3.10 notes
... Neuroscience of Memory • Procedural memories seem to be stored in the cerebellum • PET scans suggest short-term memories are stored in the prefrontal cortex and temporal lobe • Consolidation – Changes in structure and functioning of neurons when a memory is formed ...
... Neuroscience of Memory • Procedural memories seem to be stored in the cerebellum • PET scans suggest short-term memories are stored in the prefrontal cortex and temporal lobe • Consolidation – Changes in structure and functioning of neurons when a memory is formed ...
Chapter Six
... Theories of executive function In the Norman-Shallice (1980) model, action schemas are activated by stimuli or other schemas and produce a behavior. • Action schemas are like scripts in that they specify what to do in a specific situation. They control automatic attentional processes. • Action sche ...
... Theories of executive function In the Norman-Shallice (1980) model, action schemas are activated by stimuli or other schemas and produce a behavior. • Action schemas are like scripts in that they specify what to do in a specific situation. They control automatic attentional processes. • Action sche ...
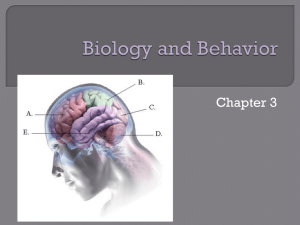
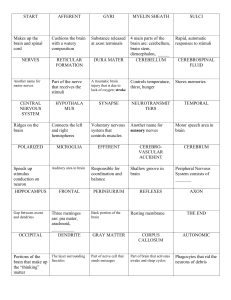
Ch 3 biology and Behavioir Notes
... Structures deep within the brain control your emotions and memories. Thalamus acts as a gatekeeper for messages passed between the spinal cord and the cerebral hemispheres. Hypothalamus controls emotions such as exhilaration and anger. ...
... Structures deep within the brain control your emotions and memories. Thalamus acts as a gatekeeper for messages passed between the spinal cord and the cerebral hemispheres. Hypothalamus controls emotions such as exhilaration and anger. ...
Reviewing the Biological Processes of the Brain
... Relays all sensory information to specific perception areas of the brain, with the exception of smell Part of the “old brain” – it controls survival elements such as hunger, thirst, emotion, sex drive and reproduction. Works in conjunction with the pituitary gland. Secretes hormones as “directed” by ...
... Relays all sensory information to specific perception areas of the brain, with the exception of smell Part of the “old brain” – it controls survival elements such as hunger, thirst, emotion, sex drive and reproduction. Works in conjunction with the pituitary gland. Secretes hormones as “directed” by ...
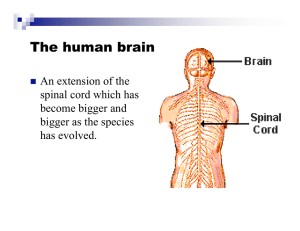
The Brain
... brainstem Enables non- verbal behavior & memory Decision making Coordinate voluntary movement and balance ...
... brainstem Enables non- verbal behavior & memory Decision making Coordinate voluntary movement and balance ...
Ch 3
... psychological functioning? 19. What is plasticity and for what mental function does it play a particularly important role? ...
... psychological functioning? 19. What is plasticity and for what mental function does it play a particularly important role? ...
Hippocampus - Solon City Schools
... • Maintains homeostasis • Brain’s Reward system – what neurotransmitter? ...
... • Maintains homeostasis • Brain’s Reward system – what neurotransmitter? ...
WebQuest: The Structure of the Nervous System
... 3. Label the cerebellum on the diagram above. 4. What does the cerebellum do? 5. The limbic system is often referred to as the ____________ brain. 6. Where is the limbic system found? 7. List the function of each of the parts of the limbic system: Thalamus: Hypothalamus: ...
... 3. Label the cerebellum on the diagram above. 4. What does the cerebellum do? 5. The limbic system is often referred to as the ____________ brain. 6. Where is the limbic system found? 7. List the function of each of the parts of the limbic system: Thalamus: Hypothalamus: ...
Memory Lecture
... 1. the nervous system is comprised of peripheral (PNS) and central (CNS) components Fig. 14.1/Table 14.1 CNS contains the brain and spinal cord PNS contains nerves which carry information to and from the CNS 2. The brain has 3 major areas (which each have subdivisions) hindbrain, midbrain and ...
... 1. the nervous system is comprised of peripheral (PNS) and central (CNS) components Fig. 14.1/Table 14.1 CNS contains the brain and spinal cord PNS contains nerves which carry information to and from the CNS 2. The brain has 3 major areas (which each have subdivisions) hindbrain, midbrain and ...
Three Types of Behavior : involuntary responses to stimuli
... Localization of Semantic Memories Semantic memories are _______________________ in the cortex ___________________________ : inability to recognize common faces Localization of Memories Encoding and retrieval may activate different areas Episodic Memory and the Cortex Greater ________________________ ...
... Localization of Semantic Memories Semantic memories are _______________________ in the cortex ___________________________ : inability to recognize common faces Localization of Memories Encoding and retrieval may activate different areas Episodic Memory and the Cortex Greater ________________________ ...
Learning and Memory Lecture Notes Page
... Localization of Semantic Memories Semantic memories are _______________________ in the cortex ___________________________ : inability to recognize common faces Localization of Memories Encoding and retrieval may activate different areas Episodic Memory and the Cortex Greater ________________________ ...
... Localization of Semantic Memories Semantic memories are _______________________ in the cortex ___________________________ : inability to recognize common faces Localization of Memories Encoding and retrieval may activate different areas Episodic Memory and the Cortex Greater ________________________ ...
Module 4 Notes
... The oldest method of studying the brain involved observing the effects of brain diseases and injuries. Powerful new techniques now reveal brain structures and activities in the living brain. By surgically lesioning and electrically stimulating specific brain areas, by recording electrical activity o ...
... The oldest method of studying the brain involved observing the effects of brain diseases and injuries. Powerful new techniques now reveal brain structures and activities in the living brain. By surgically lesioning and electrically stimulating specific brain areas, by recording electrical activity o ...
Amydala
... claustrum is also called ventral pallium and its embryological origin is not well understood. ...
... claustrum is also called ventral pallium and its embryological origin is not well understood. ...
Review #2 - Course Notes
... d. an individual reflexively withdraws from a pain stimulus. 28. The chemical messenger at every synaptic gap between a motor neuron and a muscle is: a. epinephrine. b. acetylcholine. c. curare. d. dopamine. 29. The right hemisphere is superior to the left at: a. solving arithmetic problems. b. reco ...
... d. an individual reflexively withdraws from a pain stimulus. 28. The chemical messenger at every synaptic gap between a motor neuron and a muscle is: a. epinephrine. b. acetylcholine. c. curare. d. dopamine. 29. The right hemisphere is superior to the left at: a. solving arithmetic problems. b. reco ...
STUDY GUIDE: UNIT III – BIOLOGICAL BASES OF BEHAVIOR AP
... 11-1: How do neuroscientists study the brain’s connections to behavior and mind? EEG, CT, PET, MRI, fMRI 11-2: What are the functions of important lower-level brain structures? Brainstem & its parts Cerebellum 11-3: What are the limbic system’s structures and functions? Amygdala, hypothalamu ...
... 11-1: How do neuroscientists study the brain’s connections to behavior and mind? EEG, CT, PET, MRI, fMRI 11-2: What are the functions of important lower-level brain structures? Brainstem & its parts Cerebellum 11-3: What are the limbic system’s structures and functions? Amygdala, hypothalamu ...
Nervous-System
... and where the memories are stored in the brain. It is thought that this determination is based on how huge an emotional response an event invokes Cingulate Gyrus - a fold in the brain involved with sensory input concerning emotions and the regulation of aggressive behavior. ...
... and where the memories are stored in the brain. It is thought that this determination is based on how huge an emotional response an event invokes Cingulate Gyrus - a fold in the brain involved with sensory input concerning emotions and the regulation of aggressive behavior. ...
NAlab13_LimbicSystem..
... into the basolateral, central, and corticomedial nuclei. Identify their approximate locations. The amygdala gives rise to two major pathways, the stria terminalis and the ventral amygdalofugal pathway. The stria terminalis is a C-shaped structure which exits from the caudal end of the amygdala and c ...
... into the basolateral, central, and corticomedial nuclei. Identify their approximate locations. The amygdala gives rise to two major pathways, the stria terminalis and the ventral amygdalofugal pathway. The stria terminalis is a C-shaped structure which exits from the caudal end of the amygdala and c ...
Limbic system

The limbic system (or paleomammalian brain) is a complex set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, right under the cerebrum. It is not a separate system but a collection of structures from the telencephalon, diencephalon, and mesencephalon. It includes the olfactory bulbs, hippocampus, amygdala, anterior thalamic nuclei, fornix, columns of fornix, mammillary body, septum pellucidum, habenular commissure, cingulate gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, limbic cortex, and limbic midbrain areas.The limbic system supports a variety of functions including epinephrine flow, emotion, behavior, motivation, long-term memory, and olfaction. Emotional life is largely housed in the limbic system, and it has a great deal to do with the formation of memories.Although the term only originated in the 1940s, some neuroscientists, including Joseph LeDoux, have suggested that the concept of a functionally unified limbic system should be abandoned as obsolete because it is grounded mainly in historical concepts of brain anatomy that are no longer accepted as accurate.