Earth Structure
... Explain the theory of continental drift. What are mid-ocean ridges, rift valleys, and trenches? What is the theory of sea floor spreading? What is the theory of plate tectonics Explain the difference between convergent, divergent, and ...
... Explain the theory of continental drift. What are mid-ocean ridges, rift valleys, and trenches? What is the theory of sea floor spreading? What is the theory of plate tectonics Explain the difference between convergent, divergent, and ...
Week 2 (Norton), part a (pdf, 2.2 MB)
... notion that species were not immutable, but evolved through natural selection required time—lots of time. Hence gradual-ism, not catastrophism. In Europe, particularly, many geological symptoms of damage or catastrophe previously blamed on the Biblical Flood were now re-interpreted as the results of ...
... notion that species were not immutable, but evolved through natural selection required time—lots of time. Hence gradual-ism, not catastrophism. In Europe, particularly, many geological symptoms of damage or catastrophe previously blamed on the Biblical Flood were now re-interpreted as the results of ...
Study Guide for The Theory of Plate Tectonics Chapter 3
... worked even though he provided evidence that the continents were moving. Pangea: This was a supercontinent around 300 million years ago. Wegener named this continent Pangea. Pangea began to break apart and the pieces moved to form the continents of today. Fossils: Any trace of an ancient plant or an ...
... worked even though he provided evidence that the continents were moving. Pangea: This was a supercontinent around 300 million years ago. Wegener named this continent Pangea. Pangea began to break apart and the pieces moved to form the continents of today. Fossils: Any trace of an ancient plant or an ...
chapter 11 Dynamic Planet
... – Striations and glacial deposits of the same age in the five southern ...
... – Striations and glacial deposits of the same age in the five southern ...
to an introductory Plate Tectonics exercise for a
... Background – Plate tectonics describes the Earth’s crust as being a rigid exterior, which is divided into several slabs, or “plates”, which are located above the convecting mantle and move through time. Dissipation of heat from the Earth’s interior drives plate movement. The boundaries between pl ...
... Background – Plate tectonics describes the Earth’s crust as being a rigid exterior, which is divided into several slabs, or “plates”, which are located above the convecting mantle and move through time. Dissipation of heat from the Earth’s interior drives plate movement. The boundaries between pl ...
plate tectonics - Science with Ms. Reathaford!
... The Earth’s lithosphere is broken into large slabs of rock, called plates, which moves in different directions at different speeds. These plates interact with one another at plate boundaries. Each type of boundary has specific characteristics and processes associated with it. ...
... The Earth’s lithosphere is broken into large slabs of rock, called plates, which moves in different directions at different speeds. These plates interact with one another at plate boundaries. Each type of boundary has specific characteristics and processes associated with it. ...
Chapter 10 study guide
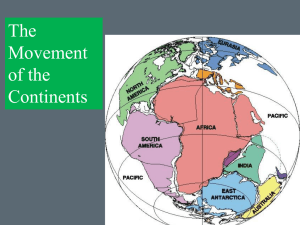
... Plate Tectonics Study Guide About 260 million years ago, Earth’s continents moved together to form the supercontinent Pangaea. Supercontinent – a single landmass once formed by the continents (Pangaea) In 1912 Alfred Wegener proposed the hypothesis of continental drift. Continental drift – hypothesi ...
... Plate Tectonics Study Guide About 260 million years ago, Earth’s continents moved together to form the supercontinent Pangaea. Supercontinent – a single landmass once formed by the continents (Pangaea) In 1912 Alfred Wegener proposed the hypothesis of continental drift. Continental drift – hypothesi ...
Plate Boundaries - Learn Earth Science
... Theory of Continental Drift? • Alfred Wegner, 1915 • The continents were once a super-continent called Pangea • the continents are plowing through the ocean floors---most people didn’t believe this ...
... Theory of Continental Drift? • Alfred Wegner, 1915 • The continents were once a super-continent called Pangea • the continents are plowing through the ocean floors---most people didn’t believe this ...
Plate Boundaries
... Theory of Continental Drift? • Alfred Wegner, 1915 • The continents were once a super-continent called Pangea • the continents are plowing through the ocean floors---most people didn’t believe this ...
... Theory of Continental Drift? • Alfred Wegner, 1915 • The continents were once a super-continent called Pangea • the continents are plowing through the ocean floors---most people didn’t believe this ...
PT Notes Fill in
... a. Mesosaurus fossils were found in _______________________________. Unlikely these animals swam across the __________________________ 3. ________________________________: Coastal mountain ranges that are widely _________________________ have similar ___________________________. a. _________________ ...
... a. Mesosaurus fossils were found in _______________________________. Unlikely these animals swam across the __________________________ 3. ________________________________: Coastal mountain ranges that are widely _________________________ have similar ___________________________. a. _________________ ...
Chap-4-Sec-2-Evidence-Supporting-Continental
... Evidence Supporting Continental Drift The Earth's crust is constantly moving, both vertically and horizontally, at rates of up to several inches a year. A widely-held theory that explains these movements is called "plate tectonics." It was developed in the mid 1960s by geophysicists. The term "plate ...
... Evidence Supporting Continental Drift The Earth's crust is constantly moving, both vertically and horizontally, at rates of up to several inches a year. A widely-held theory that explains these movements is called "plate tectonics." It was developed in the mid 1960s by geophysicists. The term "plate ...
Evidence of continental drift
... means “all the earth” in Greek. Pangaea broke up 200 mya. The northern half of Pangaea was referred to as Laurasia and the southern portion is known as Gondwanaland. ...
... means “all the earth” in Greek. Pangaea broke up 200 mya. The northern half of Pangaea was referred to as Laurasia and the southern portion is known as Gondwanaland. ...
Answers to pgs. 125 - 128 wks.
... 14. The continents once formed a single landmass, broke up, and drifted to their present locations because of a. tectonic drift. b. plate tectonics. c. continental drift. d. continental tectonics. 15. As a continent moves across Earth’s surface, a. it carries oceans with it. b. it carries rocks and ...
... 14. The continents once formed a single landmass, broke up, and drifted to their present locations because of a. tectonic drift. b. plate tectonics. c. continental drift. d. continental tectonics. 15. As a continent moves across Earth’s surface, a. it carries oceans with it. b. it carries rocks and ...
Vocabulary Quiz
... Matching: For each section, place the letter on the line which best matches each term with its’ description. Do Not draw lines! If I get confused, then it must be wrong! Part I Continental Drift _______1. Continental Drift ...
... Matching: For each section, place the letter on the line which best matches each term with its’ description. Do Not draw lines! If I get confused, then it must be wrong! Part I Continental Drift _______1. Continental Drift ...
174 CONTINENTS AND THEIR MOVEMENT B.J. Taygushanov, E.V.
... Strong evidence for the existence of Pangea, Gondwana and Laurasia were obtained by Wegener, after summarizing the paleoclimatic data. At that time it has already well known that almost all the southern continents traces of the largest ice sheet, which occurred about 280 million years ago. Glacial f ...
... Strong evidence for the existence of Pangea, Gondwana and Laurasia were obtained by Wegener, after summarizing the paleoclimatic data. At that time it has already well known that almost all the southern continents traces of the largest ice sheet, which occurred about 280 million years ago. Glacial f ...
Plate Tectonics
... Structures of Continents • continents are made and deformed by plate motion • continents are (in general) older than ocean rocks ...
... Structures of Continents • continents are made and deformed by plate motion • continents are (in general) older than ocean rocks ...
Plate Tectonics
... • Wegener’s Continental Drift Hypothesis was never accepted by the scientific community • He could not explain what forces could cause such massive movement • Wegener died in 1930, on expedition in Greenland, while collecting evidence to further support his theory ...
... • Wegener’s Continental Drift Hypothesis was never accepted by the scientific community • He could not explain what forces could cause such massive movement • Wegener died in 1930, on expedition in Greenland, while collecting evidence to further support his theory ...
Plate Tectonics
... • Wegener’s Continental Drift Hypothesis was never accepted by the scientific community • He could not explain what forces could cause such massive movement • Wegener died in 1930, on expedition in Greenland, while collecting evidence to further support his theory ...
... • Wegener’s Continental Drift Hypothesis was never accepted by the scientific community • He could not explain what forces could cause such massive movement • Wegener died in 1930, on expedition in Greenland, while collecting evidence to further support his theory ...
File
... Identify that the sources of Earth’s internal heat (radioactive decay and heat of formation) Trace the lines of scientific evidence that lead to the inference that Earth’s core, mantle and crust are each made up of different materials Trace the lines of scientific evidence that lead to the inf ...
... Identify that the sources of Earth’s internal heat (radioactive decay and heat of formation) Trace the lines of scientific evidence that lead to the inference that Earth’s core, mantle and crust are each made up of different materials Trace the lines of scientific evidence that lead to the inf ...
Presentation
... and the Americas, are Jurassic in age, showing the time of formation of the Atlantic Ocean. ...
... and the Americas, are Jurassic in age, showing the time of formation of the Atlantic Ocean. ...
Chapter 7 Section 2 Pages 198-201
... and the Americas, are Jurassic in age, showing the time of formation of the Atlantic Ocean. ...
... and the Americas, are Jurassic in age, showing the time of formation of the Atlantic Ocean. ...
mid-ocean ridges - River Mill Academy
... because no one could believe that things as large as continents could move and because Wegener could not propose a mechanism which could explain such motion. ...
... because no one could believe that things as large as continents could move and because Wegener could not propose a mechanism which could explain such motion. ...
Plate Tectonics - Georgia Standards
... Plate tectonics is the theory that all the continents of the earth were once united in a huge land mass called Pangea. The continents broke apart and began to drift on plates of the earth's lithosphere. People had been posing this idea since the 4th century B.C., when Aristotle noticed that marine a ...
... Plate tectonics is the theory that all the continents of the earth were once united in a huge land mass called Pangea. The continents broke apart and began to drift on plates of the earth's lithosphere. People had been posing this idea since the 4th century B.C., when Aristotle noticed that marine a ...
Supercontinent

In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of the Earth's continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, the definition of a supercontinent can be ambiguous. Many tectonicists such as P.F. Hoffman (1999) use the term ""supercontinent"" to mean ""a clustering of nearly all continents"". This definition leaves room for interpretation when labeling a continental body and is easier to apply to Precambrian times. Using the first definition provided here, Gondwana (aka Gondwanaland) is not considered a supercontinent, because the landmasses of Baltica, Laurentia and Siberia also existed at the same time but physically separate from each other. The landmass of Pangaea is the collective name describing all of these continental masses when they were in a close proximity to one another. This would classify Pangaea as a supercontinent. According to the definition by Rogers and Santosh (2004), a supercontinent does not exist today. Supercontinents have assembled and dispersed multiple times in the geologic past (see table). The positions of continents have been accurately determined back to the early Jurassic. However, beyond 200 Ma, continental positions are much less certain.