UsabilityPs3
... Yakking drivers are four times more likely to crash their cars. Using a hands-free headset instead of handheld phone made no difference at all. The brain can be intensely aware of what is coming through either the eyes or the ears but not both at the same time. (Certain brain regions were activate ...
... Yakking drivers are four times more likely to crash their cars. Using a hands-free headset instead of handheld phone made no difference at all. The brain can be intensely aware of what is coming through either the eyes or the ears but not both at the same time. (Certain brain regions were activate ...
Evolution2
... Cortical asymmetry: Brain specializations evolved to support the ability for language such as Wernickes and Brocas area Why is Brain Size Important? All organs and systems of the body confront design problems and limits as they become larger or smaller 2 major ways in which larger brains can b ...
... Cortical asymmetry: Brain specializations evolved to support the ability for language such as Wernickes and Brocas area Why is Brain Size Important? All organs and systems of the body confront design problems and limits as they become larger or smaller 2 major ways in which larger brains can b ...
Harnessing Plasticity to Reset Dysfunctional Neurons
... neurons and neural circuits can change their “job descriptions” and their allegiance in response to demands. The mechanisms underlying this process are complex, have varying time courses (from milliseconds to months), and are incompletely understood. They include changes in synaptic strength, the pr ...
... neurons and neural circuits can change their “job descriptions” and their allegiance in response to demands. The mechanisms underlying this process are complex, have varying time courses (from milliseconds to months), and are incompletely understood. They include changes in synaptic strength, the pr ...
Ch. 13 Central Nervous System
... In Parkinson disease, these neurons degenerate, so you don’t have the dopamine. The cerebral nuclei produce excess signals that affect the voluntary muscles. Overstimulation of the postural muscles of the neck, trunk, and upper limbs produces tremors and abnormal gait. ...
... In Parkinson disease, these neurons degenerate, so you don’t have the dopamine. The cerebral nuclei produce excess signals that affect the voluntary muscles. Overstimulation of the postural muscles of the neck, trunk, and upper limbs produces tremors and abnormal gait. ...
1. The main function of myelin is to a. form a protective coating over
... Q: Neurons send signals to…. A: the brain, muscles, and glands Q: Write the definition for the following neurons.. -Sensory Neurons ...
... Q: Neurons send signals to…. A: the brain, muscles, and glands Q: Write the definition for the following neurons.. -Sensory Neurons ...
Nature 411, 189 - 193 (2001)
... ganglia. These large subcortical structures that form the core of the cerebral hemispheres directly participate in the control of psychomotor behavior. Neuroanatomical methods combined with transmitter localization procedures were used to study the chemical organization of the forebrain in each majo ...
... ganglia. These large subcortical structures that form the core of the cerebral hemispheres directly participate in the control of psychomotor behavior. Neuroanatomical methods combined with transmitter localization procedures were used to study the chemical organization of the forebrain in each majo ...
Development of Nervous System
... The brain exhibits plasticity of function. For example, infants with intractable epilepsy may have an entire cerebral hemisphere removed.The remaining hemisphere can provide the function normally provided by bot h ...
... The brain exhibits plasticity of function. For example, infants with intractable epilepsy may have an entire cerebral hemisphere removed.The remaining hemisphere can provide the function normally provided by bot h ...
Unit 3 Notes
... brain’s surface. These waves are measured by electrodes placed on the scalp. CT (Computed Tomography) scan: a series of X-ray photographs taken from different angles and combined by computer into a composite representation of a slice of the brain’s structure. (Also called CAT scan.) PET (Positron Em ...
... brain’s surface. These waves are measured by electrodes placed on the scalp. CT (Computed Tomography) scan: a series of X-ray photographs taken from different angles and combined by computer into a composite representation of a slice of the brain’s structure. (Also called CAT scan.) PET (Positron Em ...
Artificial intelligence: Neural networks
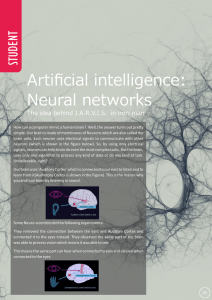
... How can a computer mimic a human brain? Well, the answer turns out pre y simple. Our brain is made of membranes of Neurons which are also called the brain cells. Each neuron uses electrical signals to communicate with other neurons (which is shown in the figure below). So, by using only electrical si ...
... How can a computer mimic a human brain? Well, the answer turns out pre y simple. Our brain is made of membranes of Neurons which are also called the brain cells. Each neuron uses electrical signals to communicate with other neurons (which is shown in the figure below). So, by using only electrical si ...
Biological and Psychology Why are psychologists concerned about
... Neurotransmitters – chemicals that transmit information from one neuron to another. Stored in small sacs within the terminal buttons Nerve impulse triggers their release Over 50 have been identified Major ones are described in the text Drugs and Neurotransmitters Agonist – mimics or enhanc ...
... Neurotransmitters – chemicals that transmit information from one neuron to another. Stored in small sacs within the terminal buttons Nerve impulse triggers their release Over 50 have been identified Major ones are described in the text Drugs and Neurotransmitters Agonist – mimics or enhanc ...
Overview of the Brain
... functions on several levels that can be broken down into both a micro and macroscopic regions. • At the microscopic level we have the basic nerve cell, the neuron, which is interconnected into a network of neurons that transects, crisscrosses, and connects every cell and sensory organs to the brain. ...
... functions on several levels that can be broken down into both a micro and macroscopic regions. • At the microscopic level we have the basic nerve cell, the neuron, which is interconnected into a network of neurons that transects, crisscrosses, and connects every cell and sensory organs to the brain. ...
Brain
... Substantia nigra inhibits activity of basal nuclei by releasing DOPAMINE Basal nuclei become more active with less Dopamine – increased muscle tone – Parkinson’s Disease have difficulty starting voluntary movements B/C opposing muscle groups DO NOT RELAX ( not enough Dopamine is excreted by substant ...
... Substantia nigra inhibits activity of basal nuclei by releasing DOPAMINE Basal nuclei become more active with less Dopamine – increased muscle tone – Parkinson’s Disease have difficulty starting voluntary movements B/C opposing muscle groups DO NOT RELAX ( not enough Dopamine is excreted by substant ...
File Now
... paradoxically both main neurotransmitter for memory and main one responsible for cell death ...
... paradoxically both main neurotransmitter for memory and main one responsible for cell death ...
Notes Module #1 - davis.k12.ut.us
... A person=s head is placed in a MAGNETIC FIELD where ATOMS are disoriented by brief PULSES . When atoms return to normal, they emit SIGNALS -- a computer generates images of the soft tissue from these signals. ...
... A person=s head is placed in a MAGNETIC FIELD where ATOMS are disoriented by brief PULSES . When atoms return to normal, they emit SIGNALS -- a computer generates images of the soft tissue from these signals. ...
Nervous System - Holy Trinity Diocesan High School
... Relay information between the brain and the body Information is electrical and chemical Receptors: specialized structures that pick up information Negative feedback to the body Stimulus-Response: much faster change but a short lasting effect compared to hormones Structures: 1. Neuron: Nerve cell; ...
... Relay information between the brain and the body Information is electrical and chemical Receptors: specialized structures that pick up information Negative feedback to the body Stimulus-Response: much faster change but a short lasting effect compared to hormones Structures: 1. Neuron: Nerve cell; ...
What do you want to know about the brain?
... They connect when you might do a maths question of anything. If you say “I can’t do it”, your neurons send messages to your brain that you can’t do it and it makes learning much harder. You have about 100 billion neurons in your body. ...
... They connect when you might do a maths question of anything. If you say “I can’t do it”, your neurons send messages to your brain that you can’t do it and it makes learning much harder. You have about 100 billion neurons in your body. ...
BIOPSYCHOLOGY notes
... This significantly increases serotonin receptor binding (more serotonin in the synapse means a greater chance for some of them to bind to the receptors). This increased receptor activity leads to significant changes in the brain's electrical firing and is primarily responsible for the MDMA experienc ...
... This significantly increases serotonin receptor binding (more serotonin in the synapse means a greater chance for some of them to bind to the receptors). This increased receptor activity leads to significant changes in the brain's electrical firing and is primarily responsible for the MDMA experienc ...
The Brain Summary Notes
... recent development in the brains evolution. It consists of the limbic system and the cortex and is involved in the processes of learning, language, memory and reasoning. The right side of the brain is linked to sensations in the left side of the body while the left side of the brain is linked to sen ...
... recent development in the brains evolution. It consists of the limbic system and the cortex and is involved in the processes of learning, language, memory and reasoning. The right side of the brain is linked to sensations in the left side of the body while the left side of the brain is linked to sen ...
Brain Facts
... Random Brain Facts • Human brain has ~100,000,000,000 neurons • If all neurons were stretched end to end, would reach to moon and back • Every second, brain receives 100 million messages from the senses • ¾ of body’s neurons are in brain • On day you are born, all brain cells are in place ...
... Random Brain Facts • Human brain has ~100,000,000,000 neurons • If all neurons were stretched end to end, would reach to moon and back • Every second, brain receives 100 million messages from the senses • ¾ of body’s neurons are in brain • On day you are born, all brain cells are in place ...
Brain Facts
... Random Brain Facts • Human brain has ~100,000,000,000 neurons • If all neurons were stretched end to end, would reach to moon and back • Every second, brain receives 100 million messages from the senses • ¾ of body’s neurons are in brain • On day you’re born, all brain cells in place ...
... Random Brain Facts • Human brain has ~100,000,000,000 neurons • If all neurons were stretched end to end, would reach to moon and back • Every second, brain receives 100 million messages from the senses • ¾ of body’s neurons are in brain • On day you’re born, all brain cells in place ...
the nervous system
... Disorders within blood vessels of the cerebrum can result in a stroke or apoplexy. Reduction of blood flow (ischaemia) within the cerebrum causes cells to die due to lack of oxygen and nutrients. As cells in this area control movements of many parts of the body, paralysis of limbs and loss of speech ...
... Disorders within blood vessels of the cerebrum can result in a stroke or apoplexy. Reduction of blood flow (ischaemia) within the cerebrum causes cells to die due to lack of oxygen and nutrients. As cells in this area control movements of many parts of the body, paralysis of limbs and loss of speech ...
Prezentacja programu PowerPoint
... Glial cells are non-neuronal cells that provide support and protection for neurons. Neuroglial cells are generally smaller than neurons and outnumber them by five to ten times. ...
... Glial cells are non-neuronal cells that provide support and protection for neurons. Neuroglial cells are generally smaller than neurons and outnumber them by five to ten times. ...
File
... myelinated and the action potential must jump from node to node down the axon. 11.What is a neurotransmitter? What is the difference between an excitatory neurotransmitter and an inhibitory neurotransmitter? Give an example of each? A neurotransmitter is a chemical that is released at a synapse to p ...
... myelinated and the action potential must jump from node to node down the axon. 11.What is a neurotransmitter? What is the difference between an excitatory neurotransmitter and an inhibitory neurotransmitter? Give an example of each? A neurotransmitter is a chemical that is released at a synapse to p ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.