Lecture 2b - Rio Hondo College
... temperature control Emotional behavior Fight or flight responses Termed a “pleasure center” ...
... temperature control Emotional behavior Fight or flight responses Termed a “pleasure center” ...
Medial Longitudinal Fissure
... Connect the Medulla to the Midbrain and Thalamus. Contains numerous tracts including the Cortico-spinal tracts and Reticular Formation ...
... Connect the Medulla to the Midbrain and Thalamus. Contains numerous tracts including the Cortico-spinal tracts and Reticular Formation ...
WHY STUDY THE BRAIN IN PSYCHOLOGY?
... • An oval mass of nerve cells • Acts as a relay station to send incoming and outgoing messages to and from various parts of brain. – Ex. If you want to move your big toe, the brain sends a message to the thalamus, which then sends it to the correct place on the motor strip. ...
... • An oval mass of nerve cells • Acts as a relay station to send incoming and outgoing messages to and from various parts of brain. – Ex. If you want to move your big toe, the brain sends a message to the thalamus, which then sends it to the correct place on the motor strip. ...
Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior
... Receives info from the sensory neurons and routes it to the higher brain regions that deal with seeing, hearing, tasting, and touching ...
... Receives info from the sensory neurons and routes it to the higher brain regions that deal with seeing, hearing, tasting, and touching ...
Chapter 17 Review Jeopardy
... – B) controls voluntary actions – C) communicates with and coordinates activities of other parts of the brain – D) all of the above are true ...
... – B) controls voluntary actions – C) communicates with and coordinates activities of other parts of the brain – D) all of the above are true ...
The Nervous System
... 4. The brain is hierarchically organized 5. The brain systems are organized so that one side of the brain controls the other side of the body ...
... 4. The brain is hierarchically organized 5. The brain systems are organized so that one side of the brain controls the other side of the body ...
From Molecules to Mind: New Discoveries in Neuroscience – Spring
... which is relatively larger in women’s brains than in men’s. The cerebrum is positioned over and around most other brain structures, and its four lobes are specialized by function but are richly connected. The outer 3 millimeters of “gray matter” is the cerebral cortex which consists of closely packe ...
... which is relatively larger in women’s brains than in men’s. The cerebrum is positioned over and around most other brain structures, and its four lobes are specialized by function but are richly connected. The outer 3 millimeters of “gray matter” is the cerebral cortex which consists of closely packe ...
NEUROBIOLOGICAL BASIS OF BEHAVIOR
... Other Functions of Limbic System • Olfactory Functions • Feeding Functions (We won’t study these, but consider the relationships between emotions, pleasure, smell, and food intake!) ...
... Other Functions of Limbic System • Olfactory Functions • Feeding Functions (We won’t study these, but consider the relationships between emotions, pleasure, smell, and food intake!) ...
The Teenage Brain - Welcome to Senior Biology
... continues from back to front through early 20’s ...
... continues from back to front through early 20’s ...
CNS: Spinal Cord Function
... information and sends it to the appropriate area of the cerebrum. • Cerebellum: Receives sensory input from the eyes, ears, joints, and muscles about the position of body parts. It also receives information from the cerebral cortex as to where those parts should be located. Therefore it plays a role ...
... information and sends it to the appropriate area of the cerebrum. • Cerebellum: Receives sensory input from the eyes, ears, joints, and muscles about the position of body parts. It also receives information from the cerebral cortex as to where those parts should be located. Therefore it plays a role ...
Wilkinson Handout 2014
... evaluative ‘top-down’ processes underlying social interactions. • In PTSD direct gaze leads to sustained activation of a sub-cortical route of eye-contact processing that is an innate alarm system Steuwe et al 2012 ...
... evaluative ‘top-down’ processes underlying social interactions. • In PTSD direct gaze leads to sustained activation of a sub-cortical route of eye-contact processing that is an innate alarm system Steuwe et al 2012 ...
Slide ()
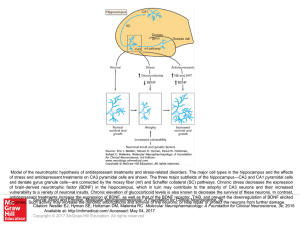
... Model of the neurotrophic hypothesis of antidepressant treatments and stress-related disorders. The major cell types in the hippocampus and the effects of stress and antidepressant treatments on CA3 pyramidal cells are shown. The three major subfields of the hippocampus—CA3 and CA1 pyramidal cells a ...
... Model of the neurotrophic hypothesis of antidepressant treatments and stress-related disorders. The major cell types in the hippocampus and the effects of stress and antidepressant treatments on CA3 pyramidal cells are shown. The three major subfields of the hippocampus—CA3 and CA1 pyramidal cells a ...
The Brain for Not-So
... Neurogenesis does not stop at birth Occurs in normal adult brain Adds neurons in hippocampus ...
... Neurogenesis does not stop at birth Occurs in normal adult brain Adds neurons in hippocampus ...
Quiz scorers
... Johns Hopkins scientists have discovered to their surprise that nerves in the mammalian brain's white matter do more than just ferry information between different brain regions, but in fact process information the way gray matter cells do. The discovery in mouse cells, outlined in Nature Neuroscienc ...
... Johns Hopkins scientists have discovered to their surprise that nerves in the mammalian brain's white matter do more than just ferry information between different brain regions, but in fact process information the way gray matter cells do. The discovery in mouse cells, outlined in Nature Neuroscienc ...
Exam 1 Review - Central Connecticut State University
... • 34. Which of the following is the most likely role of the thalamus? • A. Controlling movement • B. Initiating sleep and waking • C. Homeostasis and endocrine function • D. Acting as a sensory gateway to the cortex ...
... • 34. Which of the following is the most likely role of the thalamus? • A. Controlling movement • B. Initiating sleep and waking • C. Homeostasis and endocrine function • D. Acting as a sensory gateway to the cortex ...
Higher brain functions
... • Working memory consists of central executive in the dorsolateral part of prefrontal cortex and verbal system for retaining verbal memories and a parallel visuospatial system for retaining visual and spatial aspects of objects • Prefrontal cortex has a connection with hippocampus and parahippocampa ...
... • Working memory consists of central executive in the dorsolateral part of prefrontal cortex and verbal system for retaining verbal memories and a parallel visuospatial system for retaining visual and spatial aspects of objects • Prefrontal cortex has a connection with hippocampus and parahippocampa ...
Einstein`s Brain
... Einstein’s Brain: Parietal lobe • Parietal lobes are responsible for visual and 3D representation and mathematical reasoning. • E’s inferior parietal lobules are not divided by major cleft – Not seen in 191 controls! – Axons were connected in unusual ways • “might have allowed for his brilliance an ...
... Einstein’s Brain: Parietal lobe • Parietal lobes are responsible for visual and 3D representation and mathematical reasoning. • E’s inferior parietal lobules are not divided by major cleft – Not seen in 191 controls! – Axons were connected in unusual ways • “might have allowed for his brilliance an ...
einsteins-brain
... Einstein’s Brain: Parietal lobe • Parietal lobes are responsible for visual and 3D representation and mathematical reasoning. • E’s inferior parietal lobules are not divided by major cleft – Not seen in 191 controls! – Axons were connected in unusual ways • “might have allowed for his brilliance an ...
... Einstein’s Brain: Parietal lobe • Parietal lobes are responsible for visual and 3D representation and mathematical reasoning. • E’s inferior parietal lobules are not divided by major cleft – Not seen in 191 controls! – Axons were connected in unusual ways • “might have allowed for his brilliance an ...
Limbic system

The limbic system (or paleomammalian brain) is a complex set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, right under the cerebrum. It is not a separate system but a collection of structures from the telencephalon, diencephalon, and mesencephalon. It includes the olfactory bulbs, hippocampus, amygdala, anterior thalamic nuclei, fornix, columns of fornix, mammillary body, septum pellucidum, habenular commissure, cingulate gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, limbic cortex, and limbic midbrain areas.The limbic system supports a variety of functions including epinephrine flow, emotion, behavior, motivation, long-term memory, and olfaction. Emotional life is largely housed in the limbic system, and it has a great deal to do with the formation of memories.Although the term only originated in the 1940s, some neuroscientists, including Joseph LeDoux, have suggested that the concept of a functionally unified limbic system should be abandoned as obsolete because it is grounded mainly in historical concepts of brain anatomy that are no longer accepted as accurate.