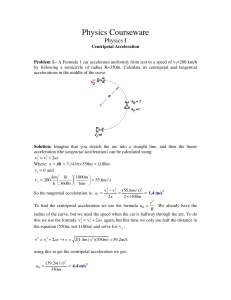
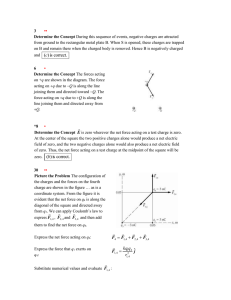
2 The slides about friction are in lecture 8!! 3 TRIGONOMETRY
... • If you are unsure about an equation that you want to use, perform the dimensional analysis and make sure that each part of the equation that is set equal/subtracted/added have the same dimensions ...
... • If you are unsure about an equation that you want to use, perform the dimensional analysis and make sure that each part of the equation that is set equal/subtracted/added have the same dimensions ...
Chapter 2 KINETICS OF PARTICLES: NEWTON`S SECOND LAW
... repulsive — describes a force that tends to push the two participating objects apart attractive — describes a force that tends to pull the two participating objects together oblique — describes a force that acts at some other angle, one that is not a direct repulsion or attraction normal force — th ...
... repulsive — describes a force that tends to push the two participating objects apart attractive — describes a force that tends to pull the two participating objects together oblique — describes a force that acts at some other angle, one that is not a direct repulsion or attraction normal force — th ...
Lorma Colleges City of San Fernando (LU) College of Arts and
... cultural backgrounds, values, practices and beliefs that would make them productive and successful in all undertakings as to become essential in the society where they belong. OBJECTIVES of COLLEGE OF ARTS AND SCIENCES: 1. To provide for a general education that will assist each individual in the pe ...
... cultural backgrounds, values, practices and beliefs that would make them productive and successful in all undertakings as to become essential in the society where they belong. OBJECTIVES of COLLEGE OF ARTS AND SCIENCES: 1. To provide for a general education that will assist each individual in the pe ...
Gravitational Forces
... This is how we put satellites into orbit around the Earth. We say that satellites are in Free Fall around the Earth. This is why astronauts experience weightlessness while orbitting the Earth, they are falling around the Earth!!! It is NOT because there is no gravity!!!!!! We can say the Moon is fa ...
... This is how we put satellites into orbit around the Earth. We say that satellites are in Free Fall around the Earth. This is why astronauts experience weightlessness while orbitting the Earth, they are falling around the Earth!!! It is NOT because there is no gravity!!!!!! We can say the Moon is fa ...
Document
... equation (1) and solve for V : Use conservation of mechanical energy to relate the kinetic energies of translation and rotation before and after the elastic collision: Substitute (2) and (3) in (4) and simplify to obtain: Solve for d: ...
... equation (1) and solve for V : Use conservation of mechanical energy to relate the kinetic energies of translation and rotation before and after the elastic collision: Substitute (2) and (3) in (4) and simplify to obtain: Solve for d: ...
6. Newton`s Laws of Motion.nb
... detail and by observation he discovered three laws of planetary motion. i) The motion of the planets about the Sun is elliptical with the Sun at one focus. ii) Equal areas are swept out in equal times: planets when closer to the Sun move faster. iii) The period T of the orbit of a planet is related ...
... detail and by observation he discovered three laws of planetary motion. i) The motion of the planets about the Sun is elliptical with the Sun at one focus. ii) Equal areas are swept out in equal times: planets when closer to the Sun move faster. iii) The period T of the orbit of a planet is related ...
James Clerk Maxwell (1831 - 1879)
... volved in the electromagnetic interactions. Some of the charges – called the source charges – have fixed and given dynamics and can be used to compute the electric and magnetic fields in a region of interest: that is, given ρ and J , one uses (8.1)) to find E and B. The remaining charges of interest ...
... volved in the electromagnetic interactions. Some of the charges – called the source charges – have fixed and given dynamics and can be used to compute the electric and magnetic fields in a region of interest: that is, given ρ and J , one uses (8.1)) to find E and B. The remaining charges of interest ...
Lecture 18
... of where we’ve put the axis of rotation, though we haven’t actually changed the masses! But what if we don’t have point masses to deal with? What if we have solid objects? It actually requires calculus to do this, so we’ve given you a table of objects to deal with (p.278). If you needed one of these ...
... of where we’ve put the axis of rotation, though we haven’t actually changed the masses! But what if we don’t have point masses to deal with? What if we have solid objects? It actually requires calculus to do this, so we’ve given you a table of objects to deal with (p.278). If you needed one of these ...
7th gd Forces
... • Velocity – measured in meters per second (m/s) • Momentum – measured in kilogram meters per second (kg·m/s) • Described by its direction as well as its quantity • An objects momentum is the same direction as it’s ...
... • Velocity – measured in meters per second (m/s) • Momentum – measured in kilogram meters per second (kg·m/s) • Described by its direction as well as its quantity • An objects momentum is the same direction as it’s ...
Newtons Law of Motion
... Imagine a block of iron resting on the surface of the Earth as seen in Figure 3. The block applies a downward force f g due to the gravitational attraction of the Earth. The magnitude of the force is mg , where m is the mass of the block and g is the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the ...
... Imagine a block of iron resting on the surface of the Earth as seen in Figure 3. The block applies a downward force f g due to the gravitational attraction of the Earth. The magnitude of the force is mg , where m is the mass of the block and g is the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the ...
r - TTU Physics
... Δθ 2π(a/b) (a, b integers) periodic, closed orbit. • If the orbit is closed, after b periods, the radius vector the of particle will have made a complete revolutions & the particle will be at its original position. • It can be shown (Prob. 8.35) that if the potential is a power law in r: U(r) = ...
... Δθ 2π(a/b) (a, b integers) periodic, closed orbit. • If the orbit is closed, after b periods, the radius vector the of particle will have made a complete revolutions & the particle will be at its original position. • It can be shown (Prob. 8.35) that if the potential is a power law in r: U(r) = ...