Yogo_et_al._Slab Edg.. - UNC
... these areas, termed `adakites', are often associated with subducting plates that are young and warm, and therefore thought to be more prone to melting5. But the subducting lithosphere in some adakite locations (such as the Aleutian islands) appears to be too old and hence too cold to melt6,7. This i ...
... these areas, termed `adakites', are often associated with subducting plates that are young and warm, and therefore thought to be more prone to melting5. But the subducting lithosphere in some adakite locations (such as the Aleutian islands) appears to be too old and hence too cold to melt6,7. This i ...
Igneous rocks freezes solid. Can be intrusive
... country rock. Sill : A nearly horizontal table-top-shaped tabular intrusion that occurs between the layers of country rock. Laccolith: A sill that domes upward (convex up). Lopolith: A sill that domes downward (concave down). Pluton: An irregular or blob-shaped intrusion; can range in size from tens ...
... country rock. Sill : A nearly horizontal table-top-shaped tabular intrusion that occurs between the layers of country rock. Laccolith: A sill that domes upward (convex up). Lopolith: A sill that domes downward (concave down). Pluton: An irregular or blob-shaped intrusion; can range in size from tens ...
chapter 3
... in age. Within this unit are preserved distinctive clasts of Chilliwack rocks, the earliest truly compelling evidence that these terranes were amalgamated at this date. The Harrison Lake Formation is represented south of the international boundary by the Wells Creek Volcanics in the Mt. Baker region ...
... in age. Within this unit are preserved distinctive clasts of Chilliwack rocks, the earliest truly compelling evidence that these terranes were amalgamated at this date. The Harrison Lake Formation is represented south of the international boundary by the Wells Creek Volcanics in the Mt. Baker region ...
Seismic reflection image of the Great Sumatra
... subduction event in the last 50 years. The rupture initiated at 30-40 km depth northwest of Simeulue Island1 and propagated for ~1300 km to the northern Andaman Islands2. The earthquake was caused by a sudden slip along the interplate boundary between the subducting Indo-Australian plate and overrid ...
... subduction event in the last 50 years. The rupture initiated at 30-40 km depth northwest of Simeulue Island1 and propagated for ~1300 km to the northern Andaman Islands2. The earthquake was caused by a sudden slip along the interplate boundary between the subducting Indo-Australian plate and overrid ...
Petrogenesis of Mafic to Felsic Plutonic Rock Associations: the Calc
... mafic magma (Fourcade & Allègre, 1981) and the intrusion of several compositionally distinct, petrogenetically unrelated intrusions (Fourcade & Allègre, 1981; Bickle et al., 1988). The isotopic signatures of the Quérigut granitoids, and other similar contemporaneous intrusive and volcanic rocks i ...
... mafic magma (Fourcade & Allègre, 1981) and the intrusion of several compositionally distinct, petrogenetically unrelated intrusions (Fourcade & Allègre, 1981; Bickle et al., 1988). The isotopic signatures of the Quérigut granitoids, and other similar contemporaneous intrusive and volcanic rocks i ...
Earth`s Layered Structure
... The average composition of the continental crust is granitic rock called granodiorite. Continental rocks have an average density of about 2.7g.cm3 and some are over 4 billion years old. The rocks of the oceanic crust are younger (180 million years or less) and have an average density of about 3.0g/c ...
... The average composition of the continental crust is granitic rock called granodiorite. Continental rocks have an average density of about 2.7g.cm3 and some are over 4 billion years old. The rocks of the oceanic crust are younger (180 million years or less) and have an average density of about 3.0g/c ...
Depositional History and Tectonic Regimes within and in
... Finland were covered by the sea, and in the Middle Ordovician, the sea reached as far as central Finland. No Late Palaeozoic (Silurian to Permian) sedimentary rocks have been recognized. The apatite fission track studies indicate, however, that extensive Silurian to Devonian deposits most likely cov ...
... Finland were covered by the sea, and in the Middle Ordovician, the sea reached as far as central Finland. No Late Palaeozoic (Silurian to Permian) sedimentary rocks have been recognized. The apatite fission track studies indicate, however, that extensive Silurian to Devonian deposits most likely cov ...
Earthquakes in NE Kansas
... Most of the movement occur along the flanks of the rift, because the volcanic rocks along the rift axis are too heavy to move This vertical movement is along vertical faults such as the Humboldt fault and the “Big Blue Fault” Movement along faults cause earthquakes ...
... Most of the movement occur along the flanks of the rift, because the volcanic rocks along the rift axis are too heavy to move This vertical movement is along vertical faults such as the Humboldt fault and the “Big Blue Fault” Movement along faults cause earthquakes ...
Origin and evolution of the lower crust in magmatic
... crustal sections in the Jurassic Talkeetna arc (south central Alaska) and the Cretaceous Kohistan arc (northwest Pakistan), together with seismic data on the lower crust and uppermost mantle. Whereas primitive arc lavas are dominantly basaltic, the Kohistan crust is clearly andesitic and the Talkeet ...
... crustal sections in the Jurassic Talkeetna arc (south central Alaska) and the Cretaceous Kohistan arc (northwest Pakistan), together with seismic data on the lower crust and uppermost mantle. Whereas primitive arc lavas are dominantly basaltic, the Kohistan crust is clearly andesitic and the Talkeet ...
1 INTERNATIONAL LITHOSPHERE PROGRAM (ILP) Proposal for
... the continental lithosphere relicts that reside within rocks of the Earth’s mantle. For understanding the assimilation of crustal C and N into the mantle by creating new ultra-high pressure minerals or through incorporation into well-known mantle high-pressure phases, we need to observe the natural ...
... the continental lithosphere relicts that reside within rocks of the Earth’s mantle. For understanding the assimilation of crustal C and N into the mantle by creating new ultra-high pressure minerals or through incorporation into well-known mantle high-pressure phases, we need to observe the natural ...
Radiometric dating results 5
... units are represented. The Archaean rocks to the north are overlain by Karelian rocks, which to the south are overlain by Svecofennian rocks. The upper part of the latter (Younger Svecofennian metasedimentary sequence) consists of clastic metasedimentary rocks, which were called the Vakko formation ...
... units are represented. The Archaean rocks to the north are overlain by Karelian rocks, which to the south are overlain by Svecofennian rocks. The upper part of the latter (Younger Svecofennian metasedimentary sequence) consists of clastic metasedimentary rocks, which were called the Vakko formation ...
Magma mixing, mingling and hybridisation at different
... features irrespective of diverse geological settings, level of emplacement in the crust and compositional range. Here we briefly discuss the main differences between the three areas in order to constrain the key responsible processes that generated the observed features. The Tasiilaq intrusion repre ...
... features irrespective of diverse geological settings, level of emplacement in the crust and compositional range. Here we briefly discuss the main differences between the three areas in order to constrain the key responsible processes that generated the observed features. The Tasiilaq intrusion repre ...
37. Igneous and Metasedimentary Basement Lithofacies of the
... Queensland Plateau acoustic basement was penetrated by rotary drilling at Sites 824 and 825, to the west and east of Holmes Reef respectively, on the western Queensland Plateau. Despite poor recovery (5%—13%), the lithologies recovered are of considerable importance as they represent the only baseme ...
... Queensland Plateau acoustic basement was penetrated by rotary drilling at Sites 824 and 825, to the west and east of Holmes Reef respectively, on the western Queensland Plateau. Despite poor recovery (5%—13%), the lithologies recovered are of considerable importance as they represent the only baseme ...
Proterozoic Rocks, Glacier NP
... – and formed another supercontinent – this one known as Pannotia – about 650 million years ago – judging by the Pan-African orogeny • the large-scale deformation that took place • in what are now the Southern Hemisphere ...
... – and formed another supercontinent – this one known as Pannotia – about 650 million years ago – judging by the Pan-African orogeny • the large-scale deformation that took place • in what are now the Southern Hemisphere ...
Notes for IUGG 2007 talk (Seismic imaging of the lithosphere
... Tasmania was the Middle to Late Cambrian Tyennan Orogeny. The East Tasmania Terrane contains no evidence of the Tyennan Orogen or Proterozoic outcrop, and it is widely thought that the two terranes were juxtaposed during th Middle Devonian Tabberabberan Orogeny. The presence of exposed Precambrian b ...
... Tasmania was the Middle to Late Cambrian Tyennan Orogeny. The East Tasmania Terrane contains no evidence of the Tyennan Orogen or Proterozoic outcrop, and it is widely thought that the two terranes were juxtaposed during th Middle Devonian Tabberabberan Orogeny. The presence of exposed Precambrian b ...
Mineralogy, geochemistry and geotectonic of plagiogranites from
... Mineralogy, Geochemistry and Geotectonic of Plagiogranites from Shahre-Babak Ophiolite, Zagros Zone, Iran into gabbros and especially dolerite dykes causes the enclosing of their parts as xenoliths or expanding of plagiogranite veins within it (Golestani, 2013). Neyriz ophiolite thrusted over limes ...
... Mineralogy, Geochemistry and Geotectonic of Plagiogranites from Shahre-Babak Ophiolite, Zagros Zone, Iran into gabbros and especially dolerite dykes causes the enclosing of their parts as xenoliths or expanding of plagiogranite veins within it (Golestani, 2013). Neyriz ophiolite thrusted over limes ...
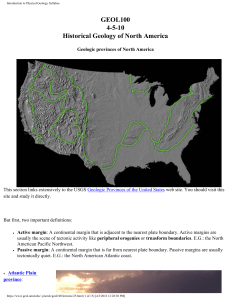
GEOL100 4-5-10 Historical Geology of North America
... Red Sea today. As it cooled, the continental crust shrank and sank. Sediments began to be deposited on it. Today, its bedrock is covered with an thick apron of nearly horizontal sediments from Jurassic to recent in age. Topographic relief is low - the classic passive margin. ● Appalachian highlands: ...
... Red Sea today. As it cooled, the continental crust shrank and sank. Sediments began to be deposited on it. Today, its bedrock is covered with an thick apron of nearly horizontal sediments from Jurassic to recent in age. Topographic relief is low - the classic passive margin. ● Appalachian highlands: ...
An Overview of the Structure and Evolution of the Ouachita Orogenic
... wide variety of data to produce a set of crustal scale transects from the continental interior to the Gulf Coast region. The key transect is based on deep reflection and refraction experiments that together extended from the Arkoma basin in Arkansas to the Sabine uplift in Louisiana. These data imag ...
... wide variety of data to produce a set of crustal scale transects from the continental interior to the Gulf Coast region. The key transect is based on deep reflection and refraction experiments that together extended from the Arkoma basin in Arkansas to the Sabine uplift in Louisiana. These data imag ...
The role of crustal and mantle sources in the genesis of granitoids of
... (Fig. 2) have also been considered to contain a significant component derived from pre-Triassic crust (Wareham et al. 1997b). In this area, the mafic end-member is thought to be derived by mixing of basaltic–andesitic arc magmas with melts of juvenile basaltic underplate at the base of the crust. Th ...
... (Fig. 2) have also been considered to contain a significant component derived from pre-Triassic crust (Wareham et al. 1997b). In this area, the mafic end-member is thought to be derived by mixing of basaltic–andesitic arc magmas with melts of juvenile basaltic underplate at the base of the crust. Th ...
Fluorine and Chlorine in Granitoids from the Basin and Range
... fluorine proviI).ces over long geologic periods and suggested instead that the regional differences in fluorine content of volcanic rocks noted by Coats et al. (1963) are the result of differences in magmatic evolution or alkalinity. The results of our investigations ...
... fluorine proviI).ces over long geologic periods and suggested instead that the regional differences in fluorine content of volcanic rocks noted by Coats et al. (1963) are the result of differences in magmatic evolution or alkalinity. The results of our investigations ...
Precambrian meta-ultramafic rocks from the
... Meta-ultramafic rocks occur as small (2 to 100 m long), podiform bodies in all three major Precambrian rock suites of the Tobacco Root Mountains of southwest Montana. Most samples consist of a randomly oriented, coarse-grained assemblage of orthopyroxene, olivine, and magnesiohornblende ± spinel, pa ...
... Meta-ultramafic rocks occur as small (2 to 100 m long), podiform bodies in all three major Precambrian rock suites of the Tobacco Root Mountains of southwest Montana. Most samples consist of a randomly oriented, coarse-grained assemblage of orthopyroxene, olivine, and magnesiohornblende ± spinel, pa ...
Long-term continental areal reduction produced by tectonic processes
... ridges). These values are in good agreement with previous studies determining present-day ocean spreading rates which also suggest that spreading rates have not varied significantly over at least the past 180 Ma [6]. Reduction in continental area by tectonic processes is mitigated by deposition of s ...
... ridges). These values are in good agreement with previous studies determining present-day ocean spreading rates which also suggest that spreading rates have not varied significantly over at least the past 180 Ma [6]. Reduction in continental area by tectonic processes is mitigated by deposition of s ...
The Sveconorwegian magmatic and tectono
... Gneisses and granites, often rat her mo notonou s, dominate, and althoug h metasedi ment s are patent in many gn eisses, the overwh elming granitization has oblitera ted th e primary structu res and th oroughl y homog enized th e rocks over large areas,» It had onl y been possible to map some late g ...
... Gneisses and granites, often rat her mo notonou s, dominate, and althoug h metasedi ment s are patent in many gn eisses, the overwh elming granitization has oblitera ted th e primary structu res and th oroughl y homog enized th e rocks over large areas,» It had onl y been possible to map some late g ...
Geology - Central Washington University Geological Sciences
... margin that was not affected by subsequent tectonic events. The Ouachita fold-and-thrust belt is a thin-skinned orogen that was thrust northward over the passive margin, but it did not result in significant shortening or crustal thickening on the margin. Mesozoic extension was focused south of the o ...
... margin that was not affected by subsequent tectonic events. The Ouachita fold-and-thrust belt is a thin-skinned orogen that was thrust northward over the passive margin, but it did not result in significant shortening or crustal thickening on the margin. Mesozoic extension was focused south of the o ...
Composition of the martian crust
... representative TES spectra, such as Sytis-type and Acidalia-type surfaces, to make a preliminary qualitative classification. Next, lab-collected spectra from infrared spectral libraries will be used as an output for a linear deconvolution algorithm to constrain quantitatively the modal mineral abund ...
... representative TES spectra, such as Sytis-type and Acidalia-type surfaces, to make a preliminary qualitative classification. Next, lab-collected spectra from infrared spectral libraries will be used as an output for a linear deconvolution algorithm to constrain quantitatively the modal mineral abund ...
Baltic Shield

The Baltic Shield (sometimes referred to as the Fennoscandian Shield) is located in Fennoscandia (Norway, Sweden and Finland), northwest Russia and under the Baltic Sea. The Baltic Shield is defined as the exposed Precambrian northwest segment of the East European Craton. It is composed mostly of Archean and Proterozoic gneisses and greenstones which have undergone numerous deformations through tectonic activity (see Geology of Fennoscandia map [1]). The Baltic Shield contains the oldest rocks of the European continent. The lithospheric thickness is about 200-300 km. During the Pleistocene epoch, great continental ice sheets scoured and depressed the shield's surface, leaving a thin covering of glacial material and innumerable lakes and streams. The Baltic Shield is still rebounding today following the melting of the thick glaciers during the Quaternary Period.