soil intro - Ms Kim`s Biology Class
... • The activity of living plants and animals (macro and microorganisms) has major significance on the development of soil. • Microorganisms help develop soils by decomposing organic matter and forming weak acids that dissolve minerals faster than would pure water. • Fibrous root systems of grasses ha ...
... • The activity of living plants and animals (macro and microorganisms) has major significance on the development of soil. • Microorganisms help develop soils by decomposing organic matter and forming weak acids that dissolve minerals faster than would pure water. • Fibrous root systems of grasses ha ...
Earth`s Crust in Motion
... • The rocks reaction to stress is called strain. The types of stress are: –Shearing –Tension –Compression ...
... • The rocks reaction to stress is called strain. The types of stress are: –Shearing –Tension –Compression ...
Weathering and Soil Formation
... differs in Bedrock is the is solid layerofofsoil rock beneath thecolor soil. and As plants shed they form a loose texture from theleaves, layers above or below it. layer called Humus is a dark-colored substance that forms as litter. The horizon is made up decay. of topsoil, a crumbly, dark plantAand ...
... differs in Bedrock is the is solid layerofofsoil rock beneath thecolor soil. and As plants shed they form a loose texture from theleaves, layers above or below it. layer called Humus is a dark-colored substance that forms as litter. The horizon is made up decay. of topsoil, a crumbly, dark plantAand ...
Organic sedimentary rocks
... Sometimes evaporites are precipitated on broad coastal salt flats called sabkhas. This specimen is from Tunisia in North Africa, where locals dig them out of the salt flats to sell to tourists. This one cost just 50 pence in 1986! ...
... Sometimes evaporites are precipitated on broad coastal salt flats called sabkhas. This specimen is from Tunisia in North Africa, where locals dig them out of the salt flats to sell to tourists. This one cost just 50 pence in 1986! ...
Many geologists study rocks and minerals, as rocks
... minerals, but their concentration may vary. For example, granite is composed primarily of quartz, feldspar and mica, but their proportion may vary from one type of granite to the next. These differences are what create the different varieties within groups of rock, such as pink granite and white gra ...
... minerals, but their concentration may vary. For example, granite is composed primarily of quartz, feldspar and mica, but their proportion may vary from one type of granite to the next. These differences are what create the different varieties within groups of rock, such as pink granite and white gra ...
Unit 3 Rocks and Minerals
... Mineral – is a naturally occurring solid crystalline substance with a distinct chemical composition and is usually inorganic. Rock – is an assemblage of minerals usually cemented together. It may contain only one type of mineral or many. Rock Type Classification – this places each rock into a catego ...
... Mineral – is a naturally occurring solid crystalline substance with a distinct chemical composition and is usually inorganic. Rock – is an assemblage of minerals usually cemented together. It may contain only one type of mineral or many. Rock Type Classification – this places each rock into a catego ...
ESCI 107 Earth Science STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY
... crustal deformation. Students learn about common earth materials that make up the Earth. The impact of weathering, erosion, running water, and glaciers on the earth’s surface and landforms is studied. Additional topics will include, but are not limited to: earthquakes, volcanoes, mass movement, geol ...
... crustal deformation. Students learn about common earth materials that make up the Earth. The impact of weathering, erosion, running water, and glaciers on the earth’s surface and landforms is studied. Additional topics will include, but are not limited to: earthquakes, volcanoes, mass movement, geol ...
Table of Contents
... and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsonglobaleditions.com © Pearson Education Limited 2015 The rights of Frederick K. Lutgens and Edward J. Tarbuck to be identified as the authors of this work have been asserted by them in accordance with the Copy ...
... and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsonglobaleditions.com © Pearson Education Limited 2015 The rights of Frederick K. Lutgens and Edward J. Tarbuck to be identified as the authors of this work have been asserted by them in accordance with the Copy ...
Y10 Earthquakes - Learning on the Loop
... Moving water is the most potent erosive force on Earth. Powered by the force of gravity, the world's rivers deliver about 20 billion tons of loose rock fragments, or sediment, to the oceans each year. Moving air, or wind, is another important transporter of sediment, especially in dry regions. When ...
... Moving water is the most potent erosive force on Earth. Powered by the force of gravity, the world's rivers deliver about 20 billion tons of loose rock fragments, or sediment, to the oceans each year. Moving air, or wind, is another important transporter of sediment, especially in dry regions. When ...
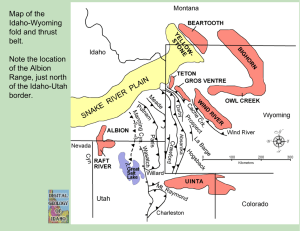
unit 1 notes - novacentral.ca
... Plains are areas of flat land with very little relief. They are found at low elevations often along coasts and in the center of continents. Plateaus are areas of flat land with little relief. They occur at high elevations and are associated with mountains. Like hills and mountains plains and plateau ...
... Plains are areas of flat land with very little relief. They are found at low elevations often along coasts and in the center of continents. Plateaus are areas of flat land with little relief. They occur at high elevations and are associated with mountains. Like hills and mountains plains and plateau ...
Minerals and Their Physical Properties
... Metamorphism is due to solid-state reactions between minerals due to change in temperature and pressure ...
... Metamorphism is due to solid-state reactions between minerals due to change in temperature and pressure ...
18 Week Review Jeopardy
... There are several different layers in the soil along a bank of a creek. Two fossils are found in the bank, one near the bottom of the bank, close to the creek, and one higher up near the top. It can probably be said that the A. fossil found near the bottom is older than the fossil found near the top ...
... There are several different layers in the soil along a bank of a creek. Two fossils are found in the bank, one near the bottom of the bank, close to the creek, and one higher up near the top. It can probably be said that the A. fossil found near the bottom is older than the fossil found near the top ...
rocks-sec 2 igneous
... elements within Earth Some heat was left over from when Earth was formed, which originally was molten ...
... elements within Earth Some heat was left over from when Earth was formed, which originally was molten ...
Unit 1: Rocks and Minerals
... Soil formation happens when rock particles, minerals, organic matter, and water are combined. The amounts of each material can be different in different types of soil. Sandy soil has more rocks and minerals. Soils in swampy areas and rain forests have more broken-down organic matter and less rock pa ...
... Soil formation happens when rock particles, minerals, organic matter, and water are combined. The amounts of each material can be different in different types of soil. Sandy soil has more rocks and minerals. Soils in swampy areas and rain forests have more broken-down organic matter and less rock pa ...
the geology of the moon
... impacts. Lunar craters resemble meteorite impact craters as the volume of displaced material is approximately equal to the estimated volume of the crater walls. (Impacts carried out in simulated laboratory environments result in craters with similar physical characteristics). They are also mostly br ...
... impacts. Lunar craters resemble meteorite impact craters as the volume of displaced material is approximately equal to the estimated volume of the crater walls. (Impacts carried out in simulated laboratory environments result in craters with similar physical characteristics). They are also mostly br ...
Document
... GL1 II KI 3c The various elements of the rock cycle may be linked directly to plate tectonic processes: (i) IGNEOUS – basaltic magmatism at oceanic spreading centres and island arcs (ii) SEDIMENTARY – erosional processes and depositional environments (iii) REGIONAL METAMORPHISM – in subduction and o ...
... GL1 II KI 3c The various elements of the rock cycle may be linked directly to plate tectonic processes: (i) IGNEOUS – basaltic magmatism at oceanic spreading centres and island arcs (ii) SEDIMENTARY – erosional processes and depositional environments (iii) REGIONAL METAMORPHISM – in subduction and o ...
left click to view and right click to download.
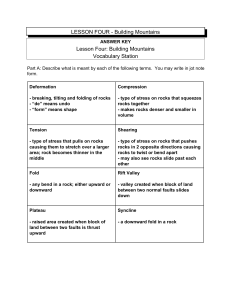
... Answers will vary. Students should include information about pressure being applied slowly will more likely cause a rock to bend. Whether or not the rock is ductile will also have an effect on folding. ...
... Answers will vary. Students should include information about pressure being applied slowly will more likely cause a rock to bend. Whether or not the rock is ductile will also have an effect on folding. ...
Word
... 13. Sedimentary rocks are the most common type of rock at the Earth’s surface, but they actually only comprise about _______ of the Earth’s crust altogether. A. 5% B. 10% C. 25% D. 50% E. 75% 13. How much of the Earth’s crust is made up of sedimentary rocks? A. 95% B. 75% C. 50% D. 25% E. 5% 13. Whi ...
... 13. Sedimentary rocks are the most common type of rock at the Earth’s surface, but they actually only comprise about _______ of the Earth’s crust altogether. A. 5% B. 10% C. 25% D. 50% E. 75% 13. How much of the Earth’s crust is made up of sedimentary rocks? A. 95% B. 75% C. 50% D. 25% E. 5% 13. Whi ...
Geol 101: Physical Geology PAST EXAM QUESTIONS LECTURE
... 13. Sedimentary rocks are the most common type of rock at the Earth’s surface, but they actually only comprise about _______ of the Earth’s crust altogether. A. 5% B. 10% C. 25% D. 50% E. 75% 13. How much of the Earth’s crust is made up of sedimentary rocks? A. 95% B. 75% C. 50% D. 25% E. 5% 13. Whi ...
... 13. Sedimentary rocks are the most common type of rock at the Earth’s surface, but they actually only comprise about _______ of the Earth’s crust altogether. A. 5% B. 10% C. 25% D. 50% E. 75% 13. How much of the Earth’s crust is made up of sedimentary rocks? A. 95% B. 75% C. 50% D. 25% E. 5% 13. Whi ...
GEOG - Unit 1
... • Weathering — processes that alter rocks • Can change landscapes over time and create soil for plant life • Sediment—mud, sand, silt created by weathering processes ...
... • Weathering — processes that alter rocks • Can change landscapes over time and create soil for plant life • Sediment—mud, sand, silt created by weathering processes ...
Weathering

Weathering is the breaking down of rocks, soil and minerals as well as artificial materials through contact with the Earth's atmosphere, biota and waters. Weathering occurs in situ, roughly translated to: ""with no movement"" , and thus should not be confused with erosion, which involves the movement of rocks and minerals by agents such as water, ice, snow, wind, waves and gravity and then being transported and deposited in other locations.Two important classifications of weathering processes exist – physical and chemical weathering; each sometimes involves a biological component. Mechanical or physical weathering involves the breakdown of rocks and soils through direct contact with atmospheric conditions, such as heat, water, ice and pressure. The second classification, chemical weathering, involves the direct effect of atmospheric chemicals or biologically produced chemicals also known as biological weathering in the breakdown of rocks, soils and minerals. While physical weathering is accentuated in very cold or very dry environments, chemical reactions are most intense where the climate is wet and hot. However, both types of weathering occur together, and each tends to accelerate the other. For example, physical abrasion (rubbing together) decreases the size of particles and therefore increases their surface area, making them more susceptible to rapid chemical reactions. The various agents act in concert to convert primary minerals (feldspars and micas) to secondary minerals (clays and carbonates) and release plant nutrient elements in soluble forms.The materials left over after the rock breaks down combined with organic material creates soil. The mineral content of the soil is determined by the parent material, thus a soil derived from a single rock type can often be deficient in one or more minerals for good fertility, while a soil weathered from a mix of rock types (as in glacial, aeolian or alluvial sediments) often makes more fertile soil. In addition, many of Earth's landforms and landscapes are the result of weathering processes combined with erosion and re-deposition.