Chapter 8
... Control of Movement by the Brain Parkinson’s Disease • Parkinson’s disease also produces a resting tremor—vibratory movements of the arms and hands that diminish somewhat when the individual makes purposeful movements. The tremor is accompanied by rigidity; the joints appear stiff. • However, the t ...
... Control of Movement by the Brain Parkinson’s Disease • Parkinson’s disease also produces a resting tremor—vibratory movements of the arms and hands that diminish somewhat when the individual makes purposeful movements. The tremor is accompanied by rigidity; the joints appear stiff. • However, the t ...
Ch14 notes Martini 9e
... • Disorders interfere with blood circulation to brain • Stroke or cerebrovascular accident (CVA) • Shuts off blood to portion of brain • Neurons die • Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB) • Isolates CNS neural tissue from general circulation • Formed by network of tight junctions • Between endothelial cells of ...
... • Disorders interfere with blood circulation to brain • Stroke or cerebrovascular accident (CVA) • Shuts off blood to portion of brain • Neurons die • Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB) • Isolates CNS neural tissue from general circulation • Formed by network of tight junctions • Between endothelial cells of ...
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
... Lower thresholds in the reticular formation (reinforcing the alert, aroused state) Elevate plasma glucose and fatty acids level (supplying more energy). On the basis of effects like these, Cannon called the emergency-induced discharge of the nor-adrenergic nervous system the “preparation for fig ...
... Lower thresholds in the reticular formation (reinforcing the alert, aroused state) Elevate plasma glucose and fatty acids level (supplying more energy). On the basis of effects like these, Cannon called the emergency-induced discharge of the nor-adrenergic nervous system the “preparation for fig ...
Trends Towards Progress of Brains and Sense Organs
... difficult. We can only distinguish between general and more specific trends. The former are of much greater interest for the understanding of evolution as they govern the development of many branches of the phylogeny of animals. However, by using the term "general trend" we do not want to characteri ...
... difficult. We can only distinguish between general and more specific trends. The former are of much greater interest for the understanding of evolution as they govern the development of many branches of the phylogeny of animals. However, by using the term "general trend" we do not want to characteri ...
Nervous system and neurons
... breathing quickens, your mouth dries and your heart pounds. Then you hear your friend call out, “Hey, wait for me! We can walk back together.” Your breathing slows down and after a couple of minutes you are walking home calmly with your friend. Explain the actions of the autonomic nervous system. Re ...
... breathing quickens, your mouth dries and your heart pounds. Then you hear your friend call out, “Hey, wait for me! We can walk back together.” Your breathing slows down and after a couple of minutes you are walking home calmly with your friend. Explain the actions of the autonomic nervous system. Re ...
Nervous Systems
... diffuse nerve net (Figure 49.2a), which controls the contraction and expansion of the gastrovascular cavity. Unlike the nervous systems of other animals, the nerve net of cnidarians lacks clusters of neurons that perform specialized functions. In more complex animals, the axons of multiple nerve ce ...
... diffuse nerve net (Figure 49.2a), which controls the contraction and expansion of the gastrovascular cavity. Unlike the nervous systems of other animals, the nerve net of cnidarians lacks clusters of neurons that perform specialized functions. In more complex animals, the axons of multiple nerve ce ...
Nervous System
... it lands on _________________________________ on the post-synaptic dendrite Its purpose is to partially _____________________ the membrane of the post-synaptic dendrite. This excites the __________________________________________. ______________________ channels on post-synaptic dendrites op ...
... it lands on _________________________________ on the post-synaptic dendrite Its purpose is to partially _____________________ the membrane of the post-synaptic dendrite. This excites the __________________________________________. ______________________ channels on post-synaptic dendrites op ...
49-Nervous System - Northwest ISD Moodle
... diffuse nerve net (Figure 49.2a), which controls the contraction and expansion of the gastrovascular cavity. Unlike the nervous systems of other animals, the nerve net of cnidarians lacks clusters of neurons that perform specialized functions. In more complex animals, the axons of multiple nerve ce ...
... diffuse nerve net (Figure 49.2a), which controls the contraction and expansion of the gastrovascular cavity. Unlike the nervous systems of other animals, the nerve net of cnidarians lacks clusters of neurons that perform specialized functions. In more complex animals, the axons of multiple nerve ce ...
Biological Foundations of Behavior
... Action Forebrain – two distinct areas Primarily cerebral cortex ...
... Action Forebrain – two distinct areas Primarily cerebral cortex ...
Circuits, Circuits
... From T to T+P/4, the peak travels across the body and meets the right eardrum, causing it to vibrate, thus generating a new peak. From T+P/4 to T+P/2, the new peak travels exactly 1/4 wavelength = ear-to-ear distance. At time T+P/2, the left ear has a) a trough on the outside, and b) a peak on the i ...
... From T to T+P/4, the peak travels across the body and meets the right eardrum, causing it to vibrate, thus generating a new peak. From T+P/4 to T+P/2, the new peak travels exactly 1/4 wavelength = ear-to-ear distance. At time T+P/2, the left ear has a) a trough on the outside, and b) a peak on the i ...
Chapter 4: The Central Nervous System
... When you play a game or sport, the sympathetic nervous system speeds up your heart rate, increases metabolism and induces sweating in order for you to perform to your maximum. When you stop playing, the parasympathetic nervous system slows your heart and breathing rate, to help the body return to it ...
... When you play a game or sport, the sympathetic nervous system speeds up your heart rate, increases metabolism and induces sweating in order for you to perform to your maximum. When you stop playing, the parasympathetic nervous system slows your heart and breathing rate, to help the body return to it ...
PPT - 서울대 Biointelligence lab
... information and how the signals are used by neuronal processes for the control of behavior “self-referencing system” “ongoing self-maintaining system” – so treating brain as an input-output system can have only limited success. Many studies in neuronal procedure and functional mechanism lacks “compr ...
... information and how the signals are used by neuronal processes for the control of behavior “self-referencing system” “ongoing self-maintaining system” – so treating brain as an input-output system can have only limited success. Many studies in neuronal procedure and functional mechanism lacks “compr ...
UNIT 4 – HOMEOSTASIS 8.1 – Human Body Systems and H
... the stomach does not secrete pepsin -> it secretes the inactive form, pepsinogen when one pepsinogen molecule becomes activated, it helps to activate other pepsinogens nearby, which in turn, can activate others. ...
... the stomach does not secrete pepsin -> it secretes the inactive form, pepsinogen when one pepsinogen molecule becomes activated, it helps to activate other pepsinogens nearby, which in turn, can activate others. ...
neural control of respiration
... actions of the pneumotaxic center and protecting the lungs from overexpansion. This response is called a Haring-Breuer reflex. In humans, it does not appear to be activated until the tidal volume reaches 1 L, so it plays no part in regulating ventilation during normal quiet breathing. Several additi ...
... actions of the pneumotaxic center and protecting the lungs from overexpansion. This response is called a Haring-Breuer reflex. In humans, it does not appear to be activated until the tidal volume reaches 1 L, so it plays no part in regulating ventilation during normal quiet breathing. Several additi ...
lec #2 By: Lubna Al-Marmori
... inferior part of brain stem then directly make crossing, then it complete its way until reach thalamus, then synap as 3rd order neuron -The axons of 3rd order neurons pass through internal capsule and corona radiata to reach the Postcentral gyrus of cerebral cortex - u should know the difference bet ...
... inferior part of brain stem then directly make crossing, then it complete its way until reach thalamus, then synap as 3rd order neuron -The axons of 3rd order neurons pass through internal capsule and corona radiata to reach the Postcentral gyrus of cerebral cortex - u should know the difference bet ...
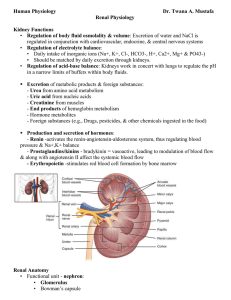
Renal Physiology
... • Solutes smaller than 180 nanometers in radius are freely filtered • Solutes greater than 360 nanometers do not • Solutes between 180 and 360 nm are filtered to various degrees • Serum albumin is anionic and has a 355 nm radius, only ~7 g is filtered per day (out of ~70 kg/day passing through glome ...
... • Solutes smaller than 180 nanometers in radius are freely filtered • Solutes greater than 360 nanometers do not • Solutes between 180 and 360 nm are filtered to various degrees • Serum albumin is anionic and has a 355 nm radius, only ~7 g is filtered per day (out of ~70 kg/day passing through glome ...
A Distinct Class of Antibodies May Be an Indicator of Gray Matter
... B cells is an effective treatment for many RRMS patients (Hauser et al., 2008). The most common multiple sclerosis (MS) lesion is characterized by deposition of both antibodies and complement, and patients with this pattern of pathology can improve with plasmapheresis treatment, which removes circula ...
... B cells is an effective treatment for many RRMS patients (Hauser et al., 2008). The most common multiple sclerosis (MS) lesion is characterized by deposition of both antibodies and complement, and patients with this pattern of pathology can improve with plasmapheresis treatment, which removes circula ...
Pathogenicity and Effects of Prions Misfolding
... function of prions is largely unknown, however it is thought that they are involved in several functions such as cellular adhesion, protection, and cell signaling. The pathogenicity of prions stems from an altered pattern of folding of the protein. The altering event that triggers change is a single ...
... function of prions is largely unknown, however it is thought that they are involved in several functions such as cellular adhesion, protection, and cell signaling. The pathogenicity of prions stems from an altered pattern of folding of the protein. The altering event that triggers change is a single ...
BIO 141 Unit 5 Learning Objectives
... 23. Explain why someone who receives damage to one side of their primary motor cortex, is unable to move the opposite side of their body. 24. Identify the cerebral lobe in which the following areas a ...
... 23. Explain why someone who receives damage to one side of their primary motor cortex, is unable to move the opposite side of their body. 24. Identify the cerebral lobe in which the following areas a ...
1 - Test Bank wizard
... 14. Which of the following techniques for imaging the brain would not be advisable for a person with a metal plate in his or her head? a. EEG b. CT c. MRI d. PET ANS: c LO=2.6 15. Which technique of studying the brain involves recording the electrical activity of large groups of cortical neurons? a. ...
... 14. Which of the following techniques for imaging the brain would not be advisable for a person with a metal plate in his or her head? a. EEG b. CT c. MRI d. PET ANS: c LO=2.6 15. Which technique of studying the brain involves recording the electrical activity of large groups of cortical neurons? a. ...
The Brain and Behaviour
... The sensory neurons then transmit the information to the . The brain then organises and interprets the information in a meaningful way, which enables you to know how hot the flame is. If you decide it is too hot, the brain sends messages via the neurons which are part of the and then the which are p ...
... The sensory neurons then transmit the information to the . The brain then organises and interprets the information in a meaningful way, which enables you to know how hot the flame is. If you decide it is too hot, the brain sends messages via the neurons which are part of the and then the which are p ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • A Simple Nerve Circuit – the Reflex Arc - Sensory neuron bings info from sense organs/receptors to spinal cord -> synapses on motor neurons that take information to the muscles/glands to contract. ...
... • A Simple Nerve Circuit – the Reflex Arc - Sensory neuron bings info from sense organs/receptors to spinal cord -> synapses on motor neurons that take information to the muscles/glands to contract. ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.