The Ventral Striatopallidum and Extended Amygdala in
... aversion (Goodson & Wang, 2006) via Vasotoxin-positive neurons. The intraamygdaloid bed nucleus of the stria terminalis contains only a few cells bordering the dorsal part of the medial nucleus laterally. It is interspersed by fibers projecting to the stria terminalis. The medial sublenticular EA is ...
... aversion (Goodson & Wang, 2006) via Vasotoxin-positive neurons. The intraamygdaloid bed nucleus of the stria terminalis contains only a few cells bordering the dorsal part of the medial nucleus laterally. It is interspersed by fibers projecting to the stria terminalis. The medial sublenticular EA is ...
Brain: The Inside Story Educator`s Guide
... The limbic system in the brains of mammals supports more complex behavior and social relations, as well as emotions like fear, rage, and desire. Primates (including humans) recognize facial expressions, communicate, and maintain complex social relationships using an area of the brain called the pref ...
... The limbic system in the brains of mammals supports more complex behavior and social relations, as well as emotions like fear, rage, and desire. Primates (including humans) recognize facial expressions, communicate, and maintain complex social relationships using an area of the brain called the pref ...
Tracking the Emergence of Conceptual Knowledge during Human
... Vargha-Khadem et al., 1997). As such, whether the hippocampus, or instead neocortical areas within the medial temporal lobe (MTL) or prefrontal cortex (PFC) (Cohen and Eichenbaum, 1993; Eichenbaum, 2004; McClelland et al., 1995; Miller et al., 2002; Norman and O’Reilly, 2003; Vargha-Khadem et al., 1 ...
... Vargha-Khadem et al., 1997). As such, whether the hippocampus, or instead neocortical areas within the medial temporal lobe (MTL) or prefrontal cortex (PFC) (Cohen and Eichenbaum, 1993; Eichenbaum, 2004; McClelland et al., 1995; Miller et al., 2002; Norman and O’Reilly, 2003; Vargha-Khadem et al., 1 ...
Cortex and Mind Chapter 5
... von Helmholtz found proof for his theory in patients with paralysis of the eye muscles. (This can also be tested experimentally by injecting curare into the eye muscles). These patients perceived that whenever they tried to move their eyes, the world would seem to jump in the same direction as the ...
... von Helmholtz found proof for his theory in patients with paralysis of the eye muscles. (This can also be tested experimentally by injecting curare into the eye muscles). These patients perceived that whenever they tried to move their eyes, the world would seem to jump in the same direction as the ...
PDF
... various combinatorial convergent inputs. As the evolutionarily conserved logic, its validation requires experimental demonstrations of the following three major properties: (1) Anatomical prevalence—FCMs are prevalent across neural circuits, regardless of gross anatomical shapes; (2) Species conserv ...
... various combinatorial convergent inputs. As the evolutionarily conserved logic, its validation requires experimental demonstrations of the following three major properties: (1) Anatomical prevalence—FCMs are prevalent across neural circuits, regardless of gross anatomical shapes; (2) Species conserv ...
Ch14 notes Martini 9e
... 14-8 The Limbic System • The Limbic System • Is a functional grouping that: • Establishes emotional states • Links conscious functions of cerebral cortex with autonomic functions of brain stem • Facilitates memory storage and retrieval © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. • Components of the Limbic System ...
... 14-8 The Limbic System • The Limbic System • Is a functional grouping that: • Establishes emotional states • Links conscious functions of cerebral cortex with autonomic functions of brain stem • Facilitates memory storage and retrieval © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. • Components of the Limbic System ...
Neurological Factors in Violent Behavior (The Dyscontrol Syndrome)
... which is interposed between the diencephalon and the neocortex. There has been much discussion as to the anatomical limits of the system, but the portions of it which are pertinent to the study of rage are the amygdala and the hippocampus in the temporal lobe, the hypothalamus, the cingulate gyri an ...
... which is interposed between the diencephalon and the neocortex. There has been much discussion as to the anatomical limits of the system, but the portions of it which are pertinent to the study of rage are the amygdala and the hippocampus in the temporal lobe, the hypothalamus, the cingulate gyri an ...
Age-related differences in brain activity underlying identification of
... Finally, the insula is thought to be critically involved in perceiving disgust (Phillips et al., 1997; Sprengelmeyer et al., 1998; Calder et al., 2000; Anderson et al., 2003), likely due to its role in visceral and somatosensory responses (Adolphs, 2002). The effect of aging on social cognition has ...
... Finally, the insula is thought to be critically involved in perceiving disgust (Phillips et al., 1997; Sprengelmeyer et al., 1998; Calder et al., 2000; Anderson et al., 2003), likely due to its role in visceral and somatosensory responses (Adolphs, 2002). The effect of aging on social cognition has ...
What do you notice? - Neural Crossroads Laboratory
... CA1 pyramidal neurons have a resonance frequency at theta when slightly depolarized or hyperpolarized: due to hyperpolarization-activated non-specific cation HCN channels ...
... CA1 pyramidal neurons have a resonance frequency at theta when slightly depolarized or hyperpolarized: due to hyperpolarization-activated non-specific cation HCN channels ...
The fish: What potential for awareness?
... in the skin form what can be called the nociceptive functional unit. The thalamus has an intricate network of connections to forebrain (cortical) structures. These include connections from lateral thalamic nuclei to the somatosensory cortex and connections from the medial thalamic nuclei to other ...
... in the skin form what can be called the nociceptive functional unit. The thalamus has an intricate network of connections to forebrain (cortical) structures. These include connections from lateral thalamic nuclei to the somatosensory cortex and connections from the medial thalamic nuclei to other ...
clinical assessment of dementia
... between age-related memory impairment and dementia for ways to better distinguish those individuals who will later develop significant cognitive impairment. The pharmaceutical industry is developing over 70 medications for specific types of dementia. Clinicians will be tasked to distinguish common t ...
... between age-related memory impairment and dementia for ways to better distinguish those individuals who will later develop significant cognitive impairment. The pharmaceutical industry is developing over 70 medications for specific types of dementia. Clinicians will be tasked to distinguish common t ...
Anatomy Written Exam #2 Cranial Nerves Introduction Embryological
... i. Afferents from thalamus and cerebral cortex ii. GABA efferents back to thalamus c. Functional Organization of Thalamic Nuclei All thalamic nuclei, except or the reticular nucleus, project to IPSILATERAL cerebral cortex 1. Specific Nuclei- have point to point projections between individual thala ...
... i. Afferents from thalamus and cerebral cortex ii. GABA efferents back to thalamus c. Functional Organization of Thalamic Nuclei All thalamic nuclei, except or the reticular nucleus, project to IPSILATERAL cerebral cortex 1. Specific Nuclei- have point to point projections between individual thala ...
Computational Intelligence in a Human Brain Model
... a) Secure their own position, a position or an action in life, similar with an action in a chess game Define securing the position in the action, in life, or in the attack in order to assure the ‘Survival’ as a being, or ‘eliminating adversaries’ in terms of assuring ‘food for life’. b) Survival as ...
... a) Secure their own position, a position or an action in life, similar with an action in a chess game Define securing the position in the action, in life, or in the attack in order to assure the ‘Survival’ as a being, or ‘eliminating adversaries’ in terms of assuring ‘food for life’. b) Survival as ...
Anatomy of Neuropsychiatry : The New Anatomy of the
... Lennart Heimer is the principal author of Chapters 1–3. Chapters 1 and 2 provide a brief description of the origin and evolution of the concept of the limbic system and some deficiencies attributed to it as a basis for understanding behavior and human neuropsychiatric disorders. Chapter 3 describes ...
... Lennart Heimer is the principal author of Chapters 1–3. Chapters 1 and 2 provide a brief description of the origin and evolution of the concept of the limbic system and some deficiencies attributed to it as a basis for understanding behavior and human neuropsychiatric disorders. Chapter 3 describes ...
The honeybee as a model for understanding the basis of cognition
... species21 (BOX 2). Cognitive aspects of learning. Learning of visual, olfactory, gustatory and mechanosensory cues at a feeding site is a fast process in foraging bees. Foragers group visual patterns into categories (‘generalizing’) that do not necessarily resemble natural patterns22, indicating tha ...
... species21 (BOX 2). Cognitive aspects of learning. Learning of visual, olfactory, gustatory and mechanosensory cues at a feeding site is a fast process in foraging bees. Foragers group visual patterns into categories (‘generalizing’) that do not necessarily resemble natural patterns22, indicating tha ...
ch14_lecture - Napa Valley College
... Introduction • The human brain is extremely complex • Brain function is associated clinically with what it means to be alive or dead • Importance of the brain hasn’t always been well understood – Aristotle thought brain just cooled blood – But Hippocrates (earlier) had more accurate view of brain’s ...
... Introduction • The human brain is extremely complex • Brain function is associated clinically with what it means to be alive or dead • Importance of the brain hasn’t always been well understood – Aristotle thought brain just cooled blood – But Hippocrates (earlier) had more accurate view of brain’s ...
Cortical Diseases and Cortical Localization
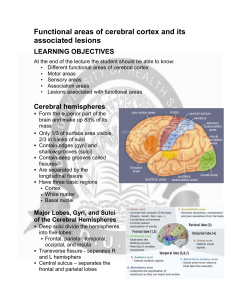
... cerebral cortex, which is the folded outer layer of the brain, is only 2-4 mm thick, and contains 50-100 billion neurons. It produces our thoughts, perceptions and emotions. Structurally, the cortex is organized into discrete sectors that contain different cell types. These components control distin ...
... cerebral cortex, which is the folded outer layer of the brain, is only 2-4 mm thick, and contains 50-100 billion neurons. It produces our thoughts, perceptions and emotions. Structurally, the cortex is organized into discrete sectors that contain different cell types. These components control distin ...
Suzuki and Eichenbaum, 2000
... somatosensory, as well as auditory and olfactory areas, reflecting the more prominent role of these other sensory modalities in this species. This difference across species can be appreciated by comparing the patterns of cortical inputs to the perirhinal cortex in monkeys (black lines) to those in r ...
... somatosensory, as well as auditory and olfactory areas, reflecting the more prominent role of these other sensory modalities in this species. This difference across species can be appreciated by comparing the patterns of cortical inputs to the perirhinal cortex in monkeys (black lines) to those in r ...
File - Joris Vangeneugden
... effects on a person’s mental sanity. Flashbacks, often expressed in nightmares, confront the person with the traumatic event otherwise avoided as much as possible in both actions and thoughts. A general hyperarousal debilitates the person and seriously constrains the outlook on the future. The combi ...
... effects on a person’s mental sanity. Flashbacks, often expressed in nightmares, confront the person with the traumatic event otherwise avoided as much as possible in both actions and thoughts. A general hyperarousal debilitates the person and seriously constrains the outlook on the future. The combi ...
Cognitive impairment and associated loss in brain white
... of aircraft cabin air by engine oil fumes poses a serious aviation safety concern for both aircrew and passengers, mainly because of its detrimental effects on white matter. The past few years this topic has received quite extensive attention in the lay press, following the deaths of two British Air ...
... of aircraft cabin air by engine oil fumes poses a serious aviation safety concern for both aircrew and passengers, mainly because of its detrimental effects on white matter. The past few years this topic has received quite extensive attention in the lay press, following the deaths of two British Air ...
Limbic system

The limbic system (or paleomammalian brain) is a complex set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, right under the cerebrum. It is not a separate system but a collection of structures from the telencephalon, diencephalon, and mesencephalon. It includes the olfactory bulbs, hippocampus, amygdala, anterior thalamic nuclei, fornix, columns of fornix, mammillary body, septum pellucidum, habenular commissure, cingulate gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, limbic cortex, and limbic midbrain areas.The limbic system supports a variety of functions including epinephrine flow, emotion, behavior, motivation, long-term memory, and olfaction. Emotional life is largely housed in the limbic system, and it has a great deal to do with the formation of memories.Although the term only originated in the 1940s, some neuroscientists, including Joseph LeDoux, have suggested that the concept of a functionally unified limbic system should be abandoned as obsolete because it is grounded mainly in historical concepts of brain anatomy that are no longer accepted as accurate.