Text
... formulation in terms of the change in momentum. One advantage of this formulation is that it can be used for processes in which the mass of the system is changing in time. There are two simple, yet very interesting conclusions we can draw from this formulation of Newton’s second law in terms of the ...
... formulation in terms of the change in momentum. One advantage of this formulation is that it can be used for processes in which the mass of the system is changing in time. There are two simple, yet very interesting conclusions we can draw from this formulation of Newton’s second law in terms of the ...
Problem 1: Three forces, given by F = −2 + 2 N, F 2 = 5 − 3
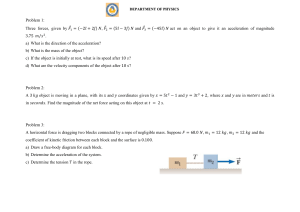
... As it can be seen from the figure below, an 18kg hanging box is connected by a light, inextensible string over a light, frictionless pulley to a 10kg block that is pulled by an external force having magnitude F=300N. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the surface and the 10kg mass is 0.1 ...
... As it can be seen from the figure below, an 18kg hanging box is connected by a light, inextensible string over a light, frictionless pulley to a 10kg block that is pulled by an external force having magnitude F=300N. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the surface and the 10kg mass is 0.1 ...
Newton`s laws of motion
... What is Newton’s law of actionreaction? • Newton’s third law of motion states whenever one object applies a force on a second object, the second object applies an equal and opposite force on the first object. • The force exerted by the first object is called the action force • The force exerted by t ...
... What is Newton’s law of actionreaction? • Newton’s third law of motion states whenever one object applies a force on a second object, the second object applies an equal and opposite force on the first object. • The force exerted by the first object is called the action force • The force exerted by t ...
second-order linear homogeneous differential equations
... 23. In each part, find a second-order linear homogeneous differential equation with constant coefficients that has the given functions as solutions. (a) y1 = e5x , y2 = e−2x (b) y1 = e4x , y2 = xe4x −x −x (c) y1 = e cos 4x, y2 = e sin 4x 24. Show that if ex and e−x are solutions of a second-order li ...
... 23. In each part, find a second-order linear homogeneous differential equation with constant coefficients that has the given functions as solutions. (a) y1 = e5x , y2 = e−2x (b) y1 = e4x , y2 = xe4x −x −x (c) y1 = e cos 4x, y2 = e sin 4x 24. Show that if ex and e−x are solutions of a second-order li ...
Foundation of Newtonian Mechanics
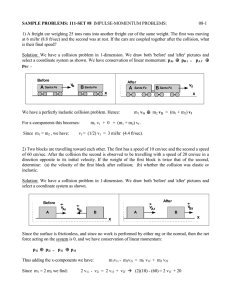
... The product of mass and velocity is momentum, denoted by the symbol “p”. Since the final momentum minus the initial momentum is the change in momentum, ...
... The product of mass and velocity is momentum, denoted by the symbol “p”. Since the final momentum minus the initial momentum is the change in momentum, ...
Experiment No : M8 Experiment Name: FREE FALL and ATWOOD`S
... Newton has also proved a theorem which states that a thin spherical shell of uniform mass distribution gravitationally interacts with its outer region like a point particle as if its total mass is concentrated at its center. (The second part of the theorem states that the shell doesn’t interact with ...
... Newton has also proved a theorem which states that a thin spherical shell of uniform mass distribution gravitationally interacts with its outer region like a point particle as if its total mass is concentrated at its center. (The second part of the theorem states that the shell doesn’t interact with ...
From Newton to Einstein: The Discovery of Laws of Motion and Gravity
... Earth is thrown off its regular orbit, and made to plunge to the Sun and burn up, or made to escape far from the Sun where the Earth and everything on its surface would freeze permanently without the heat of the Sun’s rays? We have to solve the threebody problem of the Earth, Venus and the Sun to se ...
... Earth is thrown off its regular orbit, and made to plunge to the Sun and burn up, or made to escape far from the Sun where the Earth and everything on its surface would freeze permanently without the heat of the Sun’s rays? We have to solve the threebody problem of the Earth, Venus and the Sun to se ...
Unit 1: The Chemistry of Life.docx
... (1) Given a graph of one of the kinematic quantities, position, velocity, or acceleration, as a function of time, can students recognize in what time intervals the other two are positive, negative, or zero and can students identify or sketch a graph of each as a function of time? (2) Given an expres ...
... (1) Given a graph of one of the kinematic quantities, position, velocity, or acceleration, as a function of time, can students recognize in what time intervals the other two are positive, negative, or zero and can students identify or sketch a graph of each as a function of time? (2) Given an expres ...
Galct12E2
... the Galactica software. So, below are the results obtained with its help, and the system Galactica is proposed for free access. 2. Differential equations of body’s motion and method of their solution According to the law of Newton’s gravity, the attraction force to the body numbered i by the body nu ...
... the Galactica software. So, below are the results obtained with its help, and the system Galactica is proposed for free access. 2. Differential equations of body’s motion and method of their solution According to the law of Newton’s gravity, the attraction force to the body numbered i by the body nu ...
PHYS 307 LECTURE NOTES, Daniel W. Koon, St. Lawrence Univ.
... that it allows you to begin to translate a word problem into a mathematics problem. Draw a picture of whatever situation you are considering and label it with everything that you are given, converting the word descriptions into short mathematical expressions. For a problem that you wish to consider ...
... that it allows you to begin to translate a word problem into a mathematics problem. Draw a picture of whatever situation you are considering and label it with everything that you are given, converting the word descriptions into short mathematical expressions. For a problem that you wish to consider ...
Physics 41 HW Set 1 Chapter 15
... its equilibrium position (the origin of the x axis). The object is now released from rest with an initial position of xi = 0.200 m, and it subsequently undergoes simple harmonic oscillations. Find (a) the force constant of the spring, (b) the frequency of the oscillations, and (c) the maximum speed ...
... its equilibrium position (the origin of the x axis). The object is now released from rest with an initial position of xi = 0.200 m, and it subsequently undergoes simple harmonic oscillations. Find (a) the force constant of the spring, (b) the frequency of the oscillations, and (c) the maximum speed ...
Physics C: Mechanics - Piscataway High School
... 2. Understand the work-energy theorem so they can: (a) Calculate the change in kinetic energy or speed that results from performing a specified amount of work on a body. (b) Calculate the work performed by the net force, or by each of the forces that makes up the net force, on a body that undergoes ...
... 2. Understand the work-energy theorem so they can: (a) Calculate the change in kinetic energy or speed that results from performing a specified amount of work on a body. (b) Calculate the work performed by the net force, or by each of the forces that makes up the net force, on a body that undergoes ...