
Powerpoint
... The characteristics of the continuous brainwaves can help identify abnormal brain activity and different stages of sleep and arousal By dividing the continuous wave into segments called evoked response potentials or event-related potentials (ERPs), each beginning with a particular event, one can cha ...
... The characteristics of the continuous brainwaves can help identify abnormal brain activity and different stages of sleep and arousal By dividing the continuous wave into segments called evoked response potentials or event-related potentials (ERPs), each beginning with a particular event, one can cha ...
Chapter 1
... The characteristics of the continuous brainwaves can help identify abnormal brain activity and different stages of sleep and arousal By dividing the continuous wave into segments called evoked response potentials or event-related potentials (ERPs), each beginning with a particular event, one can cha ...
... The characteristics of the continuous brainwaves can help identify abnormal brain activity and different stages of sleep and arousal By dividing the continuous wave into segments called evoked response potentials or event-related potentials (ERPs), each beginning with a particular event, one can cha ...
copyright 2004 scientific american, inc.
... stimulus is by devoting more brain cells to the processing of that stimulus. Although it is not possible to record from single neurons in humans during learning, brain-imaging studies can detect changes in the average magnitude of responses of thousands of cells in various parts of the cortex. In 19 ...
... stimulus is by devoting more brain cells to the processing of that stimulus. Although it is not possible to record from single neurons in humans during learning, brain-imaging studies can detect changes in the average magnitude of responses of thousands of cells in various parts of the cortex. In 19 ...
The ventral striatum in goal-directed behavior and - UvA-DARE
... will be spared. The ‘multiple trace’ theory posits that episodic memories exhibit a life-long dependency on the hippocampus (Nadel and Moscovitch, 1997). This theory states that the memory gains strength each time an episodic memory is retrieved and re-encoded, leading to the formation of multiple t ...
... will be spared. The ‘multiple trace’ theory posits that episodic memories exhibit a life-long dependency on the hippocampus (Nadel and Moscovitch, 1997). This theory states that the memory gains strength each time an episodic memory is retrieved and re-encoded, leading to the formation of multiple t ...
Psy I Brain and Behavior PPT 2016
... doughnut-shaped system of neural structures at the border of the brainstem and cerebrum, associated with emotions such as fear, aggression and drives for food and sex. It includes the hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus. ...
... doughnut-shaped system of neural structures at the border of the brainstem and cerebrum, associated with emotions such as fear, aggression and drives for food and sex. It includes the hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus. ...
of sleep
... “border”) the evolutionarily oldest and newest brain areas, and between the cerebral hemispheres (see next slide) • Associated with basic/primitive emotions and drives and memory formation • Includes: – Amygdala – Hypothalamus – Hippocampus ...
... “border”) the evolutionarily oldest and newest brain areas, and between the cerebral hemispheres (see next slide) • Associated with basic/primitive emotions and drives and memory formation • Includes: – Amygdala – Hypothalamus – Hippocampus ...
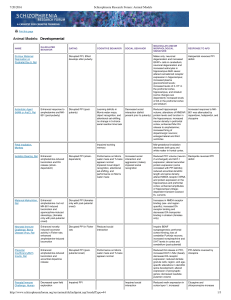
Developmental - Schizophrenia Research Forum
... Y maze and radial arm maze; no apparent deficits in latent inhibition, may or may not show spatial memory defict in water maze task ...
... Y maze and radial arm maze; no apparent deficits in latent inhibition, may or may not show spatial memory defict in water maze task ...
CNS
... from one side of the organ brain with the other side form synapses on a second common d. Locus a ii. sense Defines the location to the CNS of the ii.from Share a common function ii. Commonly referred to as the iii. Fissure: a deep grooveoccipital lobe limbic lobe caudally located occipital lobes i. ...
... from one side of the organ brain with the other side form synapses on a second common d. Locus a ii. sense Defines the location to the CNS of the ii.from Share a common function ii. Commonly referred to as the iii. Fissure: a deep grooveoccipital lobe limbic lobe caudally located occipital lobes i. ...
Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12
... to draw their own on a piece of paper. Label and discuss the functions of the parts listed above. Second, discuss the midbrain. The midbrain supports reflexes and other vital functions such as hunger. Draw the midbrain and label and discuss the parts above. Allow the students to draw it on their own ...
... to draw their own on a piece of paper. Label and discuss the functions of the parts listed above. Second, discuss the midbrain. The midbrain supports reflexes and other vital functions such as hunger. Draw the midbrain and label and discuss the parts above. Allow the students to draw it on their own ...
3A & 3B PowerPoint
... The neuron is a mini decision maker. It received info from thousands of other neurons-some excitatory (like pushing the gas pedal). Others are inhibitory (like pushing the breaks). If the excitatory signals, minus the inhibitory signals exceed a minimum intensity, called the absolute threshold, then ...
... The neuron is a mini decision maker. It received info from thousands of other neurons-some excitatory (like pushing the gas pedal). Others are inhibitory (like pushing the breaks). If the excitatory signals, minus the inhibitory signals exceed a minimum intensity, called the absolute threshold, then ...
File - Conversations
... Astonishingly, before a baby is born is has already grown DOUBLE the number of neurons that it will need. In the last month or 2 of pregnancy the brain destroys half its brain cells! However, these billions of brain cells we are born with need to be wired up. Baby’s brain signals move slowly (you ca ...
... Astonishingly, before a baby is born is has already grown DOUBLE the number of neurons that it will need. In the last month or 2 of pregnancy the brain destroys half its brain cells! However, these billions of brain cells we are born with need to be wired up. Baby’s brain signals move slowly (you ca ...
The Maternal Brain
... reproductive hormones, regulate responses such as aggression Noted neuroscientist Paul MacLean of the National Institute and sexuality in rats, hamsters, cats and dogs. Further pio- of Mental Health has proposed that the neural pathways from neering work by Daniel S. Lehrman and Jay S. Rosenblatt, t ...
... reproductive hormones, regulate responses such as aggression Noted neuroscientist Paul MacLean of the National Institute and sexuality in rats, hamsters, cats and dogs. Further pio- of Mental Health has proposed that the neural pathways from neering work by Daniel S. Lehrman and Jay S. Rosenblatt, t ...
Sonia Gasparini, PhD Degrees Assistant Professor of Cell Biology & Anatomy and
... The enthorhinal cortex is a key relay structure for the flow of information between the hippocampus and the neocortex. Not only does it act as a primary interface, it also plays a critical role in the computation of multi-sensory and cognitive modalities. The latter function is clearly supported by ...
... The enthorhinal cortex is a key relay structure for the flow of information between the hippocampus and the neocortex. Not only does it act as a primary interface, it also plays a critical role in the computation of multi-sensory and cognitive modalities. The latter function is clearly supported by ...
View Full PDF - Biochemical Society Transactions
... neuroendocrine and autonomic functions. In the hypothalamus, UCP2 mRNA is found in at least four structures, playing a very important role in the control of food intake and energy expenditure. UCP2 mRNA is indeed expressed in the paraventricular, dorsomedial, ventromedial and arcuate nuclei [21]. In ...
... neuroendocrine and autonomic functions. In the hypothalamus, UCP2 mRNA is found in at least four structures, playing a very important role in the control of food intake and energy expenditure. UCP2 mRNA is indeed expressed in the paraventricular, dorsomedial, ventromedial and arcuate nuclei [21]. In ...
The Brain and Addition
... she experiences unnaturally intense feelings of pleasure. The limbic system is flooded with dopamine. Of course, drugs have other effects, too; a first-time smoker may also cough and feel nauseous from toxic chemicals in a tobacco or marijuana cigarette. ...
... she experiences unnaturally intense feelings of pleasure. The limbic system is flooded with dopamine. Of course, drugs have other effects, too; a first-time smoker may also cough and feel nauseous from toxic chemicals in a tobacco or marijuana cigarette. ...
The seasonal hippocampus of food-storing birds.
... a relatively stable and abundant supply of new neurons to work with. Hippocampal seasonality may potentially be as variable as the seasonality of food storing itself. 1. Food-storing chickadees and non-storing sparrows If seasonal neurogenesis in the hippocampus of adult chickadees is an adaptation ...
... a relatively stable and abundant supply of new neurons to work with. Hippocampal seasonality may potentially be as variable as the seasonality of food storing itself. 1. Food-storing chickadees and non-storing sparrows If seasonal neurogenesis in the hippocampus of adult chickadees is an adaptation ...
The Chemical Senses
... some responsiveness to all 4 classic submodalities, but typically respond best to one of the 4. From the brainstem nuclei the information passes to the thalamus and then to the tongue-mouth area of the primary somatosensory cortical map. Note that this is a non-decussating pathway. ...
... some responsiveness to all 4 classic submodalities, but typically respond best to one of the 4. From the brainstem nuclei the information passes to the thalamus and then to the tongue-mouth area of the primary somatosensory cortical map. Note that this is a non-decussating pathway. ...
Limbic system

The limbic system (or paleomammalian brain) is a complex set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, right under the cerebrum. It is not a separate system but a collection of structures from the telencephalon, diencephalon, and mesencephalon. It includes the olfactory bulbs, hippocampus, amygdala, anterior thalamic nuclei, fornix, columns of fornix, mammillary body, septum pellucidum, habenular commissure, cingulate gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, limbic cortex, and limbic midbrain areas.The limbic system supports a variety of functions including epinephrine flow, emotion, behavior, motivation, long-term memory, and olfaction. Emotional life is largely housed in the limbic system, and it has a great deal to do with the formation of memories.Although the term only originated in the 1940s, some neuroscientists, including Joseph LeDoux, have suggested that the concept of a functionally unified limbic system should be abandoned as obsolete because it is grounded mainly in historical concepts of brain anatomy that are no longer accepted as accurate.



















![[j26]Chapter 8#](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009531099_1-530d7c194a24d89985e18840d7e0199e-300x300.png)


