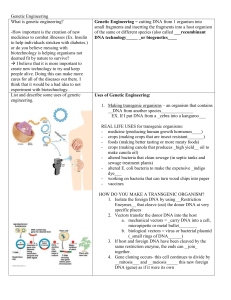
Genetic Engineering Guied Notes
... medicines to combat illnesses (Ex. Insulin to help individuals stricken with diabetes.) or do you believe messing with biotechnology is helping organisms not deemed fit by nature to survive? I believe that it is more important to create new technology to try and keep people alive. Doing this can m ...
... medicines to combat illnesses (Ex. Insulin to help individuals stricken with diabetes.) or do you believe messing with biotechnology is helping organisms not deemed fit by nature to survive? I believe that it is more important to create new technology to try and keep people alive. Doing this can m ...
Red Line - iPlant Pods
... – 19 students used Red Line to visualize next-gen RNA-Seq data to investigate presence/absence variation (PAV) in maize – 12 hours effort, each student group annotated 100 kb and then imported next-gen RNA-Seq data from 5 different tissues in 30 maize inbred lines for a gene that they had previously ...
... – 19 students used Red Line to visualize next-gen RNA-Seq data to investigate presence/absence variation (PAV) in maize – 12 hours effort, each student group annotated 100 kb and then imported next-gen RNA-Seq data from 5 different tissues in 30 maize inbred lines for a gene that they had previously ...
DNA …… solving the puzzle of life
... Replication is a very accurate process with very few errors. What is the key to this accuracy? Explain using a diagram. If there were many errors, what would be the problem? (Remember that genes often make proteins). How can we tell that an error has been ...
... Replication is a very accurate process with very few errors. What is the key to this accuracy? Explain using a diagram. If there were many errors, what would be the problem? (Remember that genes often make proteins). How can we tell that an error has been ...
Bulletin 1 - DNA: The Cookbook of Life - ctahr
... All living things contain DNA recipes and use them to make proteins. This amazing commonality across all forms of life has made possible many practical uses of our DNA knowledge, some of which have been widely embraced, and some of which remain controversial. Our next issue of Biotech In Focus will ...
... All living things contain DNA recipes and use them to make proteins. This amazing commonality across all forms of life has made possible many practical uses of our DNA knowledge, some of which have been widely embraced, and some of which remain controversial. Our next issue of Biotech In Focus will ...
name period ______ date
... 4. What is the name given to the point where replication starts on a DNA molecule? 5. How does the replicated daughter molecule of DNA compare to the parent molecule of DNA? 6. What would the complementary bases be if one side of a DNA molecule had the bases adenine, cytosine, cytosine, thymine, thy ...
... 4. What is the name given to the point where replication starts on a DNA molecule? 5. How does the replicated daughter molecule of DNA compare to the parent molecule of DNA? 6. What would the complementary bases be if one side of a DNA molecule had the bases adenine, cytosine, cytosine, thymine, thy ...
Test Study Guide
... 4. What are the 3 essential functions of DNA (In the text, they compared this to a book)? 5. DNA is a _________________________ made up of many small repeating units called ________________________. ...
... 4. What are the 3 essential functions of DNA (In the text, they compared this to a book)? 5. DNA is a _________________________ made up of many small repeating units called ________________________. ...
epigenome
... genes allows cells to use the same genetic code in different ways. Fun fact: only 10-20% of genes are active in a differentiated cell ...
... genes allows cells to use the same genetic code in different ways. Fun fact: only 10-20% of genes are active in a differentiated cell ...
Genetic Engineering
... specific genes in the cells of living organisms causing them to produce new or unusual substances • Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): uses DNA polymerase to create thousands of copies of a gene ...
... specific genes in the cells of living organisms causing them to produce new or unusual substances • Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): uses DNA polymerase to create thousands of copies of a gene ...
Slide 1
... 4.1 Chromosomes, genes, alleles and mutation State that eukaryotic chromosomes are made of DNA and proteins Define- gene, allele, and genome Define mutation Explain the consequences of a base substitution mutation in relation to the processes of transcription and translation ...
... 4.1 Chromosomes, genes, alleles and mutation State that eukaryotic chromosomes are made of DNA and proteins Define- gene, allele, and genome Define mutation Explain the consequences of a base substitution mutation in relation to the processes of transcription and translation ...
Inheritance Patterns - Bergen County Technical Schools
... • These sex linked alleles are forms of genes found on the X chromosome. A male has only one X chromosome – Examples: hemophilia, red-green color blindness – These are mostly seen in males, but can be seen in females. – A male receives a single X-linked allele from his mother, and will have the diso ...
... • These sex linked alleles are forms of genes found on the X chromosome. A male has only one X chromosome – Examples: hemophilia, red-green color blindness – These are mostly seen in males, but can be seen in females. – A male receives a single X-linked allele from his mother, and will have the diso ...
History of Genetics
... Despite knowing about inheritance in general, a number of incorrect ideas had to be generated and overcome before modern genetics could arise. 1. All life comes from other life. Living organisms are not spontaneously generated from non-living material. Big exception: origin of life. 2. Species conce ...
... Despite knowing about inheritance in general, a number of incorrect ideas had to be generated and overcome before modern genetics could arise. 1. All life comes from other life. Living organisms are not spontaneously generated from non-living material. Big exception: origin of life. 2. Species conce ...
Salmonella typhimurium
... • Some alleles directly cause specific traits, such as (in humans) rare genetic diseases e.g. Cystic fibrosis, sickle-cell anaemia; (in bacteria) ability to grow on certain sugars • Many alleles contribute to many traits of an organism such as size, shape, intelligence, behaviour, and risk of gettin ...
... • Some alleles directly cause specific traits, such as (in humans) rare genetic diseases e.g. Cystic fibrosis, sickle-cell anaemia; (in bacteria) ability to grow on certain sugars • Many alleles contribute to many traits of an organism such as size, shape, intelligence, behaviour, and risk of gettin ...
Microbial Genetics
... mRNA is copy of DNA gene Created by transcription Protein made during translation ...
... mRNA is copy of DNA gene Created by transcription Protein made during translation ...
Human Genome Project
... • The genome database has many tools to locate a gene of interest or search for potential traits of the gene. • Example–chromosomal map search result for the "breast cancer–causing gene" BRCA2: ...
... • The genome database has many tools to locate a gene of interest or search for potential traits of the gene. • Example–chromosomal map search result for the "breast cancer–causing gene" BRCA2: ...
World.GeographyWeek2Extension
... University of the Witwatersrand, in South Africa, found the carving on land owned by his grandfather, near the southern tip of the African continent. Over the years, he had identified and excavated nine sites on the property, none more than 6,500 years old, and was not at first interested in this cl ...
... University of the Witwatersrand, in South Africa, found the carving on land owned by his grandfather, near the southern tip of the African continent. Over the years, he had identified and excavated nine sites on the property, none more than 6,500 years old, and was not at first interested in this cl ...
Study Questions – Chapter 1
... 1. Genome-wide associations have been hailed for providing breakthroughs in our understanding of the underlying basis of complex genetic traits, but they can be a real challenge to carry out. What are some of the factors that can make a difference in how successful such studies are? As you consider ...
... 1. Genome-wide associations have been hailed for providing breakthroughs in our understanding of the underlying basis of complex genetic traits, but they can be a real challenge to carry out. What are some of the factors that can make a difference in how successful such studies are? As you consider ...
Red line Introduction
... – 19 students used Red Line to visualize next-gen RNA-Seq data to investigate presence/absence variation (PAV) in maize – 12 hours effort, each student group annotated 100 kb and then imported next-gen RNA-Seq data from 5 different tissues in 30 maize inbred lines for a gene that they had previously ...
... – 19 students used Red Line to visualize next-gen RNA-Seq data to investigate presence/absence variation (PAV) in maize – 12 hours effort, each student group annotated 100 kb and then imported next-gen RNA-Seq data from 5 different tissues in 30 maize inbred lines for a gene that they had previously ...
Mitochondriontoplastid DNA transfer: it happens
... the plastid or how it integrated into the plastid genome, be it by retrotransposition, homologous recombination, or some other process. The complete plastid genome sequences of D. carota and A. syriaca were both available for some time before the proposed mtDNA insert was discovered, hinting that th ...
... the plastid or how it integrated into the plastid genome, be it by retrotransposition, homologous recombination, or some other process. The complete plastid genome sequences of D. carota and A. syriaca were both available for some time before the proposed mtDNA insert was discovered, hinting that th ...
genetics i - Indian School Al Wadi Al Kabir
... 1. List the salient features of double helix structure of DNA. 2. (a) In the eukaryotes the DNA molecules are organized within the nucleus. How is the DNA molecule organized in a bacterial cell in absence of a nucleus? (b) Explain the packaging of DNA in eukaryotes. 3. Why is DNA considered a better ...
... 1. List the salient features of double helix structure of DNA. 2. (a) In the eukaryotes the DNA molecules are organized within the nucleus. How is the DNA molecule organized in a bacterial cell in absence of a nucleus? (b) Explain the packaging of DNA in eukaryotes. 3. Why is DNA considered a better ...
Big_Idea_3_Multiple_Choice_Questions-2013-03
... b. The mtDNA of sperm is destroyed after fertilization of the egg c. Only eggs contain mtDNA d. The genes coding for mitochondria are located on the X chromosome 35. Mitochondrial diseases are a group of disorders caused by malfunctioning mitochondria. Which of the following statements is true regar ...
... b. The mtDNA of sperm is destroyed after fertilization of the egg c. Only eggs contain mtDNA d. The genes coding for mitochondria are located on the X chromosome 35. Mitochondrial diseases are a group of disorders caused by malfunctioning mitochondria. Which of the following statements is true regar ...
Document
... of different mutations and environmental factors • Mendelian inheritance: Presence or absence of the phenotype depends on the genotype at a single locus ...
... of different mutations and environmental factors • Mendelian inheritance: Presence or absence of the phenotype depends on the genotype at a single locus ...
phylogenetic tree.
... genome to another; therefore, comparing these different sequences helps us to investigate relationships between groups of organisms that diverges a long time ago. DNA that codes for ribosomal RNA changes relatively slowly and is useful ...
... genome to another; therefore, comparing these different sequences helps us to investigate relationships between groups of organisms that diverges a long time ago. DNA that codes for ribosomal RNA changes relatively slowly and is useful ...
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is only a small portion of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell; most of the DNA can be found in the cell nucleus and, in plants, in the chloroplast.In humans, mitochondrial DNA can be assessed as the smallest chromosome coding for 37 genes and containing approximately 16,600 base pairs. Human mitochondrial DNA was the first significant part of the human genome to be sequenced. In most species, including humans, mtDNA is inherited solely from the mother.The DNA sequence of mtDNA has been determined from a large number of organisms and individuals (including some organisms that are extinct), and the comparison of those DNA sequences represents a mainstay of phylogenetics, in that it allows biologists to elucidate the evolutionary relationships among species. It also permits an examination of the relatedness of populations, and so has become important in anthropology and field biology.























