Chem+174–Lecture+12a..
... The extreme cases are PCl3 and PF3, which is equivalent to CO in its p-acidity because more electronegative elements on the phosphorous atom stabilize the s-bond and lower the energy of the s*-orbital (see diagram) The contribution of the phosphorus atom to the s*-orbital increases and the size ...
... The extreme cases are PCl3 and PF3, which is equivalent to CO in its p-acidity because more electronegative elements on the phosphorous atom stabilize the s-bond and lower the energy of the s*-orbital (see diagram) The contribution of the phosphorus atom to the s*-orbital increases and the size ...
Nomenclature for d-block complexes Writing chemical names
... Same as for neutral, but use square brackets to enclose ions. For complete complexes (in which both cation and anion are shown), cation(s) comes first followed by anion(s). If only one of the two ions is “complex”, that ion can be shown by itself with charge indicated (and the understanding that the ...
... Same as for neutral, but use square brackets to enclose ions. For complete complexes (in which both cation and anion are shown), cation(s) comes first followed by anion(s). If only one of the two ions is “complex”, that ion can be shown by itself with charge indicated (and the understanding that the ...
Chapter 24: Transition Metals Coordination Compounds Part 1
... So you could easily form the salt [Ag(NH3)2]Cl. Note how the Cl- anion is outside the brackets. The coordination number of a coordination compound is simply the number of ligand atoms which are directly covalently attached to the transition metal atom or ion. So the coordination number of [Ag(NH3)2] ...
... So you could easily form the salt [Ag(NH3)2]Cl. Note how the Cl- anion is outside the brackets. The coordination number of a coordination compound is simply the number of ligand atoms which are directly covalently attached to the transition metal atom or ion. So the coordination number of [Ag(NH3)2] ...
Powerpoint - mvhs
... ball-and-stick model, the chlorides serve as counter ions to the cobalt/ammonia coordiation complex in the orange compound, while one of the ammonia molecules is replaced by Cl in the purple compound. In both cases, the coordination geometry is octahedral around Co. ...
... ball-and-stick model, the chlorides serve as counter ions to the cobalt/ammonia coordiation complex in the orange compound, while one of the ammonia molecules is replaced by Cl in the purple compound. In both cases, the coordination geometry is octahedral around Co. ...
Problem set 1
... The bulky, rigid tridentate ligand NNN is a good ligand for Ln3+ ions. Its rigidity means that it always coordinates in such a way as to occupy a triangular face: ...
... The bulky, rigid tridentate ligand NNN is a good ligand for Ln3+ ions. Its rigidity means that it always coordinates in such a way as to occupy a triangular face: ...
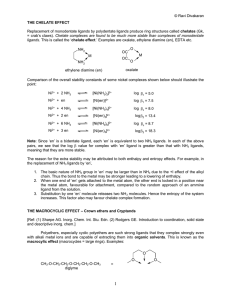
© Ravi Divakaran THE CHELATE EFFECT Replacement of
... The Template Effect: [Ref: Shriver & Atkins, Inorganic Chemistry, 3rd edn., Oxford, 1999] A metal ion such as nickel may be used to assemble a group of small ligands around it by coordination. Members of the group then may undergo condensation reactions among them, if they have suitable reactive fun ...
... The Template Effect: [Ref: Shriver & Atkins, Inorganic Chemistry, 3rd edn., Oxford, 1999] A metal ion such as nickel may be used to assemble a group of small ligands around it by coordination. Members of the group then may undergo condensation reactions among them, if they have suitable reactive fun ...
Metal Catalysts - UZH - Department of Chemistry
... attached. Mobile cations or counterions are said to be in the outer or secondary coordination sphere. ...
... attached. Mobile cations or counterions are said to be in the outer or secondary coordination sphere. ...
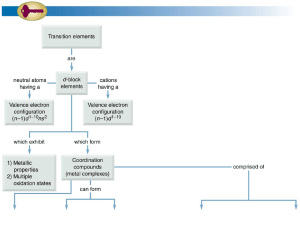
Transition Metals introduction
... A special property of transition metals, making them very useful in Biology and Chemistry, is the formation of complexes. A complex contains a metal ion in the centre, with other molecules surrounding it. The attached substances are known as ligands. They attach via dative covalent bonding, with the ...
... A special property of transition metals, making them very useful in Biology and Chemistry, is the formation of complexes. A complex contains a metal ion in the centre, with other molecules surrounding it. The attached substances are known as ligands. They attach via dative covalent bonding, with the ...
Chapter 14: Complex-Formation Titrations
... of ammonia would produce the copper-ammonia complex, Cu(NH3)42+, a bright blue complex. The donor species, or ligand, must have at least one pair of unshared electrons available for bond formations. Ligands are defined as ions or molecules that form covalent bonds with a cation or a nuetral metal at ...
... of ammonia would produce the copper-ammonia complex, Cu(NH3)42+, a bright blue complex. The donor species, or ligand, must have at least one pair of unshared electrons available for bond formations. Ligands are defined as ions or molecules that form covalent bonds with a cation or a nuetral metal at ...
Homework 5 Insert space or answer ques
... Draw the splitting diagram for a square planar complex Be SURE to identify which d orbitals are located where!! 5.) What is the distinction between a weak field and a strong field ligand? What does it mean for electrons filling the d orbitals? Give an example of a weak field ligand. Give an exampl ...
... Draw the splitting diagram for a square planar complex Be SURE to identify which d orbitals are located where!! 5.) What is the distinction between a weak field and a strong field ligand? What does it mean for electrons filling the d orbitals? Give an example of a weak field ligand. Give an exampl ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
... 1) trans-Influence = ground state effect where the strong T—Pt sigma bond using the px and dx2-y2 orbitals prevents the trans leaving group Pt—X bond from being strong. a) The weak bond makes Pt—X a high energy ground state b) The Ea required to get X to leave is small c) Doesn’t quite give the corr ...
... 1) trans-Influence = ground state effect where the strong T—Pt sigma bond using the px and dx2-y2 orbitals prevents the trans leaving group Pt—X bond from being strong. a) The weak bond makes Pt—X a high energy ground state b) The Ea required to get X to leave is small c) Doesn’t quite give the corr ...
InorgCh425
... 1) trans-Influence = ground state effect where the strong T—Pt sigma bond using the px and dx2-y2 orbitals prevents the trans leaving group Pt—X bond from being strong. a) The weak bond makes Pt—X a high energy ground state b) The Ea required to get X to leave is small c) Doesn’t quite give the corr ...
... 1) trans-Influence = ground state effect where the strong T—Pt sigma bond using the px and dx2-y2 orbitals prevents the trans leaving group Pt—X bond from being strong. a) The weak bond makes Pt—X a high energy ground state b) The Ea required to get X to leave is small c) Doesn’t quite give the corr ...
study questions/guide
... 1. Provide the splitting pattern for octahedral and tetrahedral complexes, including providing the symmetry labels (egt2g, etc.) and the orbital labels (dxy, dyz, etc.). 2. Be able to explain the basis for the splitting of the d orbitals in an octahedral field (crystal field approach). 3. Understand ...
... 1. Provide the splitting pattern for octahedral and tetrahedral complexes, including providing the symmetry labels (egt2g, etc.) and the orbital labels (dxy, dyz, etc.). 2. Be able to explain the basis for the splitting of the d orbitals in an octahedral field (crystal field approach). 3. Understand ...
29th Annual Meeting | American Society of Preventive Oncology
... Our laboratory is involved in the development of safe organo-metallic complexes using natural biological molecules as ligands. These are nutritional supplements as well as candidate chemotherapy agents. The initial phase of development of these materials is based on the electronic signaling properti ...
... Our laboratory is involved in the development of safe organo-metallic complexes using natural biological molecules as ligands. These are nutritional supplements as well as candidate chemotherapy agents. The initial phase of development of these materials is based on the electronic signaling properti ...
Synthesis and Crystal Structure of Nicotinamide Cobalt (II) Complexes
... Nicotinamide (NA) is one form of niacin. A deficiency of this vitamin leads to loss of copper from the body, known as pellagra disease. Victims of pellagra show unusually high serum and urinary copper levels (1). The nicotinic acid derivative N,N-diethylnicotinamide (DENA) is an important respirator ...
... Nicotinamide (NA) is one form of niacin. A deficiency of this vitamin leads to loss of copper from the body, known as pellagra disease. Victims of pellagra show unusually high serum and urinary copper levels (1). The nicotinic acid derivative N,N-diethylnicotinamide (DENA) is an important respirator ...
Lecture 04 Chem 3
... capable of wrapping around a metal in multiple bonds thus competing with other molecules (e.g., proteins, nucleic acids) for the metal. Multidentate: ( Lat: dentate, teeth) Referring to a molecule that has multiple binding groups within the same chain capable of forming multiple bonds with the metal ...
... capable of wrapping around a metal in multiple bonds thus competing with other molecules (e.g., proteins, nucleic acids) for the metal. Multidentate: ( Lat: dentate, teeth) Referring to a molecule that has multiple binding groups within the same chain capable of forming multiple bonds with the metal ...
Nomenclature of Coordination Complexes Rule 1
... the latter two standing for meridional or facial, respectively. Rule 9: Bridging ligands are designated with the prefix - . When there are two bridging ligands of the same kind, the prefix di-- is used. Bridging ligands are listed in order with other ligands, according to Rule 6, and set off betw ...
... the latter two standing for meridional or facial, respectively. Rule 9: Bridging ligands are designated with the prefix - . When there are two bridging ligands of the same kind, the prefix di-- is used. Bridging ligands are listed in order with other ligands, according to Rule 6, and set off betw ...
Key Concepts PowerPoint
... What is the general trend in the following properties from left to right across the first transition series (Sc to Zn)? Explain each trend. (a) Atomic radius (b) Density (c) Ionization energy ...
... What is the general trend in the following properties from left to right across the first transition series (Sc to Zn)? Explain each trend. (a) Atomic radius (b) Density (c) Ionization energy ...
Michael Carney - University of Wisconsin
... K over a fairly wide range, with, in most cases, relatively small changes in ligand structure, has fueled our interest in this area. Control over K is particularly important in an industrial setting where the ability to modify the product distribution via catalyst modification can provide a-olefin p ...
... K over a fairly wide range, with, in most cases, relatively small changes in ligand structure, has fueled our interest in this area. Control over K is particularly important in an industrial setting where the ability to modify the product distribution via catalyst modification can provide a-olefin p ...
Transition Metal Complexes
... ammi ne( not i ce2m’ s) H2O aqua CO carbonyl NO nitrosyl PR3 trialkyl- or triarylphosphine ...
... ammi ne( not i ce2m’ s) H2O aqua CO carbonyl NO nitrosyl PR3 trialkyl- or triarylphosphine ...
1.1 Werner`s Coordination Theory 1.2 Coordination
... 2.8 Writing Formulas A compound with composition CuCl2 4NH3 is comprised of a Cu2+ ion and has an overall metal complex charge of 2+ ...
... 2.8 Writing Formulas A compound with composition CuCl2 4NH3 is comprised of a Cu2+ ion and has an overall metal complex charge of 2+ ...
Ligand
4-3D-balls.png?width=300)
In coordination chemistry, a ligand (/lɪɡənd/) is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs. The nature of metal-ligand bonding can range from covalent to ionic. Furthermore, the metal-ligand bond order can range from one to three. Ligands are viewed as Lewis bases, although rare cases are known to involve Lewis acidic ""ligand.""Metals and metalloids are bound to ligands in virtually all circumstances, although gaseous ""naked"" metal ions can be generated in high vacuum. Ligands in a complex dictate the reactivity of the central atom, including ligand substitution rates, the reactivity of the ligands themselves, and redox. Ligand selection is a critical consideration in many practical areas, including bioinorganic and medicinal chemistry, homogeneous catalysis, and environmental chemistry.Ligands are classified in many ways like : their charge, their size (bulk), the identity of the coordinating atom(s), and the number of electrons donated to the metal (denticity or hapticity). The size of a ligand is indicated by its cone angle.