15.2 COMPLEX FORMATION And THE SHAPE OF COMPLEX IONS
... CO-ORDINATION NUMBER & SHAPE the shape of a complex is governed by the number of ligands around the central ion the co-ordination number gives the number of ligands around the central ion a change of ligand can affect the co-ordination number Co-ordination No. Shape ...
... CO-ORDINATION NUMBER & SHAPE the shape of a complex is governed by the number of ligands around the central ion the co-ordination number gives the number of ligands around the central ion a change of ligand can affect the co-ordination number Co-ordination No. Shape ...
Complexes_naming(download)
... Rules for determining geometry are more involved than the simple VSEPR approach that works well with covalent compounds Note: same composition may adopt different geometries Will be dealt with using ligand-field theory ...
... Rules for determining geometry are more involved than the simple VSEPR approach that works well with covalent compounds Note: same composition may adopt different geometries Will be dealt with using ligand-field theory ...
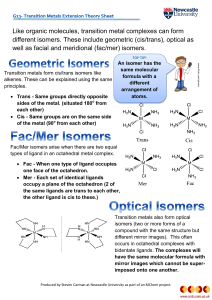
Like organic molecules, transition metal complexes can form
... Transition metals also form optical isomers (two or more forms of a compound with the same structure but different mirror images). This often occurs in octahedral complexes with bidentate ligands. The complexes will have the same molecular formula with mirror images which cannot be superimposed onto ...
... Transition metals also form optical isomers (two or more forms of a compound with the same structure but different mirror images). This often occurs in octahedral complexes with bidentate ligands. The complexes will have the same molecular formula with mirror images which cannot be superimposed onto ...
Polydentate ligand (macrocycle) bound to Fe via 4 N atoms. This is
... Transition metals are widely used materials in many different areas in science including biology and catalysis. The properties of transition metals arise from their d-orbitals. Transition metals complexes are formed when the metal centre is bound to ligands or anions. These complexes can take many s ...
... Transition metals are widely used materials in many different areas in science including biology and catalysis. The properties of transition metals arise from their d-orbitals. Transition metals complexes are formed when the metal centre is bound to ligands or anions. These complexes can take many s ...
The catalytic hydrogenolysis of esters to the two corresponding
... with phosphines. Upon coordination to transition metals, these ligands give the resulting metal complex stability and electron density that is needed for the formation of hydride species. Hydride species are important intermediates in the catalytic cycle of hydrogenolysis and hydrogenation reactions ...
... with phosphines. Upon coordination to transition metals, these ligands give the resulting metal complex stability and electron density that is needed for the formation of hydride species. Hydride species are important intermediates in the catalytic cycle of hydrogenolysis and hydrogenation reactions ...
Chapter 24: Transition Metals Coordination Compounds Part 2
... • We see the color which is NOT absorbed, but which was reflected or transmitted. • We see the complementary color of what was absorbed. ...
... • We see the color which is NOT absorbed, but which was reflected or transmitted. • We see the complementary color of what was absorbed. ...
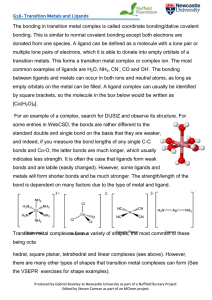
The bonding in transition metal complex is called coordinate
... bonding. This is similar to normal covalent bonding except both electrons are donated from one species. A ligand can be defined as a molecule with a lone pair or multiple lone pairs of electrons, which it is able to donate into empty orbitals of a transition metals. This forms a transition metal com ...
... bonding. This is similar to normal covalent bonding except both electrons are donated from one species. A ligand can be defined as a molecule with a lone pair or multiple lone pairs of electrons, which it is able to donate into empty orbitals of a transition metals. This forms a transition metal com ...
Lecture 3
... access dissolved Fe from the FeL1 complex, resulting in excess L1 between dissolved Fe and L1 ligand concentrations in samples with intermediate dissolved Fe, and this is a seemingly ubiquitous feature of dissolved Fe cycling in the marine environment.” ...
... access dissolved Fe from the FeL1 complex, resulting in excess L1 between dissolved Fe and L1 ligand concentrations in samples with intermediate dissolved Fe, and this is a seemingly ubiquitous feature of dissolved Fe cycling in the marine environment.” ...
Abstract Coordination Chemistry of Tetra(pyrazolyl)
... Substitution along the pyrzolyl periphery with various alklyl groups (4-methyl, 3,5dimethyl, 3,5-diisopropyl) provided a way to examine the effects of substitution on binding behavior with transition metals. Cobalt(II) complexes tend to be thermo and solvatochromic giving both pink κ5 octahedral com ...
... Substitution along the pyrzolyl periphery with various alklyl groups (4-methyl, 3,5dimethyl, 3,5-diisopropyl) provided a way to examine the effects of substitution on binding behavior with transition metals. Cobalt(II) complexes tend to be thermo and solvatochromic giving both pink κ5 octahedral com ...
lect4b
... Level-3 Organometallics L4b Complexes with -acceptor ligands There are many of these type of ligand (E/S Ch 15 S/A Ch 16) Some bond to metal through one atom - described as 1 (eta-one) ligands, while others (described later) bind through more than one. Examples of 1 ligands M-CO ...
... Level-3 Organometallics L4b Complexes with -acceptor ligands There are many of these type of ligand (E/S Ch 15 S/A Ch 16) Some bond to metal through one atom - described as 1 (eta-one) ligands, while others (described later) bind through more than one. Examples of 1 ligands M-CO ...
Ligand
4-3D-balls.png?width=300)
In coordination chemistry, a ligand (/lɪɡənd/) is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs. The nature of metal-ligand bonding can range from covalent to ionic. Furthermore, the metal-ligand bond order can range from one to three. Ligands are viewed as Lewis bases, although rare cases are known to involve Lewis acidic ""ligand.""Metals and metalloids are bound to ligands in virtually all circumstances, although gaseous ""naked"" metal ions can be generated in high vacuum. Ligands in a complex dictate the reactivity of the central atom, including ligand substitution rates, the reactivity of the ligands themselves, and redox. Ligand selection is a critical consideration in many practical areas, including bioinorganic and medicinal chemistry, homogeneous catalysis, and environmental chemistry.Ligands are classified in many ways like : their charge, their size (bulk), the identity of the coordinating atom(s), and the number of electrons donated to the metal (denticity or hapticity). The size of a ligand is indicated by its cone angle.