of mitochondria, disruption of energy metabolism and abnormal calcium (Ca2+) buffering, has been extensively implicated in neurodegenerative di ...
B4 B5 B6 Revision B6 Growth and Development
... In a human embryo, up to the eight cell stage, all the cells are identical and could produce any sort of cell required by the organism (embryonic stem cells); After this point the cells become specialised and form different types of tissue. Adult and embryonic stem cells have the potential to produ ...
... In a human embryo, up to the eight cell stage, all the cells are identical and could produce any sort of cell required by the organism (embryonic stem cells); After this point the cells become specialised and form different types of tissue. Adult and embryonic stem cells have the potential to produ ...
neurons
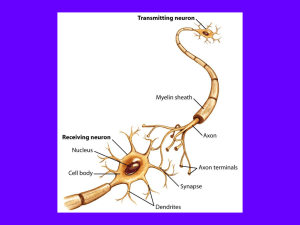
... contains genetic material and other structures that are found in virtually all the cells in the body. Extending out from the cell body are many short, branching fibers, called dendrites. Dendrites receive messages from other neurons or specialized cells. The axon is a single, elongated tube that ext ...
... contains genetic material and other structures that are found in virtually all the cells in the body. Extending out from the cell body are many short, branching fibers, called dendrites. Dendrites receive messages from other neurons or specialized cells. The axon is a single, elongated tube that ext ...
Chapter 11
... Humans secrete approx. 500ml of CSF daily. Only about 150 ml in CNS at any given time (continuously reabsorbed) CSF - ...
... Humans secrete approx. 500ml of CSF daily. Only about 150 ml in CNS at any given time (continuously reabsorbed) CSF - ...
PSC - University of Pittsburgh
... R. Clay Reid, Jeff Lichtman, Wei-Chung Allen Lee Harvard Medical School, Allen Institute for Brain Science Center for Brain Science, Harvard University Davi Bock ...
... R. Clay Reid, Jeff Lichtman, Wei-Chung Allen Lee Harvard Medical School, Allen Institute for Brain Science Center for Brain Science, Harvard University Davi Bock ...
Brain Presentation1
... • Action Potential- Enough stimulation received from another cell that causes the axon membrane to become permeable that opens gates that causes depolarization (cell becomes positively charged) to occur that allow positively charged particles (sodium ions) to enter the cell • Neurons can fire up to ...
... • Action Potential- Enough stimulation received from another cell that causes the axon membrane to become permeable that opens gates that causes depolarization (cell becomes positively charged) to occur that allow positively charged particles (sodium ions) to enter the cell • Neurons can fire up to ...
Week 1a Lecture Notes
... “When the patient was admitted to Bicêtre, at the age of 21, he had lost, for a some time, the use of speech; he could no longer pronounce more than a single syllable, which he ordinarily repeated twice at a time; whenever a question was asked of him, he [p. 236] would always reply tan, tan, in conj ...
... “When the patient was admitted to Bicêtre, at the age of 21, he had lost, for a some time, the use of speech; he could no longer pronounce more than a single syllable, which he ordinarily repeated twice at a time; whenever a question was asked of him, he [p. 236] would always reply tan, tan, in conj ...
Dopamine
... Dopamine-rich brain regions such as the ventral tegmental area (VTA), nucleus accumbens (nAC), and prefrontal cortex (PFC) are frequent targets of cocaine addiction research. Of particular interest is the pathway consisting of dopaminergic neurons originating in the VTA that terminate in the nAC. Th ...
... Dopamine-rich brain regions such as the ventral tegmental area (VTA), nucleus accumbens (nAC), and prefrontal cortex (PFC) are frequent targets of cocaine addiction research. Of particular interest is the pathway consisting of dopaminergic neurons originating in the VTA that terminate in the nAC. Th ...
The Nervous System - Thomas C. Cario Middle School
... responses that are under your control - feeling and itch on your skin and scratching it, or giving someone a high five ...
... responses that are under your control - feeling and itch on your skin and scratching it, or giving someone a high five ...
File - firestone falcons
... up of nerves that connect to the heart, blood vessels, smooth muscles, and glands • Sympathetic Division – is the branch of the ANS that mobilizes the body’s resources for emergencies. • Parasympathetic Division – is the branch of the ANS that generally conserves bodily resources. ...
... up of nerves that connect to the heart, blood vessels, smooth muscles, and glands • Sympathetic Division – is the branch of the ANS that mobilizes the body’s resources for emergencies. • Parasympathetic Division – is the branch of the ANS that generally conserves bodily resources. ...
Frontal Lobe - Washington School Counselor Association
... This link is especially important because it will provide you with a list of all treatment agencies and the s This site includes treatment data and admission statistics. This document provides trends in adolescent substance abuse. ...
... This link is especially important because it will provide you with a list of all treatment agencies and the s This site includes treatment data and admission statistics. This document provides trends in adolescent substance abuse. ...
Regulation of systemic circulation
... • Smooth muscles of vessels wall don’t relax whole. It all time has some tension – muscular tone. Tonic condition is connect with changes of electrical characteristic and some contraction of muscles. Tone of smooth muscles support by two mechanisms: myogenic and neuro-humoral. Miogenic regulation pl ...
... • Smooth muscles of vessels wall don’t relax whole. It all time has some tension – muscular tone. Tonic condition is connect with changes of electrical characteristic and some contraction of muscles. Tone of smooth muscles support by two mechanisms: myogenic and neuro-humoral. Miogenic regulation pl ...
Sheep Brain Dissection
... 1. You can use your knife to cut cross sections of the brain (see next page). Beginning near the front of the brain (in a region called the “prefrontal lobe”), make a series of sections, each about one inch thick. In this way you will be able to see how the internal structure of the brain changes, a ...
... 1. You can use your knife to cut cross sections of the brain (see next page). Beginning near the front of the brain (in a region called the “prefrontal lobe”), make a series of sections, each about one inch thick. In this way you will be able to see how the internal structure of the brain changes, a ...
A nerve cell
... production of endorphins (morphin-like hormones), which enhance the production of nerve growth factors, which then cause new neurons to form ...
... production of endorphins (morphin-like hormones), which enhance the production of nerve growth factors, which then cause new neurons to form ...
Chapter 9
... 2. List the order of the connective tissue meninges that line the spinal cord. Are they also found around the brain? 3. In the adult does the spinal cord extend through all vertebrae? What is the conus medullaris and caudae equinae? 4. Describe the 2 roots that make up each spinal nerve. What types ...
... 2. List the order of the connective tissue meninges that line the spinal cord. Are they also found around the brain? 3. In the adult does the spinal cord extend through all vertebrae? What is the conus medullaris and caudae equinae? 4. Describe the 2 roots that make up each spinal nerve. What types ...
Nervous - Lamont High
... • 3 substances in choc act as cannabinoids (mimic cannibis (marijuana)) • Active ingredient in marijuana is THC (tetrahydrocannabiol) • When THC binds to receptors, person feels high!!! • No THC in chocolate, but there are chemicals in choc that act like THC • You would have to eat 25 lbs of choc to ...
... • 3 substances in choc act as cannabinoids (mimic cannibis (marijuana)) • Active ingredient in marijuana is THC (tetrahydrocannabiol) • When THC binds to receptors, person feels high!!! • No THC in chocolate, but there are chemicals in choc that act like THC • You would have to eat 25 lbs of choc to ...
Synthesis Intro Workshop
... exposure have been shown to decrease intracellular Ca2+ concentration by altering calcium channels (Kumada et al, 2006). Calcium dyes were used to trace Ca2+ concentration in cells with varying concentrations of ethanol, and it was found that levels decreased dose-dependently, suggesting that since ...
... exposure have been shown to decrease intracellular Ca2+ concentration by altering calcium channels (Kumada et al, 2006). Calcium dyes were used to trace Ca2+ concentration in cells with varying concentrations of ethanol, and it was found that levels decreased dose-dependently, suggesting that since ...
Nerve Hormone WebQuest 2015
... 4. Return to the “Amazing Cells” Page. Now click the link on Dropping Signals. Of the five options: muscle cells, photoreceptor, cancer, leaf parenchyma or fibroblast, choose three cell types – run the animation of the effect of the four signal molecules – complete the table on the next page highlig ...
... 4. Return to the “Amazing Cells” Page. Now click the link on Dropping Signals. Of the five options: muscle cells, photoreceptor, cancer, leaf parenchyma or fibroblast, choose three cell types – run the animation of the effect of the four signal molecules – complete the table on the next page highlig ...
Brain growth, development and Autism
... can help direct research into potential factors that might put children at risk for ASD and help them identify potential environmental factors that can affect brain development. Children and adolescents with autism have a surplus of synapses in the brain, and this excess is due to a slowdown in a no ...
... can help direct research into potential factors that might put children at risk for ASD and help them identify potential environmental factors that can affect brain development. Children and adolescents with autism have a surplus of synapses in the brain, and this excess is due to a slowdown in a no ...
doc Chapter 15 Notes
... hemorrhagic stroke from weak/malformed blood vessels brain surgery that seals off the faulty vessel to prevent further strokes obstructive by thrombus anticoagulant drugs that make blood less likely to clot obstructive by embolus from bacterial infection antibiotics ...
... hemorrhagic stroke from weak/malformed blood vessels brain surgery that seals off the faulty vessel to prevent further strokes obstructive by thrombus anticoagulant drugs that make blood less likely to clot obstructive by embolus from bacterial infection antibiotics ...
Brain Development
... • Axons elongate as they grow toward specific targets – Myelination begins prenatally and continues at least into adolescence ...
... • Axons elongate as they grow toward specific targets – Myelination begins prenatally and continues at least into adolescence ...
File
... ● Identify basic processes and systems in the biological bases of behavior, including parts of the neuron and the process of transmission of a signal between neurons. ● Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters (e.g., reuptake mechanisms, agonists, antagonists). ● Discuss the effect of the ...
... ● Identify basic processes and systems in the biological bases of behavior, including parts of the neuron and the process of transmission of a signal between neurons. ● Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters (e.g., reuptake mechanisms, agonists, antagonists). ● Discuss the effect of the ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.