Chapter 4 Sports-Injury Prevention Sport Injury Prevention
... • Identify any preexisting conditions that may make the athlete vulnerable to specific medical problems. • For example, sickle cell trait, diabetes, epilepsy, and drug allergies • Absence of paired organ (e.g., eyes, kidney) is a complex issue and a number of variables must be considered including t ...
... • Identify any preexisting conditions that may make the athlete vulnerable to specific medical problems. • For example, sickle cell trait, diabetes, epilepsy, and drug allergies • Absence of paired organ (e.g., eyes, kidney) is a complex issue and a number of variables must be considered including t ...
Muscle
... spanning the space between the T tubules and the sarcoplasmic reticulum to produce the calcium transient responsible for allowing contraction. ...
... spanning the space between the T tubules and the sarcoplasmic reticulum to produce the calcium transient responsible for allowing contraction. ...
7vitamin-and-minerals
... Choline is used up during exercise in the production of acetylcholine Recommended Choline intake is often found in nutritional diets, but is found in foods such as egg yolk, nuts and spinach if more is needed Minerals and Performance Part 2 Natural minerals are extremely important to exercisers ...
... Choline is used up during exercise in the production of acetylcholine Recommended Choline intake is often found in nutritional diets, but is found in foods such as egg yolk, nuts and spinach if more is needed Minerals and Performance Part 2 Natural minerals are extremely important to exercisers ...
Chapter 13
... program are related to the following: a lower O2 deficit, and increased utilization of FFA and a sparing of blood glucose and muscle glycogen, a reduction in lactate and H+ formation, and an increase in lactate removal • Discuss how changes in “central command” and “peripheral feedback” following an ...
... program are related to the following: a lower O2 deficit, and increased utilization of FFA and a sparing of blood glucose and muscle glycogen, a reduction in lactate and H+ formation, and an increase in lactate removal • Discuss how changes in “central command” and “peripheral feedback” following an ...
How Much Protein? - Hammer Nutrition
... Research confirms that rate of recovery and muscle synthesis rate are dramatically increased if amino acids and carbohydrates is consumed together immediately after the exercise training. Intense training may increase dietary protein requirements to as high as 1.7 grams protein per kilogram bodyweig ...
... Research confirms that rate of recovery and muscle synthesis rate are dramatically increased if amino acids and carbohydrates is consumed together immediately after the exercise training. Intense training may increase dietary protein requirements to as high as 1.7 grams protein per kilogram bodyweig ...
Ch47_Lecture
... Proportion of fast- and slow-twitch fibers in skeletal muscles is determined mostly by genetic heritage. ...
... Proportion of fast- and slow-twitch fibers in skeletal muscles is determined mostly by genetic heritage. ...
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) and Metabolic Systems (cont`d)
... acidosis. Higher lactate concentrations are seen following anaerobic training with concomitant improvements in performance. Enhanced buffer capacity prolongs high-intensity exercise. Trained individuals have a greater buffer capacity than untrained individuals. Muscle buffer capacity may increase by ...
... acidosis. Higher lactate concentrations are seen following anaerobic training with concomitant improvements in performance. Enhanced buffer capacity prolongs high-intensity exercise. Trained individuals have a greater buffer capacity than untrained individuals. Muscle buffer capacity may increase by ...
Sports nutrition - Healthy Hearts Nutrition, LLC
... Acts as a diuretic by increasing urine volume and interfering with rehydration ...
... Acts as a diuretic by increasing urine volume and interfering with rehydration ...
PP - Chemistry Courses: About
... • Non-enzymatic glycosylation • Sorbitol production leads to tissue damage • Drugs aimed at undoing metabolic problems • Metformin – Activates AMPK » Suppress gluconeogenesis – Activates glucose and fatty acid uptake in muscle ...
... • Non-enzymatic glycosylation • Sorbitol production leads to tissue damage • Drugs aimed at undoing metabolic problems • Metformin – Activates AMPK » Suppress gluconeogenesis – Activates glucose and fatty acid uptake in muscle ...
Energy Systems for Exercise
... Oral Cr increases muscle C~P 3g/d over time = 20g/d loading “Exercise performance involving short periods of extremely powerful activity can be enhanced, especially during repeated bouts of activity.” ...
... Oral Cr increases muscle C~P 3g/d over time = 20g/d loading “Exercise performance involving short periods of extremely powerful activity can be enhanced, especially during repeated bouts of activity.” ...
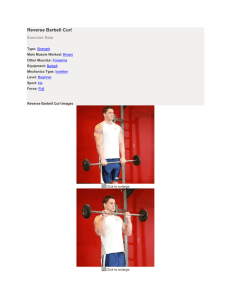
Reverse Barbell Curl Exercise Data :
... The palm of your hands should be facing down (pronated grip). This will be your starting position. While holding the upper arms stationary, curl the weights while contracting the biceps as you breathe out. Only the forearms should move. Continue the movement until your biceps are fully contracted an ...
... The palm of your hands should be facing down (pronated grip). This will be your starting position. While holding the upper arms stationary, curl the weights while contracting the biceps as you breathe out. Only the forearms should move. Continue the movement until your biceps are fully contracted an ...
Gene–Nutrition Interaction in Human Performance and Exercise
... upregulated in exercising skeletal muscle. Richter et al.23 reported that a single exercise bout can alter glucose transport and insulin sensitivity in skeletal muscle of rats, and subsequent work has confirmed these findings in humans.26 Use of specific fuel types can be enhanced by exercise, and t ...
... upregulated in exercising skeletal muscle. Richter et al.23 reported that a single exercise bout can alter glucose transport and insulin sensitivity in skeletal muscle of rats, and subsequent work has confirmed these findings in humans.26 Use of specific fuel types can be enhanced by exercise, and t ...
Energy Systems for Exercise
... Oral Cr increases muscle C~P 3g/d over time = 20g/d loading “Exercise performance involving short periods of extremely powerful activity can be enhanced, especially during repeated bouts of activity.” ...
... Oral Cr increases muscle C~P 3g/d over time = 20g/d loading “Exercise performance involving short periods of extremely powerful activity can be enhanced, especially during repeated bouts of activity.” ...
Chapter #4
... • Obese is defined as the 95th percentile or higher."Extreme obesity is defined as 120% of the 95th percentile for weight for age and sex” • For a 10-year-old boy or girl, you would expect him or her to weigh about 70 pounds." If the child weighs 140 pounds, that would be extreme obesity, she ...
... • Obese is defined as the 95th percentile or higher."Extreme obesity is defined as 120% of the 95th percentile for weight for age and sex” • For a 10-year-old boy or girl, you would expect him or her to weigh about 70 pounds." If the child weighs 140 pounds, that would be extreme obesity, she ...
glycogen disappears
... • In the liver, its major function is to provide glucose for extrahepatic tissues. In muscle, it serves mainly as a ready source of metabolic fuel for use in muscle. • Glycogen is synthesized from glucose by the pathway of glycogenesis. It is broken down by a separate pathway known as glycogenolysis ...
... • In the liver, its major function is to provide glucose for extrahepatic tissues. In muscle, it serves mainly as a ready source of metabolic fuel for use in muscle. • Glycogen is synthesized from glucose by the pathway of glycogenesis. It is broken down by a separate pathway known as glycogenolysis ...
HS 200 Continue with electronic journal entries
... –Spina Bifida (defects of spine) –Anencephaly (defects of brain) –Up to 70% of Neural tube Defects (NFD’s) could be prevented -400 micrograms of folic acid BEFORE and during pregnancy. Glycemic Index •Distinguishing between good and bad starches. The glycemic index (GI) is a ranking of carbohydrates ...
... –Spina Bifida (defects of spine) –Anencephaly (defects of brain) –Up to 70% of Neural tube Defects (NFD’s) could be prevented -400 micrograms of folic acid BEFORE and during pregnancy. Glycemic Index •Distinguishing between good and bad starches. The glycemic index (GI) is a ranking of carbohydrates ...
Berry Malynn Berry Dr. Bert Ely Genetics 303 6 November 2009
... comparing vascular smooth muscle cells from mutant and from wild type mice in culture, the researchers determined that the cells in the mutant mice were noticeably smaller than those of wild type mice. The cells of the mutants also showed fewer actin fibers within highly organized stress fibers. The ...
... comparing vascular smooth muscle cells from mutant and from wild type mice in culture, the researchers determined that the cells in the mutant mice were noticeably smaller than those of wild type mice. The cells of the mutants also showed fewer actin fibers within highly organized stress fibers. The ...
The Dancer in Training
... Dance tends to use mostly anaerobic activity – during technique class, performing repetitive movements will improve muscular endurance. However some choreographers may also place vigorous demands on the dancer’s aerobic endurance. This will result in progressive overload on the muscles and cardiovas ...
... Dance tends to use mostly anaerobic activity – during technique class, performing repetitive movements will improve muscular endurance. However some choreographers may also place vigorous demands on the dancer’s aerobic endurance. This will result in progressive overload on the muscles and cardiovas ...
Protection, Support, and Locomotion
... white blood cells, and cell fragments involved in blood clotting Yellow marrow- found in many other bones, consist of stored fat ...
... white blood cells, and cell fragments involved in blood clotting Yellow marrow- found in many other bones, consist of stored fat ...
2008 Review
... 5. Distinguish between the terms autocrine and exocrine. How is a pheromone different? 6. How are release of hormones and neurotransmitters functionally similar? 7. What is one reason that hormones have been historically difficult to study? 8. Is testosterone an amine hormone or a steroid hormone? H ...
... 5. Distinguish between the terms autocrine and exocrine. How is a pheromone different? 6. How are release of hormones and neurotransmitters functionally similar? 7. What is one reason that hormones have been historically difficult to study? 8. Is testosterone an amine hormone or a steroid hormone? H ...
Document
... Anaerobic metabolic processes have the capacity to provide ATP energy immediately but only for a short duration, while aerobic metabolic processes begin providing ATP energy more slowly but for long durations, provided there is sufficient substrate and oxygen available to the cells. We have large st ...
... Anaerobic metabolic processes have the capacity to provide ATP energy immediately but only for a short duration, while aerobic metabolic processes begin providing ATP energy more slowly but for long durations, provided there is sufficient substrate and oxygen available to the cells. We have large st ...