the passira anorthositic complex and associated granites
... the Rio Capibaribe Terrain of the Borborema Province. Host rocks are rhiacian migmatitic gneisses. The PAC is a massif-type complex of batholithic proportions composed mainly of metamorphosed anorthosite, gabbro, norite, diorite and ultramafic lenses mineralized in Fe-Ti oxide minerals. A dyke swarm ...
... the Rio Capibaribe Terrain of the Borborema Province. Host rocks are rhiacian migmatitic gneisses. The PAC is a massif-type complex of batholithic proportions composed mainly of metamorphosed anorthosite, gabbro, norite, diorite and ultramafic lenses mineralized in Fe-Ti oxide minerals. A dyke swarm ...
Metamorphic conditions of the omphacite
... © 2016 Authors. This is an open access publication, which can be used, distributed and reproduced in any medium according to the Creative Commons CC-BY 4.0 License requiring that the original work has been properly cited. ...
... © 2016 Authors. This is an open access publication, which can be used, distributed and reproduced in any medium according to the Creative Commons CC-BY 4.0 License requiring that the original work has been properly cited. ...
I. Archaean specificities
... The main component of the grey gneisses is made of calc-alkaline granitoids (≈ Itypes), with some differences from modern I-type plutons: - They are rich in Na, and consequently in sodic plagioclage (albite) (whereas modern I-types are rich in K and K-Spar). They therefore are made of tonalites, tro ...
... The main component of the grey gneisses is made of calc-alkaline granitoids (≈ Itypes), with some differences from modern I-type plutons: - They are rich in Na, and consequently in sodic plagioclage (albite) (whereas modern I-types are rich in K and K-Spar). They therefore are made of tonalites, tro ...
Document
... Volcanoes get hotter as magma pushes closer to the surface. A geyser is a hot spring with narrow spaces in its plumbing which erupts periodically and forcibly ejects hot water. A hot spring has an open plumbing system and the superheated water is able to rise freely to the surface. Old Faithfu ...
... Volcanoes get hotter as magma pushes closer to the surface. A geyser is a hot spring with narrow spaces in its plumbing which erupts periodically and forcibly ejects hot water. A hot spring has an open plumbing system and the superheated water is able to rise freely to the surface. Old Faithfu ...
Zircon geochronology of intrusive rocks from Cap de Creus, Eastern
... yield inherited ages from the Precambrian metasedimentary protolith (with two main age clusters at c. 730–542 Ma and c. 2.9–2.2 Ga). However, field structural relationships indicate that migmatization occurred synchronously with the emplacement of the quartz dioritic magmas at c. 299 Ma. Thus, the r ...
... yield inherited ages from the Precambrian metasedimentary protolith (with two main age clusters at c. 730–542 Ma and c. 2.9–2.2 Ga). However, field structural relationships indicate that migmatization occurred synchronously with the emplacement of the quartz dioritic magmas at c. 299 Ma. Thus, the r ...
The Fossil Record and Evolution
... Problem exists that new cosmogenic isotopes are always being created. Not constant number like non-cosmogenic isotopes. Also dealing with very small amounts of daughter isotopes. May be lost due to erosion. ...
... Problem exists that new cosmogenic isotopes are always being created. Not constant number like non-cosmogenic isotopes. Also dealing with very small amounts of daughter isotopes. May be lost due to erosion. ...
Name _________________________________ ... 13. How do seismologists locate the epicenters...
... Scientists have discovered that earthquake waves penetrate Earth. The study of these waves provides scientists with valuable information about the structure of the interior of our planet. ...
... Scientists have discovered that earthquake waves penetrate Earth. The study of these waves provides scientists with valuable information about the structure of the interior of our planet. ...
Plate Tectonics
... properties of a solid but it can also flow A core – made of molten nickel and iron. Outer part is liquid and inner part is solid The average density of the Earth is much higher than the crust, so the inner core must be very dense ...
... properties of a solid but it can also flow A core – made of molten nickel and iron. Outer part is liquid and inner part is solid The average density of the Earth is much higher than the crust, so the inner core must be very dense ...
A note on the gravitational field of the right rectangular prism
... The recently released global crustal model CRUST 2.0 has been validated both globally and regionally focusing on its information content regarding the crust-mantle boundary. The numerical assessment of the metric information given by the database in terms of thickness and position of individual crus ...
... The recently released global crustal model CRUST 2.0 has been validated both globally and regionally focusing on its information content regarding the crust-mantle boundary. The numerical assessment of the metric information given by the database in terms of thickness and position of individual crus ...
Geochemical characteristics of granitic rocks underlying ion
... minerals of granitic rocks underlying ion-adsorption type rare earth elements (REE) deposits were studied in order to understand the genesis of the heavy REE (HREE)-rich deposits, because they are more critical than light REE (LREE). The REE grades of the ion-adsorption type deposits range widely fr ...
... minerals of granitic rocks underlying ion-adsorption type rare earth elements (REE) deposits were studied in order to understand the genesis of the heavy REE (HREE)-rich deposits, because they are more critical than light REE (LREE). The REE grades of the ion-adsorption type deposits range widely fr ...
Geology :: 7. Plate interiors
... The abyssal plains are found at depths between 3,000 and 6,000 meters. Lying generally between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plains cover more than 50% of the Earth’s surface. They are among the flattest, smoothest and least explored regions on Earth. Abyssal plains a ...
... The abyssal plains are found at depths between 3,000 and 6,000 meters. Lying generally between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plains cover more than 50% of the Earth’s surface. They are among the flattest, smoothest and least explored regions on Earth. Abyssal plains a ...
Tectonic Evolution of the Eastern Continental Margins of India and
... Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400 076, India, E-mail: mradhakrishna@iitb.ac.in ...
... Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400 076, India, E-mail: mradhakrishna@iitb.ac.in ...
ch08 - earthjay science
... carbonaceous chondrite (220): Meteorites that take their name from spherical bodies called chondrites which contain nitrogen, hydrogen, carbon, dark iron, and magnesium silicates and water. chemosynthesis (240): A means by which organisms derive their energy by oxidizing such inorganic substances as ...
... carbonaceous chondrite (220): Meteorites that take their name from spherical bodies called chondrites which contain nitrogen, hydrogen, carbon, dark iron, and magnesium silicates and water. chemosynthesis (240): A means by which organisms derive their energy by oxidizing such inorganic substances as ...
A major crustal discontinuity in George V Land: new - MNA
... coastal segment of East Antarctica is also important to gain new insights into the tectonic relations between East Antarctic Craton (EAC) and the Ross Mobile Belt. Furthermore, it potentially retains records of the younger (?late Mesozoic-Cenozoic) crustal structures and tectonic evolution of a key ...
... coastal segment of East Antarctica is also important to gain new insights into the tectonic relations between East Antarctic Craton (EAC) and the Ross Mobile Belt. Furthermore, it potentially retains records of the younger (?late Mesozoic-Cenozoic) crustal structures and tectonic evolution of a key ...
Metamorphic. evolution of high-pressure, low
... foliation. The eclogites at Kini, composed of omphacite, glaucophane, zoisite, rutile, garnet, and titanite, do not have a measurable foliation or lineation. Omphacite-zoisite rock is coarsegrained (1-2.5 cm crystals) with little fabric. Locally, the eclogite and the omphacite-zoisite rocks are cros ...
... foliation. The eclogites at Kini, composed of omphacite, glaucophane, zoisite, rutile, garnet, and titanite, do not have a measurable foliation or lineation. Omphacite-zoisite rock is coarsegrained (1-2.5 cm crystals) with little fabric. Locally, the eclogite and the omphacite-zoisite rocks are cros ...
Archean sedimentary rocks
... • By about 4 b.y. ago, the Earth had probably cooled sufficiently for plate formation. • Once plate tectonics was in progress, it generated crustal rock that could be partially melted in subduction zones and added to the continental crust. • Continents also increased in size by addition of microcont ...
... • By about 4 b.y. ago, the Earth had probably cooled sufficiently for plate formation. • Once plate tectonics was in progress, it generated crustal rock that could be partially melted in subduction zones and added to the continental crust. • Continents also increased in size by addition of microcont ...
6 - Bal Bharati Public School
... Our lithosphere is broken into a number of plates called Lithospheric plates. The plates move because of molten magma inside the earth. Q7. What are minerals? How are they useful? Minerals are naturally occurring substances which have certain physical properties and definite chemical composition. So ...
... Our lithosphere is broken into a number of plates called Lithospheric plates. The plates move because of molten magma inside the earth. Q7. What are minerals? How are they useful? Minerals are naturally occurring substances which have certain physical properties and definite chemical composition. So ...
Drillers propose deep-Earth quest By Jonathan Amos Science
... The mantle makes up the bulk of our planet's volume and mass. It stretches from the bottom of the crust down to the Earth's iron-nickel core some 2,900km further down. Its rocks are distinct in composition from those that make up the continents and the ocean floor. They are thought predominantly to ...
... The mantle makes up the bulk of our planet's volume and mass. It stretches from the bottom of the crust down to the Earth's iron-nickel core some 2,900km further down. Its rocks are distinct in composition from those that make up the continents and the ocean floor. They are thought predominantly to ...
Heterogeneous Growth and Dissolution of Sillimanite
... Archean Rocks of the Wyoming Province Archean rocks exposed in the eastern and central Beartooth Mountains, Bighorn Mountains, and samples from deep-drill cores in eastern Wyoming and Montana are dominantly Late Archean granitoids, members of the tonalite-trondhjemitegranodiorite suite, with inclusi ...
... Archean Rocks of the Wyoming Province Archean rocks exposed in the eastern and central Beartooth Mountains, Bighorn Mountains, and samples from deep-drill cores in eastern Wyoming and Montana are dominantly Late Archean granitoids, members of the tonalite-trondhjemitegranodiorite suite, with inclusi ...
Nascent continental crust in oceanic island arcs: insights from the
... δ18O suggest that the batholith evolved from mantle-derived melts with limited incorporation of isotopically evolved crustal components. The batholith exhibits spatiotemporal and geochemical patterns. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns vary with age from old samples characterized by flat patterns int ...
... δ18O suggest that the batholith evolved from mantle-derived melts with limited incorporation of isotopically evolved crustal components. The batholith exhibits spatiotemporal and geochemical patterns. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns vary with age from old samples characterized by flat patterns int ...
Ancient crust rises from the deep
... typically found in Earth’s crust. Although biological processes can generate such an anomaly, they would simultaneously generate abnormally high concentrations of sulphur-34 — which are not present in the Mangaia samples. The most likely source of the sulphur-33depleted rocks, the team says, is mant ...
... typically found in Earth’s crust. Although biological processes can generate such an anomaly, they would simultaneously generate abnormally high concentrations of sulphur-34 — which are not present in the Mangaia samples. The most likely source of the sulphur-33depleted rocks, the team says, is mant ...
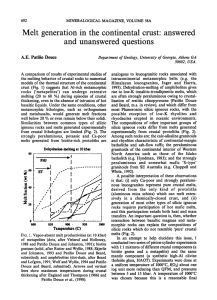
Melt generation in the continental crust: answered and unanswered
... 1993). Dehydration-melting of amphibolites gives rise to low-K tonalitic-trondhjemitic melts, which are often strongly peraluminous owing to crystallization of restitic clinopyroxene (Patifio Douce and Beard, m.s. in review), and which differ from most Phanerozoic silicic igneous rocks, with the pos ...
... 1993). Dehydration-melting of amphibolites gives rise to low-K tonalitic-trondhjemitic melts, which are often strongly peraluminous owing to crystallization of restitic clinopyroxene (Patifio Douce and Beard, m.s. in review), and which differ from most Phanerozoic silicic igneous rocks, with the pos ...
Isotope Geochemistry of the Continents
... in a 3 Ga meta-sedimentary conglomerate, surround by the Narryer gneisses (3.653.3 Ga). ...
... in a 3 Ga meta-sedimentary conglomerate, surround by the Narryer gneisses (3.653.3 Ga). ...
Fold Movement – Teacher Notes File
... 2. Plates Moving Together - The Continental Crust Crumples and Shortens When plastic rocks move together they crumple and form folds. A demonstration of folding can be made using soft fabrics such as towels pressed together by large books. ...
... 2. Plates Moving Together - The Continental Crust Crumples and Shortens When plastic rocks move together they crumple and form folds. A demonstration of folding can be made using soft fabrics such as towels pressed together by large books. ...
Baltic Shield

The Baltic Shield (sometimes referred to as the Fennoscandian Shield) is located in Fennoscandia (Norway, Sweden and Finland), northwest Russia and under the Baltic Sea. The Baltic Shield is defined as the exposed Precambrian northwest segment of the East European Craton. It is composed mostly of Archean and Proterozoic gneisses and greenstones which have undergone numerous deformations through tectonic activity (see Geology of Fennoscandia map [1]). The Baltic Shield contains the oldest rocks of the European continent. The lithospheric thickness is about 200-300 km. During the Pleistocene epoch, great continental ice sheets scoured and depressed the shield's surface, leaving a thin covering of glacial material and innumerable lakes and streams. The Baltic Shield is still rebounding today following the melting of the thick glaciers during the Quaternary Period.