1 - Port Fest Baltimore
... solution. He divided the plants into six groups, measured the initial height of each plant, and calculated the average height for each group. Once a week for two months, he watered the plants in each group using a different sugar solution for each plant group. At the end of two months, he measured t ...
... solution. He divided the plants into six groups, measured the initial height of each plant, and calculated the average height for each group. Once a week for two months, he watered the plants in each group using a different sugar solution for each plant group. At the end of two months, he measured t ...
Cells - WordPress.com
... I have explored the structure and function of organs and organ systems and can relate this to the basic biological processes required to ...
... I have explored the structure and function of organs and organ systems and can relate this to the basic biological processes required to ...
Understanding Cells: The Basic Units of Life Cells make up the
... The factory of the cell: The endoplasmic reticulum The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a series of canals that connects the nucleus to the cytoplasm of the cell. The part of the ER that is dotted with ribosomes is called rough ER; the part of the ER that has no ribosomes is called smooth ER. Ribosome ...
... The factory of the cell: The endoplasmic reticulum The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a series of canals that connects the nucleus to the cytoplasm of the cell. The part of the ER that is dotted with ribosomes is called rough ER; the part of the ER that has no ribosomes is called smooth ER. Ribosome ...
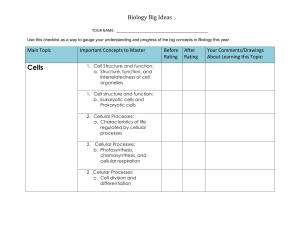
Biology Standards Checklist
... Use this checklist as a way to gauge your understanding and progress of the big concepts in Biology this year. ...
... Use this checklist as a way to gauge your understanding and progress of the big concepts in Biology this year. ...
Review PPT – Life Science – Cells and Human
... larger food molecules into small food molecules • Digest old cell parts ...
... larger food molecules into small food molecules • Digest old cell parts ...
Characteristics of life
... Excretion is the removal of waste products of metabolism e.g. urea and carbon dioxide from the body. These waste products can become toxic to the cell if allowed to accumulate. The organism tries to maintain a constant internal environment (homeostasis). Plants have less need for excretion because t ...
... Excretion is the removal of waste products of metabolism e.g. urea and carbon dioxide from the body. These waste products can become toxic to the cell if allowed to accumulate. The organism tries to maintain a constant internal environment (homeostasis). Plants have less need for excretion because t ...
The Cell in Action
... layers will blur. The tiny moving particles (which everything is made of) travel from where they are crowded to where they are ...
... layers will blur. The tiny moving particles (which everything is made of) travel from where they are crowded to where they are ...
Cell Theory Cell Structure, Cell Transport and Mitosis
... The liquid part of cytoplasm is --------------Structures formed of membranes and molecules, present in cytoplasm, doing a special function, are ------------------------2 halves of cell membrane are held together by -------------- bonds Cell membrane is fluid due to --------------- molecules Membrane ...
... The liquid part of cytoplasm is --------------Structures formed of membranes and molecules, present in cytoplasm, doing a special function, are ------------------------2 halves of cell membrane are held together by -------------- bonds Cell membrane is fluid due to --------------- molecules Membrane ...
Stem Cells and cell division
... • Mitosis is only one step of a larger process called the cell cycle. • The proper functioning of multicellular organisms depends on the regulation and integration of the process in all cells, particularly in the process of cell division. • Normal cells grow only a small fraction of the time ...
... • Mitosis is only one step of a larger process called the cell cycle. • The proper functioning of multicellular organisms depends on the regulation and integration of the process in all cells, particularly in the process of cell division. • Normal cells grow only a small fraction of the time ...
cell structure - Madison County Schools
... • Unicellular organisms are made of one cell only • The cells of multicellular organisms are specialized to perform different functions ...
... • Unicellular organisms are made of one cell only • The cells of multicellular organisms are specialized to perform different functions ...
7th Grade
... mitochondria - A spherical or elongated organelle in the cytoplasm of nearly all eukaryotic cells, containing genetic material and many enzymes important for cell metabolism, including those responsible for the conversion of food to usable energy. nuclear - Of, relating to, or forming a nucleus. nuc ...
... mitochondria - A spherical or elongated organelle in the cytoplasm of nearly all eukaryotic cells, containing genetic material and many enzymes important for cell metabolism, including those responsible for the conversion of food to usable energy. nuclear - Of, relating to, or forming a nucleus. nuc ...
CHAPTER 2: CELL AS THE BASIC UNIT OF LIFE 2.1 What is a cell
... The cell membrane is the structure that controls what substances move into or out of the cell. Food passes through the cell membrane before it enters the cell. Waste materials pass through the cell membrane before they leave the cell. The cell wall is a strong structure that gives the plant cell a r ...
... The cell membrane is the structure that controls what substances move into or out of the cell. Food passes through the cell membrane before it enters the cell. Waste materials pass through the cell membrane before they leave the cell. The cell wall is a strong structure that gives the plant cell a r ...
File - Mr. Krueger`s Biology
... Cell Theory – cells are the basic unit of life, cells come form other cells Prokaryotes – no nucleus, DO have circular DNA a. Example: bacteria Eukaryotes – DO have a nucleus, DNA enclosed in the nucleus a. Examples: animal and plant cells ...
... Cell Theory – cells are the basic unit of life, cells come form other cells Prokaryotes – no nucleus, DO have circular DNA a. Example: bacteria Eukaryotes – DO have a nucleus, DNA enclosed in the nucleus a. Examples: animal and plant cells ...
AP Biology Study Guide
... Themes in the Study of Biology 2. Describe the levels of biological organization from molecules to the biosphere, noting the interrelationships between levels. 3. Compare the flow of chemical nutrients and the flow of energy in an ecosystem. 4. Explain how cells function as the structural and functi ...
... Themes in the Study of Biology 2. Describe the levels of biological organization from molecules to the biosphere, noting the interrelationships between levels. 3. Compare the flow of chemical nutrients and the flow of energy in an ecosystem. 4. Explain how cells function as the structural and functi ...
LS.3 Cellular Organization
... 11. What is the name for a group of cells that work together to perform a certain task in an organism? a. tissue c. species b. organ d. genius ...
... 11. What is the name for a group of cells that work together to perform a certain task in an organism? a. tissue c. species b. organ d. genius ...
1 Unit 1: The Body as a Whole
... electrical potential against diffusion. When nerve cell "fires", momentary gates open to let diffusion occur. Then pumps are turned back on to restore potential. f) Types of Active Transport • Symport system • Antiport system • Primary active transport • Secondary active transport g) Vesicular Trans ...
... electrical potential against diffusion. When nerve cell "fires", momentary gates open to let diffusion occur. Then pumps are turned back on to restore potential. f) Types of Active Transport • Symport system • Antiport system • Primary active transport • Secondary active transport g) Vesicular Trans ...
The Big Picture: A Review of Biology
... Ø Homologous structures are body structures on different organisms that are similar. Evidence of a recent common ancestor/divergent evolution. Example: human arm and whale fin. Ø Analogous structures are different body structures that serve a common purpose. Evidence of convergent evolution. Examp ...
... Ø Homologous structures are body structures on different organisms that are similar. Evidence of a recent common ancestor/divergent evolution. Example: human arm and whale fin. Ø Analogous structures are different body structures that serve a common purpose. Evidence of convergent evolution. Examp ...
Unit C: Cell Structure and Function
... The microscope is a vital scientific tool that aids in scientific advancement. All living organisms are made of cells with specialized parts and functions. ...
... The microscope is a vital scientific tool that aids in scientific advancement. All living organisms are made of cells with specialized parts and functions. ...
Test Review Mrs. Benham
... 10. What is the Chloroplast? Organelles found in plant cells and other eukaryotic organisms that perform photosynthesis (take energy from the sun, water and carbon dioxide and make sugar and oxygen). 11. What is the Cytoplasm? A thick liquid residing between the cell membrane holding all organelles, ...
... 10. What is the Chloroplast? Organelles found in plant cells and other eukaryotic organisms that perform photosynthesis (take energy from the sun, water and carbon dioxide and make sugar and oxygen). 11. What is the Cytoplasm? A thick liquid residing between the cell membrane holding all organelles, ...
EOCT REVIEW STUDY GUIDE
... Cells can be grouped according to their similarities and differences. All cells can be divided into two categories – prokaryotes and eukaryotes. A PROKARYOTE is a cell that lacks a true nucleus and does not have membrane bound organelles. They do have a cell wall and a cell membrane. Bacteria and bl ...
... Cells can be grouped according to their similarities and differences. All cells can be divided into two categories – prokaryotes and eukaryotes. A PROKARYOTE is a cell that lacks a true nucleus and does not have membrane bound organelles. They do have a cell wall and a cell membrane. Bacteria and bl ...
Moore 1 Timothy Moore Life Science: Semester 1 Assessment 22
... capillaries which can get so small that cells can pass only sigle-file. It is here that exchange of gas, nutrients, and wastes occur. The wastes make a return path with the oxygen depleted, blue colored blood to the heart to once again make the path to become oxygenated and flow to the body's system ...
... capillaries which can get so small that cells can pass only sigle-file. It is here that exchange of gas, nutrients, and wastes occur. The wastes make a return path with the oxygen depleted, blue colored blood to the heart to once again make the path to become oxygenated and flow to the body's system ...
Cell (biology)

The cell (from Latin cella, meaning ""small room"") is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently, and are often called the ""building blocks of life"". The study of cells is called cell biology.Cells consist of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, which contains many biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. Organisms can be classified as unicellular (consisting of a single cell; including bacteria) or multicellular (including plants and animals). While the number of cells in plants and animals varies from species to species, humans contain more than 10 trillion (1013) cells. Most plant and animal cells are visible only under the microscope, with dimensions between 1 and 100 micrometres.The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665, who named the biological unit for its resemblance to cells inhabited by Christian monks in a monastery. Cell theory, first developed in 1839 by Matthias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, states that all organisms are composed of one or more cells, that cells are the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms, that all cells come from preexisting cells, and that all cells contain the hereditary information necessary for regulating cell functions and for transmitting information to the next generation of cells. Cells emerged on Earth at least 3.5 billion years ago.