Course Guide - Universitat de València
... components, plant cell wall and extracellular matrix of animal cells, establish fundamental differences between both type of cells: Plant cell wall allows life in non-isotonic conditions, while extracellular matrix of plant cells influences intercellular junctions, cell communication and intercellul ...
... components, plant cell wall and extracellular matrix of animal cells, establish fundamental differences between both type of cells: Plant cell wall allows life in non-isotonic conditions, while extracellular matrix of plant cells influences intercellular junctions, cell communication and intercellul ...
Chapter 1
... The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is the system of folded membranes in which proteins, lipids, and other cells parts are made. -Many of the cell’s chemical reactions occur in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). -The ER acts as an internal delivery system because substances move through the ER to different ...
... The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is the system of folded membranes in which proteins, lipids, and other cells parts are made. -Many of the cell’s chemical reactions occur in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). -The ER acts as an internal delivery system because substances move through the ER to different ...
Chapter 1 Biology Exam Study Guide
... Which stage of cellular respiration produces the most ATP? ...
... Which stage of cellular respiration produces the most ATP? ...
Chapter 1 Biology Exam Study Guide
... Which stage of cellular respiration produces the most ATP? ...
... Which stage of cellular respiration produces the most ATP? ...
Body Systems Unit Review part 2
... ORGANS: Muscles, there are many! Examples: bicep and triceps (tendons too) COMPARISON TO CELL FUNCTION: Some single celled creatures have small hairs called flagella that allow them to move. ...
... ORGANS: Muscles, there are many! Examples: bicep and triceps (tendons too) COMPARISON TO CELL FUNCTION: Some single celled creatures have small hairs called flagella that allow them to move. ...
study guide - cvadultcma
... Chapter 18: Hematology Mrs. Dasalla 1. Which of the following tests is not included in a CBC? a Differential white blood cell count b Hemoglobin c Hematocrit d Prothrombin time e Red and white blood cell counts 2. The plasma functions in a Transporting electrolytes needed by the cells b Transporting ...
... Chapter 18: Hematology Mrs. Dasalla 1. Which of the following tests is not included in a CBC? a Differential white blood cell count b Hemoglobin c Hematocrit d Prothrombin time e Red and white blood cell counts 2. The plasma functions in a Transporting electrolytes needed by the cells b Transporting ...
The Amazing Cell
... • Play key role in cell’s ability to change shape, break apart during cell division and form outpouchings and involutions. • Are assembled where and when needed. • Depends on what cell is doing as to how many are found within cell. ...
... • Play key role in cell’s ability to change shape, break apart during cell division and form outpouchings and involutions. • Are assembled where and when needed. • Depends on what cell is doing as to how many are found within cell. ...
The Amazing Celllesspics
... • Play key role in cell’s ability to change shape, break apart during cell division and form outpouchings and involutions. • Are assembled where and when needed. • Depends on what cell is doing as to how many are found within cell. ...
... • Play key role in cell’s ability to change shape, break apart during cell division and form outpouchings and involutions. • Are assembled where and when needed. • Depends on what cell is doing as to how many are found within cell. ...
Cell
... of long lengths of DNA that code for many characteristics Short lengths of DNA on a chromosome form genes that code for a single characteristic Chemical reactions occur here ...
... of long lengths of DNA that code for many characteristics Short lengths of DNA on a chromosome form genes that code for a single characteristic Chemical reactions occur here ...
EOC_CUMMULATIVE_REVIEW
... or gametes have ____________________ 6. For every chromosome your mother gave you, there is a _________________ chromosome from your father with information regarding the same trait(s). 7. When a cell has a full complement of homologues or homologous chromosomes from each parent, the cell is said to ...
... or gametes have ____________________ 6. For every chromosome your mother gave you, there is a _________________ chromosome from your father with information regarding the same trait(s). 7. When a cell has a full complement of homologues or homologous chromosomes from each parent, the cell is said to ...
Biology I Outline
... from food into smaller molecules that can be used by cells for energy and for repair and growth b. Explain how the circulatory system transports nutrients and oxygen to cell and removes cell wastes c. Describe how the kidneys and the liver are closely associated with the circulatory system as they p ...
... from food into smaller molecules that can be used by cells for energy and for repair and growth b. Explain how the circulatory system transports nutrients and oxygen to cell and removes cell wastes c. Describe how the kidneys and the liver are closely associated with the circulatory system as they p ...
S2 Final Exam Review Guide
... 56. Identify the following as transcription or translation: Happens in the nucleus __________________________________________ Happens in the ribosome __________________________________________ Involves DNA __________________________________________ Involves tRNA _____________________________________ ...
... 56. Identify the following as transcription or translation: Happens in the nucleus __________________________________________ Happens in the ribosome __________________________________________ Involves DNA __________________________________________ Involves tRNA _____________________________________ ...
Yr 7 Cells, Tissues and Organs Topic vocabulary list
... Plant organ used to make food by photosynthesis. ...
... Plant organ used to make food by photosynthesis. ...
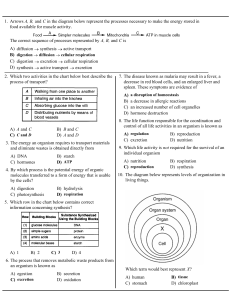
1. Arrows A, B, and C in the diagram below represent the processes
... 26. Base your answer to the following question on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. A solution of an enzyme normally found in the human body was added to a flask containing a solution of proteins in distilled water, and then the flask was stoppered. This mixture was then mainta ...
... 26. Base your answer to the following question on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. A solution of an enzyme normally found in the human body was added to a flask containing a solution of proteins in distilled water, and then the flask was stoppered. This mixture was then mainta ...
CELL WALL - Winona ISD
... • The nervous system connects all the tissues and organs to your brain. • It consists of two parts: The central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. • The central nervous system consists of brain and spinal cord. • The peripheral nervous system consists of sensory organs, such as eyes, ears ...
... • The nervous system connects all the tissues and organs to your brain. • It consists of two parts: The central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. • The central nervous system consists of brain and spinal cord. • The peripheral nervous system consists of sensory organs, such as eyes, ears ...
Rotating Review Lab DOL Rotating Review Lab-
... c. stores food, water, and waste d. protects the outside of the cell ...
... c. stores food, water, and waste d. protects the outside of the cell ...
Macromolecules are very large biomolecules formed by a process of
... 1. Carbohydrates – composed of sugar molecules. Used to store energy for cells. (Polysaccharides) 2. Lipids – composed of glycerin and fatty acids. Used to store energy for cells. 3. Nucleic acids – composed of a sugar, a nitrogen base, and a phosphate group. (C, H, O, N) Contains the genetic code. ...
... 1. Carbohydrates – composed of sugar molecules. Used to store energy for cells. (Polysaccharides) 2. Lipids – composed of glycerin and fatty acids. Used to store energy for cells. 3. Nucleic acids – composed of a sugar, a nitrogen base, and a phosphate group. (C, H, O, N) Contains the genetic code. ...
Titan Tutoring for Biology
... some are _______________________ or opportunistic (strep throat, pneumonia, salmonella, etc.) Eukaryotic Kingdoms: 2) Kingdom Protista mostly ______________________, some multicellular mostly ____________________ reproduction Classified based on way they obtain their nutrients: 4) animal-like ...
... some are _______________________ or opportunistic (strep throat, pneumonia, salmonella, etc.) Eukaryotic Kingdoms: 2) Kingdom Protista mostly ______________________, some multicellular mostly ____________________ reproduction Classified based on way they obtain their nutrients: 4) animal-like ...
2015-16 Fall Semester Exam REVIEW KEY
... a. Chloroplast – used in photosynthesis; contain green pigment called chlorophyll b. Cell Wall – plants only – surrounds membrane to provide additional support c. Vacuole – large water container in center of the cell d. Cell Membrane – selectively permeable – regulates what goes in and out of cell e ...
... a. Chloroplast – used in photosynthesis; contain green pigment called chlorophyll b. Cell Wall – plants only – surrounds membrane to provide additional support c. Vacuole – large water container in center of the cell d. Cell Membrane – selectively permeable – regulates what goes in and out of cell e ...
Quiz 4 1407 - HCC Learning Web
... B) the portal systems of mammals, where two capillary beds occur sequentially, without passage of blood through a pumping chamber C) those of sponges, where gas exchange in all cells occurs directly with the external environment D) those of humans, where there are four pumping chambers to drive bloo ...
... B) the portal systems of mammals, where two capillary beds occur sequentially, without passage of blood through a pumping chamber C) those of sponges, where gas exchange in all cells occurs directly with the external environment D) those of humans, where there are four pumping chambers to drive bloo ...
Cells and Systems Notes
... In multi-cellular organisms, substances must be brought to the cells and this is done by the blood. Blood also takes wastes away from the body’s cells. Blood is made of: Plasma - Liquid portion of blood that carry nutrients, waste products and blood cells Red Blood Cells – carry oxygen White Blood C ...
... In multi-cellular organisms, substances must be brought to the cells and this is done by the blood. Blood also takes wastes away from the body’s cells. Blood is made of: Plasma - Liquid portion of blood that carry nutrients, waste products and blood cells Red Blood Cells – carry oxygen White Blood C ...
BASIC INTRO TAXONOMY CELL THEORY PROKARYOTES
... ◼ Obligate anaerobes- cannot survive in the presence of oxygen. ◼ Obligate aerobe- needs oxygen to survive ◼ Facultative aerobe- can survive whether or not oxygen is present. ...
... ◼ Obligate anaerobes- cannot survive in the presence of oxygen. ◼ Obligate aerobe- needs oxygen to survive ◼ Facultative aerobe- can survive whether or not oxygen is present. ...
Levels of Organization
... Specialized cells function together in tissues, organs, organ systems, and the whole organism. If you think about your body, you cannot help but notice that there is more to you than individual cells. You also have tissues and organs. In fact, there are five levels of organization in a human body. 1 ...
... Specialized cells function together in tissues, organs, organ systems, and the whole organism. If you think about your body, you cannot help but notice that there is more to you than individual cells. You also have tissues and organs. In fact, there are five levels of organization in a human body. 1 ...
animal phyla
... Is It True? Ecosystems and Energy Flow Instructions: Read each statement below and decide if it is true or false based on your own background knowledge. In the blank mark “T” for True and “F” for False. Use the resources provided by your instructor to determine if you were right or wrong after you h ...
... Is It True? Ecosystems and Energy Flow Instructions: Read each statement below and decide if it is true or false based on your own background knowledge. In the blank mark “T” for True and “F” for False. Use the resources provided by your instructor to determine if you were right or wrong after you h ...
Cell (biology)

The cell (from Latin cella, meaning ""small room"") is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently, and are often called the ""building blocks of life"". The study of cells is called cell biology.Cells consist of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, which contains many biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. Organisms can be classified as unicellular (consisting of a single cell; including bacteria) or multicellular (including plants and animals). While the number of cells in plants and animals varies from species to species, humans contain more than 10 trillion (1013) cells. Most plant and animal cells are visible only under the microscope, with dimensions between 1 and 100 micrometres.The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665, who named the biological unit for its resemblance to cells inhabited by Christian monks in a monastery. Cell theory, first developed in 1839 by Matthias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, states that all organisms are composed of one or more cells, that cells are the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms, that all cells come from preexisting cells, and that all cells contain the hereditary information necessary for regulating cell functions and for transmitting information to the next generation of cells. Cells emerged on Earth at least 3.5 billion years ago.