Biology 6 Test 2 Study Guide
... i. E. coli has 4.6 million bp. This is about 1 mistake in 250 cells replicated. ii. Each gene has about 1000 bp and with 1/109 mistakes, 1/106 chance a gene will be mutated every replication. iii. Theory is that mistakes are allowed for evolution to occur. e. Creating and selecting mutants i. Negati ...
... i. E. coli has 4.6 million bp. This is about 1 mistake in 250 cells replicated. ii. Each gene has about 1000 bp and with 1/109 mistakes, 1/106 chance a gene will be mutated every replication. iii. Theory is that mistakes are allowed for evolution to occur. e. Creating and selecting mutants i. Negati ...
Genetic Technology
... Insertion into a vector • If a plasmid and foreign DNA have been cleaved with the same restriction enzyme, the ends of each will match and they will join together, reconnecting the plasmid ring. • The foreign DNA is recombined into a plasmid or viral DNA with the help of a second enzyme. ...
... Insertion into a vector • If a plasmid and foreign DNA have been cleaved with the same restriction enzyme, the ends of each will match and they will join together, reconnecting the plasmid ring. • The foreign DNA is recombined into a plasmid or viral DNA with the help of a second enzyme. ...
Partial Sequence Analysis of the 5S to 18S rRNA Gene Region of
... different from the rRNA genes of the chloroplast and nucleus in maize. In spite of the close eubacterial homology observed in the 18S sequence, the organization of rRNA genes is also different from the prokaryotic prototype. Earlier, Gray and Doolittle (1 1) argued that the strongest evidence for th ...
... different from the rRNA genes of the chloroplast and nucleus in maize. In spite of the close eubacterial homology observed in the 18S sequence, the organization of rRNA genes is also different from the prokaryotic prototype. Earlier, Gray and Doolittle (1 1) argued that the strongest evidence for th ...
HW7 key - WordPress.com
... (b) Suppose a motif occurs once on average in the genome. You can model this as a binomial distribution with 3 × 109 attempts and a success rate of p per attempt. What is p? Modeling this process as binomial distributions assumes that we have 3 × 109 attempts; i.e. 3 × 109 observations of motifs of ...
... (b) Suppose a motif occurs once on average in the genome. You can model this as a binomial distribution with 3 × 109 attempts and a success rate of p per attempt. What is p? Modeling this process as binomial distributions assumes that we have 3 × 109 attempts; i.e. 3 × 109 observations of motifs of ...
The Mitochondrial Genome of Chara vulgaris
... Département de Biochimie et de Microbiologie, Université Laval, Québec, Québec G1K 7P4, Canada ...
... Département de Biochimie et de Microbiologie, Université Laval, Québec, Québec G1K 7P4, Canada ...
Exhibit Guide for Grades 6-9 - Museum of Science and Industry
... Wonder: After the Spark activities (used as introductions to the 5 areas of the exhibit) are complete, divide your students into 5 groups. Each group is assigned one of the Genetics topics and is given the article that relates to that component of the exhibit. For example, the Cloning group will rea ...
... Wonder: After the Spark activities (used as introductions to the 5 areas of the exhibit) are complete, divide your students into 5 groups. Each group is assigned one of the Genetics topics and is given the article that relates to that component of the exhibit. For example, the Cloning group will rea ...
Biology 30 - Patricia Schwandt Courses
... Since it is only possible to make 16 different codons if two nucleotides are used for each (4x4=16), there must be at least three nucleotides in each codon. This means that there are 64 possible combinations (4x4x4). A series of biochemical studies in the early 1960’s confirmed this number, and also ...
... Since it is only possible to make 16 different codons if two nucleotides are used for each (4x4=16), there must be at least three nucleotides in each codon. This means that there are 64 possible combinations (4x4x4). A series of biochemical studies in the early 1960’s confirmed this number, and also ...
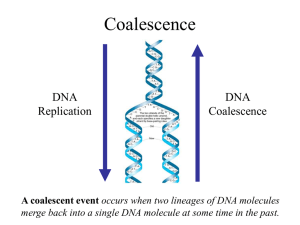
t - nslc.wustl.edu
... • In practice, real populations are not ideal, so pretend the population is ideal but with an “inbreeding effective size” of an idealized population of size Nef♀; Therefore, the prob. of coalescence in one generation is 1/(Nef♀) ...
... • In practice, real populations are not ideal, so pretend the population is ideal but with an “inbreeding effective size” of an idealized population of size Nef♀; Therefore, the prob. of coalescence in one generation is 1/(Nef♀) ...
The amount if DNA in each human cell nucleus is
... generally have no effect on a gene’s protein product. Since there are so many transposons in every cell, and since insertions into exons can have serious consequences, it is often asked if transposons can have any benefits. One school of thought is that the many transposon copies increase the probab ...
... generally have no effect on a gene’s protein product. Since there are so many transposons in every cell, and since insertions into exons can have serious consequences, it is often asked if transposons can have any benefits. One school of thought is that the many transposon copies increase the probab ...
Construction of a Fibrobacter succinogenes Genomic Map and
... the genome were determined by combining two approaches: isolation of linking clones and crosshybridization of restriction fragments. The genome of F. succinogenes was found to be represented by the single circular DNA molecule. Southern hybridization with specific probes allowed the eight genetic ma ...
... the genome were determined by combining two approaches: isolation of linking clones and crosshybridization of restriction fragments. The genome of F. succinogenes was found to be represented by the single circular DNA molecule. Southern hybridization with specific probes allowed the eight genetic ma ...
source file
... Explore the imgACT web portal • All students will be assigned at least one gene, which should be used to navigate through the imgACT online lab notebook (Modules #1 – 8) and the lab report • Note that students are not responsible for annotating this gene. It may be used to help students get used to ...
... Explore the imgACT web portal • All students will be assigned at least one gene, which should be used to navigate through the imgACT online lab notebook (Modules #1 – 8) and the lab report • Note that students are not responsible for annotating this gene. It may be used to help students get used to ...
Midterm #1 Study Guide
... What is the difference between mitosis and meiosis? Where do these processes occur? What are the results from each? Proteins associated with DNA in eukaryotes are called ______. Histone–DNA units are called _______. Chromatids that are attached at the centromere are called what kind of chromatids? ...
... What is the difference between mitosis and meiosis? Where do these processes occur? What are the results from each? Proteins associated with DNA in eukaryotes are called ______. Histone–DNA units are called _______. Chromatids that are attached at the centromere are called what kind of chromatids? ...
Mutation is (Not) Random
... There are several different types of randomness, and each of them has slightly different meanings and sometimes drastically different implications. All of them involve some sense of unpredictability, but that is as far as they are similar. We will look at three different kinds of randomness. Probab ...
... There are several different types of randomness, and each of them has slightly different meanings and sometimes drastically different implications. All of them involve some sense of unpredictability, but that is as far as they are similar. We will look at three different kinds of randomness. Probab ...
Preparation of SCRATCHY Hybrid Protein Libraries
... hybrids can be of interest to the studies of fundamental questions of protein evolution and folding, as well as to the tailoring of enzymes for therapeutic and industrial applications. The experimental implementation of SCRATCHY consists of two successive steps, an initial creation of an ITCHY libra ...
... hybrids can be of interest to the studies of fundamental questions of protein evolution and folding, as well as to the tailoring of enzymes for therapeutic and industrial applications. The experimental implementation of SCRATCHY consists of two successive steps, an initial creation of an ITCHY libra ...
Molecular methods for bacterial genotyping
... The 16S rRNA gene rRNA genes are the essential genes for the survival of all organisms due to their role in protein synthesis.1 The 16S rRNA gene is about 1500 bp long and it is a composed of well conserved 10 regions and 10 divergent regions.4 There is a constant mutation rate of about 1% per 50 ye ...
... The 16S rRNA gene rRNA genes are the essential genes for the survival of all organisms due to their role in protein synthesis.1 The 16S rRNA gene is about 1500 bp long and it is a composed of well conserved 10 regions and 10 divergent regions.4 There is a constant mutation rate of about 1% per 50 ye ...
ch. 12 Biotechnology-notes-ppt
... transforming agriculture • New genetic varieties of animals and plants are being produced – A plant with a new trait can be created using the Ti plasmid ...
... transforming agriculture • New genetic varieties of animals and plants are being produced – A plant with a new trait can be created using the Ti plasmid ...
Mutations - GK-12 Program at the University of Houston
... by their effect on the structure of DNA or a chromosome. For this categorization, mutations can be separated into two main groups, each with multiple specific types. The two general categories are large-scale and small-scale mutations. Small-Scale Mutations Small-scale mutations are those which effe ...
... by their effect on the structure of DNA or a chromosome. For this categorization, mutations can be separated into two main groups, each with multiple specific types. The two general categories are large-scale and small-scale mutations. Small-Scale Mutations Small-scale mutations are those which effe ...
Intraspecies variation in bacterial genomes: the need for a
... whole genes or clusters of mapping, genomic subtraction and this all-important sequence, genes. In most eukaryotes, an complete genome sequencing. Genes can but that is expensive and has individual genome sequence also be lost in response to selection or by only been completed for two will provide u ...
... whole genes or clusters of mapping, genomic subtraction and this all-important sequence, genes. In most eukaryotes, an complete genome sequencing. Genes can but that is expensive and has individual genome sequence also be lost in response to selection or by only been completed for two will provide u ...
Biology STAAR EOC Fall 2011
... evidence of how microorganisms work to maintain homeostasis in organisms and ecosystems in the following: plants, humans, and the environment. TEK 11D: Describe how events and processes that occur during ecological succession can change population and species diversity. (Readiness Standard) 39. Pick ...
... evidence of how microorganisms work to maintain homeostasis in organisms and ecosystems in the following: plants, humans, and the environment. TEK 11D: Describe how events and processes that occur during ecological succession can change population and species diversity. (Readiness Standard) 39. Pick ...
The role of DNA damage in laminopathy progeroid syndromes
... compared with wild-type MEFs, in which telomeres were distributed throughout the nucleus. This abnormal distribution of telomeric DNA was correlated with a modest, but significant, shortening of telomere length, but highly significantly impaired H4 methylation and accumulation of H2AX in telomeric c ...
... compared with wild-type MEFs, in which telomeres were distributed throughout the nucleus. This abnormal distribution of telomeric DNA was correlated with a modest, but significant, shortening of telomere length, but highly significantly impaired H4 methylation and accumulation of H2AX in telomeric c ...
Lecture 35: Basics of DNA Cloning-I
... Type II restriction endonucleases are homodimeric polypeptide. These homodimer enzymes recognize short nucleotide sequences of about 4-8 bp known as restriction site and are usually palindromic in nature (Fig. 2). Most of the restriction enzymes used in molecular biology research are six base cutter ...
... Type II restriction endonucleases are homodimeric polypeptide. These homodimer enzymes recognize short nucleotide sequences of about 4-8 bp known as restriction site and are usually palindromic in nature (Fig. 2). Most of the restriction enzymes used in molecular biology research are six base cutter ...
Structure and function of DNA
... Explain why it is important that non-coding regions are removed from the primary transcript of this gene before translation. The wrong / extra amino acids are not placed in the protein / polypeptide formed OR so that the correct functional protein is formed ...
... Explain why it is important that non-coding regions are removed from the primary transcript of this gene before translation. The wrong / extra amino acids are not placed in the protein / polypeptide formed OR so that the correct functional protein is formed ...
DNA - Gene - Website Staff UI
... a mutant phenotype forward mutation. When a second mutation restores the original phenotype, the process is called reverse mutation. Reverse mutation may occur in two different ways, 1) by back mutation, a second mutation at the same site in the gene as the original mutation, restoring the wild ty ...
... a mutant phenotype forward mutation. When a second mutation restores the original phenotype, the process is called reverse mutation. Reverse mutation may occur in two different ways, 1) by back mutation, a second mutation at the same site in the gene as the original mutation, restoring the wild ty ...
dna extraction - Medical Research Council
... Every living thing contains DNA. It is the unique set of instructions that tells a seed how to grown into a plant or a baby into adult. Everyone’s DNA is different. DNA controls the colour of your eyes, skin and hair. DNA is wrapped tight inside the nucleus of every cell that builds a living thing. ...
... Every living thing contains DNA. It is the unique set of instructions that tells a seed how to grown into a plant or a baby into adult. Everyone’s DNA is different. DNA controls the colour of your eyes, skin and hair. DNA is wrapped tight inside the nucleus of every cell that builds a living thing. ...
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is only a small portion of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell; most of the DNA can be found in the cell nucleus and, in plants, in the chloroplast.In humans, mitochondrial DNA can be assessed as the smallest chromosome coding for 37 genes and containing approximately 16,600 base pairs. Human mitochondrial DNA was the first significant part of the human genome to be sequenced. In most species, including humans, mtDNA is inherited solely from the mother.The DNA sequence of mtDNA has been determined from a large number of organisms and individuals (including some organisms that are extinct), and the comparison of those DNA sequences represents a mainstay of phylogenetics, in that it allows biologists to elucidate the evolutionary relationships among species. It also permits an examination of the relatedness of populations, and so has become important in anthropology and field biology.