Anatomy Info Pack. - Keswick School PE Department.
... Muscles tend to be composed of both types of fibres, although the amounts may vary from muscle to muscle and from person to person. Top endurance athletes have a greater proportion of slow twitch fibres whereas sprinters and power athletes have more fast twitch fibres. Team sports players often have ...
... Muscles tend to be composed of both types of fibres, although the amounts may vary from muscle to muscle and from person to person. Top endurance athletes have a greater proportion of slow twitch fibres whereas sprinters and power athletes have more fast twitch fibres. Team sports players often have ...
how exercise builds muscle
... which muscle cells respond biochemically to mechanical stress by becoming stronger and thicker. The University College researchers themselves view their discovery with a mixture of enthusiasm and uneasiness. On the one hand, the findings could be invaluable for treating muscular dystrophy and possib ...
... which muscle cells respond biochemically to mechanical stress by becoming stronger and thicker. The University College researchers themselves view their discovery with a mixture of enthusiasm and uneasiness. On the one hand, the findings could be invaluable for treating muscular dystrophy and possib ...
Physiology
... from a single motor unit, but rather we are recording from multiple cells/fibrils that: – Each generate an AP – The AP’s do not have to be in phase – Some may fire multiple times…others only once – The amplitudes of the AP’s can be different, too – The position of the ...
... from a single motor unit, but rather we are recording from multiple cells/fibrils that: – Each generate an AP – The AP’s do not have to be in phase – Some may fire multiple times…others only once – The amplitudes of the AP’s can be different, too – The position of the ...
Sample 2 Core 2 Summary (Syllabus pre 2010)
... Examples: marathon, long distance walking, netball triathlon ...
... Examples: marathon, long distance walking, netball triathlon ...
Circulatory System - Total Care International
... to do. Smooth muscle tissue is commonly found in hollow organs such as the stomach, the bladder, and the respiratory passages. Smooth muscles tissue main function is to propel objects down a certain path. Smooth muscle tissue is spindle shaped. Smooth muscle tissue is arranged in sheets or layers. T ...
... to do. Smooth muscle tissue is commonly found in hollow organs such as the stomach, the bladder, and the respiratory passages. Smooth muscles tissue main function is to propel objects down a certain path. Smooth muscle tissue is spindle shaped. Smooth muscle tissue is arranged in sheets or layers. T ...
The Human Body: An Orientation
... The apparent complexity of the human body represents multiple levels of organization. Each level is more complex than the previous level, but all can be broken down into similar ...
... The apparent complexity of the human body represents multiple levels of organization. Each level is more complex than the previous level, but all can be broken down into similar ...
1. Maxillary bone 2. Maxillary teeth 3. Mandibular arch 4. Vomerine
... Cerebellum (metencephalon) (97) That part of the brain which coordinates muscular activity. Cerebral lobes (93) That part of the brain which in higher animals is the center for memory and learning. It is relatively small in the frog. Cloaca (55) The posterior most part of the large intestine. It act ...
... Cerebellum (metencephalon) (97) That part of the brain which coordinates muscular activity. Cerebral lobes (93) That part of the brain which in higher animals is the center for memory and learning. It is relatively small in the frog. Cloaca (55) The posterior most part of the large intestine. It act ...
Supplemental notes in pdf
... The brain is the control center of our bodies, consisting of 100 billion nerve cells (neurons) that transmit electrical information along the neuronal axon using action potentials that are driven by changes in charge distribution across the plasma membrane. The key to these electrical impulses are i ...
... The brain is the control center of our bodies, consisting of 100 billion nerve cells (neurons) that transmit electrical information along the neuronal axon using action potentials that are driven by changes in charge distribution across the plasma membrane. The key to these electrical impulses are i ...
Document
... 3. Other functions of the cell such as protein expression Note that during heavy activity, cross-bridges formation is the main drain on ATP stores in muscle cell. Rate and amount of ATP consumption varies with the intensity and duration of the exercise ...
... 3. Other functions of the cell such as protein expression Note that during heavy activity, cross-bridges formation is the main drain on ATP stores in muscle cell. Rate and amount of ATP consumption varies with the intensity and duration of the exercise ...
Unit 3 - Energy Systems and Muscle Fibres
... We have different types of muscle fibres in our body and each type of muscle fibre is more adapted to a certain energy system. Slow Twitch Muscle Fibres ▪ Generate and relax tension slowly but are able to maintain lower levels of tension for a long period of ...
... We have different types of muscle fibres in our body and each type of muscle fibre is more adapted to a certain energy system. Slow Twitch Muscle Fibres ▪ Generate and relax tension slowly but are able to maintain lower levels of tension for a long period of ...
Max ARM PDS pg1
... Each serving of Max ARM provides 32 grams of multi-source carbohydrates with rapid to extended absorption rates including, waxy maize starch (amylopectin), maltodextrin, fructose and dextrose. Max ARM provides the ideal forms and amounts of carbohydrates to pack glycogen in muscles for maximum recov ...
... Each serving of Max ARM provides 32 grams of multi-source carbohydrates with rapid to extended absorption rates including, waxy maize starch (amylopectin), maltodextrin, fructose and dextrose. Max ARM provides the ideal forms and amounts of carbohydrates to pack glycogen in muscles for maximum recov ...
Cricket – Intercostal Injuries (Sidestrain)
... internal oblique muscle is likely to rupture. A similar mechanism can be proposed for other throwing sports [7, 8]. A high percentage of type II or fast twitch fibers may also be a predisposing factor to tearing [9, 10]. The mechanism for injury in rowing is different: the shoulder is behind the hip ...
... internal oblique muscle is likely to rupture. A similar mechanism can be proposed for other throwing sports [7, 8]. A high percentage of type II or fast twitch fibers may also be a predisposing factor to tearing [9, 10]. The mechanism for injury in rowing is different: the shoulder is behind the hip ...
Physiology of Training #1
... • the training effect is specific to the – tissue or system stressed (eg. Arms do not adapt to cycling stimulus) – the mode of stress imposed (eg. Strength training does not result in endurance adaptations) – eg. Run training vs. Cycle training and LT (58% & 20% vs. 39% alone) ...
... • the training effect is specific to the – tissue or system stressed (eg. Arms do not adapt to cycling stimulus) – the mode of stress imposed (eg. Strength training does not result in endurance adaptations) – eg. Run training vs. Cycle training and LT (58% & 20% vs. 39% alone) ...
Musculoskeletal notes (Human Body I)
... bones have many functions a. provide a rigid framework for muscles to pull against b. give shape and structure to the body c. protect delicate internal organs d. store minerals such as calcium and phosphorus i. bones are actually dynamic—they store calcium until it is needed for metabolic function, ...
... bones have many functions a. provide a rigid framework for muscles to pull against b. give shape and structure to the body c. protect delicate internal organs d. store minerals such as calcium and phosphorus i. bones are actually dynamic—they store calcium until it is needed for metabolic function, ...
Molecular Motors
... http://programs.northlandcollege.edu/biology/Biology1111 /animations/flagellum.html ...
... http://programs.northlandcollege.edu/biology/Biology1111 /animations/flagellum.html ...
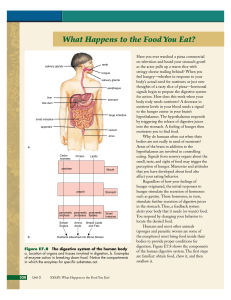
What Happens to the Food You Eat?
... the muscle again. That is, when a muscle relaxes, it cannot return to its normal length by itself. Because a muscle cannot lengthen, a muscle cannot push on anything. It can only pull. For every set of muscles that pulls a limb bone in one direction, another set pulls it back the other way. Were tha ...
... the muscle again. That is, when a muscle relaxes, it cannot return to its normal length by itself. Because a muscle cannot lengthen, a muscle cannot push on anything. It can only pull. For every set of muscles that pulls a limb bone in one direction, another set pulls it back the other way. Were tha ...
chapter 4: bone, muscle, and connective tissue adaptations
... Number of repetitions is not a significant stimulus (more is not better). Look at page ...
... Number of repetitions is not a significant stimulus (more is not better). Look at page ...
St Peter the Apostle High School BIOLOGY DEPARTMENT
... C They are better for activities like weightlifting and sprinting than fast twitch fibres. D They store fuel mainly as glycogen while fast twitch muscle fibres store fuel as fat. ...
... C They are better for activities like weightlifting and sprinting than fast twitch fibres. D They store fuel mainly as glycogen while fast twitch muscle fibres store fuel as fat. ...
BE112A Topic 1: Introduction to Biomechanics
... Cardiac muscle fibers (cells) are short and rod-shaped but are connected by intercalated disks and collagen matrix into a spiral-wound laminar fibrous architecture The cardiac sarcomere is similar to the skeletal muscle sarcomere Cardiac muscle has a very slow twitch but it can not be tetanized beca ...
... Cardiac muscle fibers (cells) are short and rod-shaped but are connected by intercalated disks and collagen matrix into a spiral-wound laminar fibrous architecture The cardiac sarcomere is similar to the skeletal muscle sarcomere Cardiac muscle has a very slow twitch but it can not be tetanized beca ...
Winter 2014 Colloquium Posters
... “Acylcarnitines and inherited disorders of fatty acid oxidation: From clinical diagnostics to active players driving inflammation and myopathy.” ...
... “Acylcarnitines and inherited disorders of fatty acid oxidation: From clinical diagnostics to active players driving inflammation and myopathy.” ...
Point:Counterpoint Comments The following letters are in response
... contraction may augment force production by relieving inhibition of excitation-contraction coupling processes at the sarcolemma, SR and contractile apparatus. The reductionist approaches give insight to mechanisms that may be involved in the regulation of cellular processes, but the results are init ...
... contraction may augment force production by relieving inhibition of excitation-contraction coupling processes at the sarcolemma, SR and contractile apparatus. The reductionist approaches give insight to mechanisms that may be involved in the regulation of cellular processes, but the results are init ...
Lecture 4
... Overview of blood glucose regulation and the consequences of dysregulation 1. Glucose ---- obligatory fuel for CNS and RBC’s Liver Storage ----> ~100gms (~400kcals) Whole body oxidation of glucose ------> ~160-200gms/day (basal condition) CNS ------> ~70 -75% (~120gms) Consequences Depletion of hepa ...
... Overview of blood glucose regulation and the consequences of dysregulation 1. Glucose ---- obligatory fuel for CNS and RBC’s Liver Storage ----> ~100gms (~400kcals) Whole body oxidation of glucose ------> ~160-200gms/day (basal condition) CNS ------> ~70 -75% (~120gms) Consequences Depletion of hepa ...