Media Advisory – Tip Sheet Seismological Society of America 2009
... The Cascadia subduction zone is likely to produce the strongest shaking experienced in the lower 48 states. Although seismic activity in the Pacific Northwest has been relatively low in the past two centuries, there is a growing consensus that this fault zone ruptures in giant earthquakes (magnitude ...
... The Cascadia subduction zone is likely to produce the strongest shaking experienced in the lower 48 states. Although seismic activity in the Pacific Northwest has been relatively low in the past two centuries, there is a growing consensus that this fault zone ruptures in giant earthquakes (magnitude ...
SCIENCE 6 3rd rating part 2
... 2. What is the intensity of an earthquake when people become panicky as a small landslide occur? a. Intensity I c. Intensity II b. Intensity III d. Intensity IV V. ASSIGNMENT: Describe the Ring of Fire and how it is related to the frequent occurrence of earthquakes. ...
... 2. What is the intensity of an earthquake when people become panicky as a small landslide occur? a. Intensity I c. Intensity II b. Intensity III d. Intensity IV V. ASSIGNMENT: Describe the Ring of Fire and how it is related to the frequent occurrence of earthquakes. ...
Volcanoes, and Earthquakes, and Hot Spots . . . Oh Myyyyyyy!
... • Occur along fault lines, plate boundaries, and during after shocks • Transfer energy in the form of waves • P-Waves • S-Waves • Surface Waves or Love Waves: can move items up and down and left to right; they are the slowest waves ...
... • Occur along fault lines, plate boundaries, and during after shocks • Transfer energy in the form of waves • P-Waves • S-Waves • Surface Waves or Love Waves: can move items up and down and left to right; they are the slowest waves ...
Unit 5 Earthquakes P.T. Review
... estimates the total energy released by an earthquake Can be used for any kind of earthquakes, near or far Some news reports may mention the Richter scale, but the magnitude number they quote is almost always the moment magnitude for that earthquake ...
... estimates the total energy released by an earthquake Can be used for any kind of earthquakes, near or far Some news reports may mention the Richter scale, but the magnitude number they quote is almost always the moment magnitude for that earthquake ...
Earthquake Waves
... 3. Suggest how earthquake waves have been used to develop our model of the Earth’s interior? Think about what the inside of Earth looks like. ...
... 3. Suggest how earthquake waves have been used to develop our model of the Earth’s interior? Think about what the inside of Earth looks like. ...
disaster visits afghanistan again
... Hindu Kush, villages are likely to be located on the valley floors or along the edges of the valley floors because this is were the agricultural lands are located. Intermittent streams have deposited loose, unconsolidated alluvial soils, which are very subject to lateral surface movements. For examp ...
... Hindu Kush, villages are likely to be located on the valley floors or along the edges of the valley floors because this is were the agricultural lands are located. Intermittent streams have deposited loose, unconsolidated alluvial soils, which are very subject to lateral surface movements. For examp ...
Test 4 - GEOCITIES.ws
... 10. Which of the following provides most of the energy for earthquakes? (a) foreshocks (b) solar energy (c) tectonic forces (d) tidal energy 11. (T/F) The Mercalli scale is more precise than the Richter scale in measuring earthquake magnitude. 12. The fact that a p-wave travels faster than an s-wave ...
... 10. Which of the following provides most of the energy for earthquakes? (a) foreshocks (b) solar energy (c) tectonic forces (d) tidal energy 11. (T/F) The Mercalli scale is more precise than the Richter scale in measuring earthquake magnitude. 12. The fact that a p-wave travels faster than an s-wave ...
5. Where would you find the least number of earthquakes?
... Ash can suffocate or burn you, gas can poison, “bombs” and cinder can hit and burn or kill you, steam can burn or kill you, mudflows, lahars, lava, and pyroclastic flows can bury you! Large amounts of ash can drop the temperature of earth and cause crop failure. Acids or poisons in the air can kill ...
... Ash can suffocate or burn you, gas can poison, “bombs” and cinder can hit and burn or kill you, steam can burn or kill you, mudflows, lahars, lava, and pyroclastic flows can bury you! Large amounts of ash can drop the temperature of earth and cause crop failure. Acids or poisons in the air can kill ...
The Northridge Earthquake
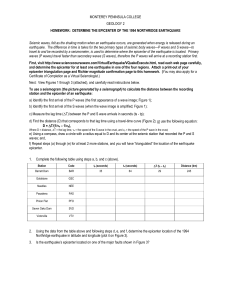
... HOMEWORK: DETERMINE THE EPICENTER OF THE 1994 NORTHRIDGE EARTHQUAKE Seismic waves, felt as the shaking motion when an earthquake occurs, are generated when energy is released during an earthquake. The difference in time is takes for the two primary types of seismic body waves—P waves and S waves—to ...
... HOMEWORK: DETERMINE THE EPICENTER OF THE 1994 NORTHRIDGE EARTHQUAKE Seismic waves, felt as the shaking motion when an earthquake occurs, are generated when energy is released during an earthquake. The difference in time is takes for the two primary types of seismic body waves—P waves and S waves—to ...
Earth`s Systems and Resources Quiz 2
... D) when movement along a fault stops. 19) Some convergent boundaries form subduction zones. Along what kind of fault are most of the earthquakes likely to occur along these boundaries? A)horizontal faults B) strike-slip faults ...
... D) when movement along a fault stops. 19) Some convergent boundaries form subduction zones. Along what kind of fault are most of the earthquakes likely to occur along these boundaries? A)horizontal faults B) strike-slip faults ...
Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries
... Ultimately it is the plate densities that determines which of the two lithospheric plates will ride over the other. The plates density along with the Slab Pull helps move the plate along. The largest subduction zone in the world runs along the entire Pacific Ocean and is known as the ‘Ring of Fire’. ...
... Ultimately it is the plate densities that determines which of the two lithospheric plates will ride over the other. The plates density along with the Slab Pull helps move the plate along. The largest subduction zone in the world runs along the entire Pacific Ocean and is known as the ‘Ring of Fire’. ...
Document
... a. tilting of surface rock c. movement along a fault b. folding of surface rock d. an igneous intrusion ...
... a. tilting of surface rock c. movement along a fault b. folding of surface rock d. an igneous intrusion ...
Divergent Seismicity Convergent Seismicity Transform Seismicity
... http://www.guardian.co.uk/world/video/2011/mar/11/japan‐earthquake‐tsunami‐video http://www.guardian.co.uk/world/video/2011/mar/14/japan‐tsunami‐amateur‐footage‐ ...
... http://www.guardian.co.uk/world/video/2011/mar/11/japan‐earthquake‐tsunami‐video http://www.guardian.co.uk/world/video/2011/mar/14/japan‐tsunami‐amateur‐footage‐ ...
Plate Tectonics, Volcano and Earthquake Webquest
... rough edges and lines. The energy stored here causes the pieces to slide, glide, knock and move around each piece. These pieces best describe what we call ‘_______________’. iii. After a period of time, the built up energy and movement causes huge ________________ in the plates, and there is massive ...
... rough edges and lines. The energy stored here causes the pieces to slide, glide, knock and move around each piece. These pieces best describe what we call ‘_______________’. iii. After a period of time, the built up energy and movement causes huge ________________ in the plates, and there is massive ...
The mechanics of tectonics
... When the plates of the earth’s crust exert pressure on one another as they move, the rocks that make up these plates are subject to extreme stress. During a latent period, this stress is absorbed by a certain elasticity. But beyond a particular point, a sudden rupture occurs, either along an existin ...
... When the plates of the earth’s crust exert pressure on one another as they move, the rocks that make up these plates are subject to extreme stress. During a latent period, this stress is absorbed by a certain elasticity. But beyond a particular point, a sudden rupture occurs, either along an existin ...
Movements of Earth`s Major Plates PPT
... • The Andes Mountains in South America formed where two tectonic plates converge or collide. • When tectonic plates undergo ________________ or ____________, ...
... • The Andes Mountains in South America formed where two tectonic plates converge or collide. • When tectonic plates undergo ________________ or ____________, ...
Top 10 Earthquakes since 1900
... Use the ESRT y-axis scale to mark off the time gap on scrap paper Match the time gap to p and s waves curves on ESRT to find distance from the epicenter on x-axis Use map scale + compass to draw circle from seismic station on map Remember – you need at least 3 seismic stations to locate the epicente ...
... Use the ESRT y-axis scale to mark off the time gap on scrap paper Match the time gap to p and s waves curves on ESRT to find distance from the epicenter on x-axis Use map scale + compass to draw circle from seismic station on map Remember – you need at least 3 seismic stations to locate the epicente ...
Studying the Earth s Interior Layers using Earthquakes What can
... Note the large changes in velocity at the Moho and the base of the lithosphere. Also note the relatively low velocities of the Asthenosphere (lowvelocity zone). Fig. 11-5 Chernicoff Geology 2nd Edition ...
... Note the large changes in velocity at the Moho and the base of the lithosphere. Also note the relatively low velocities of the Asthenosphere (lowvelocity zone). Fig. 11-5 Chernicoff Geology 2nd Edition ...
Natural Disasters
... boundaries. When the ocean floor at a plate boundary rises or falls suddenly it displaces the water above it and launches the rolling waves that will become a tsunami. Most tsunamis, about 80 percent, happen within the Pacific Ocean’s “Ring of Fire,” a geologically active area where tectonic shifts ...
... boundaries. When the ocean floor at a plate boundary rises or falls suddenly it displaces the water above it and launches the rolling waves that will become a tsunami. Most tsunamis, about 80 percent, happen within the Pacific Ocean’s “Ring of Fire,” a geologically active area where tectonic shifts ...
Earth`s interior volc eq2
... • Seismic waves (indirect evidence) – Vibrations that travel through Earth carrying energy released during an earthquake. – The speed and paths of waves reveal the structure of the planet. – We will learn more about these later. ...
... • Seismic waves (indirect evidence) – Vibrations that travel through Earth carrying energy released during an earthquake. – The speed and paths of waves reveal the structure of the planet. – We will learn more about these later. ...
In-Class Earthquake/Volcano Project
... The purpose of this project is to explore volcanoes and earthquakes, the hazards associated with them and to investigate how people prepare or prevent them. This project has 2 parts – a presentation and a written part. If you want to make a movie – TALK TO Mrs. Hanson or Mr. Godette. Part 1: Written ...
... The purpose of this project is to explore volcanoes and earthquakes, the hazards associated with them and to investigate how people prepare or prevent them. This project has 2 parts – a presentation and a written part. If you want to make a movie – TALK TO Mrs. Hanson or Mr. Godette. Part 1: Written ...
glossary of seismic terminology
... earthquake size which describes the amount of energy released. The measure is determined by taking the common logarithm (base 10) of the largest ground motion observed during the arrival of a P-wave or seismic surface wave and applying a standard correction for distance to the epicenter. (Each unit ...
... earthquake size which describes the amount of energy released. The measure is determined by taking the common logarithm (base 10) of the largest ground motion observed during the arrival of a P-wave or seismic surface wave and applying a standard correction for distance to the epicenter. (Each unit ...
Earthquake

An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the perceptible shaking of the surface of the Earth, which can be violent enough to destroy major buildings and kill thousands of people. The severity of the shaking can range from barely felt to violent enough to toss people around. Earthquakes have destroyed whole cities. They result from the sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. The seismicity, seismism or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time.Earthquakes are measured using observations from seismometers. The moment magnitude is the most common scale on which earthquakes larger than approximately 5 are reported for the entire globe. The more numerous earthquakes smaller than magnitude 5 reported by national seismological observatories are measured mostly on the local magnitude scale, also referred to as the Richter magnitude scale. These two scales are numerically similar over their range of validity. Magnitude 3 or lower earthquakes are mostly almost imperceptible or weak and magnitude 7 and over potentially cause serious damage over larger areas, depending on their depth. The largest earthquakes in historic times have been of magnitude slightly over 9, although there is no limit to the possible magnitude. The most recent large earthquake of magnitude 9.0 or larger was a 9.0 magnitude earthquake in Japan in 2011 (as of March 2014), and it was the largest Japanese earthquake since records began. Intensity of shaking is measured on the modified Mercalli scale. The shallower an earthquake, the more damage to structures it causes, all else being equal.At the Earth's surface, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and sometimes displacement of the ground. When the epicenter of a large earthquake is located offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to cause a tsunami. Earthquakes can also trigger landslides, and occasionally volcanic activity.In its most general sense, the word earthquake is used to describe any seismic event — whether natural or caused by humans — that generates seismic waves. Earthquakes are caused mostly by rupture of geological faults, but also by other events such as volcanic activity, landslides, mine blasts, and nuclear tests. An earthquake's point of initial rupture is called its focus or hypocenter. The epicenter is the point at ground level directly above the hypocenter.