Dens et al.
... explanations for specific observed results. This application of theoretical modeling can be particularly useful when results are unexpected. Therefore—as a practical matter—the insights gained from theoretical ecology may help to avert potentially unproductive disagreements arising from seemingly co ...
... explanations for specific observed results. This application of theoretical modeling can be particularly useful when results are unexpected. Therefore—as a practical matter—the insights gained from theoretical ecology may help to avert potentially unproductive disagreements arising from seemingly co ...
Interspecific Competition and Species` Distributions
... a section titled "Competition and Succession" he says (p. 198): One of the most important factors which will be at once met with in this field is competition, the competition of plants of the same species and of plants of different species growing in the same community. A closed plant community, suc ...
... a section titled "Competition and Succession" he says (p. 198): One of the most important factors which will be at once met with in this field is competition, the competition of plants of the same species and of plants of different species growing in the same community. A closed plant community, suc ...
The ecology of recovery
... (Andersen & Vollestad 1996). Thus, life-history characteristics and the dynamics of recovering populations are crucially interdependent, and their interrelationship can even affect interactions between species, with further repercussions for population recov ...
... (Andersen & Vollestad 1996). Thus, life-history characteristics and the dynamics of recovering populations are crucially interdependent, and their interrelationship can even affect interactions between species, with further repercussions for population recov ...
Phloem-feeding specialists sharing a host tree: resource partitioning
... normal-sized trees were colonized by F. marginata, facilitating a comparison of its gall distribution on the two types of trees (Table 2). When it does (rarely) occur on normal-sized trees, its galls are found on low branches, less than 1 m above ground, where few other galls occur (Table 2). Final ...
... normal-sized trees were colonized by F. marginata, facilitating a comparison of its gall distribution on the two types of trees (Table 2). When it does (rarely) occur on normal-sized trees, its galls are found on low branches, less than 1 m above ground, where few other galls occur (Table 2). Final ...
View as PDF - Montana State University
... Ecologists have long observed that consumers can maintain species diversity in communities of their prey. Many theories of how consumers mediate diversity invoke a tradeoff between species’ competitive ability and their ability to withstand predation. Under this constraint, the best competitors are ...
... Ecologists have long observed that consumers can maintain species diversity in communities of their prey. Many theories of how consumers mediate diversity invoke a tradeoff between species’ competitive ability and their ability to withstand predation. Under this constraint, the best competitors are ...
AP BIOLOGY – CHRISTMAS BREAK WORK
... Parasitism: Mutualism and commensalism: endoparasites and ectoparasites: species richness and relative abundance: food chain and food web: primary and secondary succession: Define an ecological niche and explain the competitive exclusion principle in terms of the niche concept ...
... Parasitism: Mutualism and commensalism: endoparasites and ectoparasites: species richness and relative abundance: food chain and food web: primary and secondary succession: Define an ecological niche and explain the competitive exclusion principle in terms of the niche concept ...
national 4 and national 5 biology homework
... NATIONAL 4 AND NATIONAL 5 BIOLOGY HOMEWORK LIFE ON EARTH ...
... NATIONAL 4 AND NATIONAL 5 BIOLOGY HOMEWORK LIFE ON EARTH ...
Critical Biodiversity
... model. Because we want the system to select the “favorable” interactions while increasing fitness quasi-statically, we set 60% of mutations to result in a shift in competitiveness (“neutral” speciation) and 40% to an increase in competitiveness (“advantageous” speciation). In both types of mutation ...
... model. Because we want the system to select the “favorable” interactions while increasing fitness quasi-statically, we set 60% of mutations to result in a shift in competitiveness (“neutral” speciation) and 40% to an increase in competitiveness (“advantageous” speciation). In both types of mutation ...
Community Ecology in a Restoration Context
... – Composition and abundance – Richness and evenness – Typically, few species are abundant and most are rare ...
... – Composition and abundance – Richness and evenness – Typically, few species are abundant and most are rare ...
Energetic Adaptations Along a Broad Latitudinal Gradient
... outcome of competitive interactions (Lawler and Morin J993). These relative timing effects also are important for larval fishes> affecting interspecific competition and thus the relative growth, surviva.I, 3Jld abundance of species within a community (Ga rvey and Stein 1998a ). With respect to preda ...
... outcome of competitive interactions (Lawler and Morin J993). These relative timing effects also are important for larval fishes> affecting interspecific competition and thus the relative growth, surviva.I, 3Jld abundance of species within a community (Ga rvey and Stein 1998a ). With respect to preda ...
BIO1100 AN INTRODUCTION TO MARINE BIOLOGY Lecturer: Prof
... environmental conditions that are neither fully terrestrial, nor fully marine. As a result, the biotic assemblages found on rocky shores do not survive full immersion or full emersion, but conditions of wetness between these two extremes. The pattern of zonation on rocky shores results from the grad ...
... environmental conditions that are neither fully terrestrial, nor fully marine. As a result, the biotic assemblages found on rocky shores do not survive full immersion or full emersion, but conditions of wetness between these two extremes. The pattern of zonation on rocky shores results from the grad ...
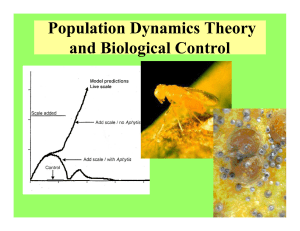
Biocontrol and Population Dynamics Theory
... Why is Biological Control Useful? • All populations eventually reach a carrying capacity and either level off or decrease. • If caused by starvation or species-induced pollution, the habitat may be damaged. • Biological control is valuable because natural enemies often cause populations to level of ...
... Why is Biological Control Useful? • All populations eventually reach a carrying capacity and either level off or decrease. • If caused by starvation or species-induced pollution, the habitat may be damaged. • Biological control is valuable because natural enemies often cause populations to level of ...
BCS311 Module 5
... population during a period of time (I) is a function of r. The stability of the population size depends on the balance between the existing number of individuals (N) and the environment’s carrying capacity (K) for individuals. It will be a positive number and the population may grow if N is less tha ...
... population during a period of time (I) is a function of r. The stability of the population size depends on the balance between the existing number of individuals (N) and the environment’s carrying capacity (K) for individuals. It will be a positive number and the population may grow if N is less tha ...
Effects of neighboring organisms on the growth of three intertidal
... acrylic sheet the same size as the panel. This was laid over the panel to fix the exact positions of the colonies during observations. Panels were put in a tray containing seawater while the colonies were traced under a stereomicroscope. The panels were observed 5 times during the study at about 2 w ...
... acrylic sheet the same size as the panel. This was laid over the panel to fix the exact positions of the colonies during observations. Panels were put in a tray containing seawater while the colonies were traced under a stereomicroscope. The panels were observed 5 times during the study at about 2 w ...
SF3-it3-doc1 Methodology risk assessments
... particular on: - measures to prevent introduction, establishment and spread into (new areas in) the EU - early detection and rapid eradication measures; - management measures where the species is widely spread (techniques for eradication, population control or containment of a population) Coverage o ...
... particular on: - measures to prevent introduction, establishment and spread into (new areas in) the EU - early detection and rapid eradication measures; - management measures where the species is widely spread (techniques for eradication, population control or containment of a population) Coverage o ...
Organic versus conventional arable farming systems
... fungivores or predators, and some are known to parasitize diptera pupae (Fournet et al., 2000), while a few species are associated with ants (Päivinen et al., 2003). Staphylinids are active at the ground surface but also in the leaf litter and within the soil. They play an important part both above ...
... fungivores or predators, and some are known to parasitize diptera pupae (Fournet et al., 2000), while a few species are associated with ants (Päivinen et al., 2003). Staphylinids are active at the ground surface but also in the leaf litter and within the soil. They play an important part both above ...
AP Biology
... D) a situation in which the populations of a predator species and a prey species oscillate in unison ___14) An ecologist hypothesizes that predation by a particular owl species is the major factor controlling the population of a particular rabbit species. The first step in testing this hypothesis wo ...
... D) a situation in which the populations of a predator species and a prey species oscillate in unison ___14) An ecologist hypothesizes that predation by a particular owl species is the major factor controlling the population of a particular rabbit species. The first step in testing this hypothesis wo ...
Linking Nature`s services to ecosystems: some general ecological
... generation time is strongly correlated to the body size of the organism. However, optimal conditions seldom occur in nature and thus physical factors, such as temperature, light, or availability of water, regulates the performance of species. ...
... generation time is strongly correlated to the body size of the organism. However, optimal conditions seldom occur in nature and thus physical factors, such as temperature, light, or availability of water, regulates the performance of species. ...
Ecology (Bio 47) Fall 2002 Friday 6:00 – 7:50 Saturday 9:00 – 9:50
... Ecology is the study of the interactions between organisms and between organisms and their environment. ...
... Ecology is the study of the interactions between organisms and between organisms and their environment. ...
From Population to the Biosphere
... These types of migrations move entire populations from one location to another. ...
... These types of migrations move entire populations from one location to another. ...
Habitat subdivision causes changes in food web structure
... energy requirements) and diet specialization make species rare and susceptible to extinction; this suggestion is in agreement with modelling of food chains (Sterner et al. 1997), and omnivory (feeding on more than one species), which may also allow species at higher trophic levels to persist (McCann ...
... energy requirements) and diet specialization make species rare and susceptible to extinction; this suggestion is in agreement with modelling of food chains (Sterner et al. 1997), and omnivory (feeding on more than one species), which may also allow species at higher trophic levels to persist (McCann ...
Ecology Unit HW
... 5. Explain how carrying capacity & how it affects population growth 6. Compare/Contrast & list how density independent.- vs dependent factors affect population growth 7. Explain how predation can affect life history through natural selection 8. Distinguish between r-selected and K-selected populatio ...
... 5. Explain how carrying capacity & how it affects population growth 6. Compare/Contrast & list how density independent.- vs dependent factors affect population growth 7. Explain how predation can affect life history through natural selection 8. Distinguish between r-selected and K-selected populatio ...