Our Earth
... mantle. it forces the cooler rock aside. What effect does this have on the crust above? 4. When a continent on the edge of a tectonic plate is forced against a sea floor on the edge of another plate, the sea floor is always the loser. It returns to the mantle. Why? 5. What example is shown in the pr ...
... mantle. it forces the cooler rock aside. What effect does this have on the crust above? 4. When a continent on the edge of a tectonic plate is forced against a sea floor on the edge of another plate, the sea floor is always the loser. It returns to the mantle. Why? 5. What example is shown in the pr ...
4/21/2012- Sedimentary Rocks, Metamorphic Rocks, and The Rock
... • Mechanical weathering processes break down rocks into smaller clasts. • When clasts are transported to new locations, they often become rounded before being deposited. • When clasts are loose on Earth’s surface, they don’t fit together perfectly. The empty space in between the grains is called por ...
... • Mechanical weathering processes break down rocks into smaller clasts. • When clasts are transported to new locations, they often become rounded before being deposited. • When clasts are loose on Earth’s surface, they don’t fit together perfectly. The empty space in between the grains is called por ...
Extra Credit
... 13. True or False: During the wet times, the water table will fall because it gets too heavy. a. The water table will rise during the wet times, just like a sponge would, and sink during the dry times. 14. True or False: Areas in the river where rocks pile up results in the river ceasing to exist fr ...
... 13. True or False: During the wet times, the water table will fall because it gets too heavy. a. The water table will rise during the wet times, just like a sponge would, and sink during the dry times. 14. True or False: Areas in the river where rocks pile up results in the river ceasing to exist fr ...
Compared to the desolate surface of the Moon, Earth must
... 1. Magma—molten (liquid) rock that forms in certain places in the Earth’s interior where temperatures and pressures are such that rock melts - migrates up into crust 2. Crystallization - magma cools and solidifies a. It can erupt in a volcano and then it cools at the Earth’s surface - extrusive b. O ...
... 1. Magma—molten (liquid) rock that forms in certain places in the Earth’s interior where temperatures and pressures are such that rock melts - migrates up into crust 2. Crystallization - magma cools and solidifies a. It can erupt in a volcano and then it cools at the Earth’s surface - extrusive b. O ...
Rock On - Cabrillo Education
... and fused together with no surrounding cement. Some wellknown types of igneous rocks include granite, rhyolite, andesite, diorite, obsidian, gabbro, and basalt. Sedimentary rocks take their compositional elements from other sources that have been weathered to sediment, redeposited, and re solidif ...
... and fused together with no surrounding cement. Some wellknown types of igneous rocks include granite, rhyolite, andesite, diorite, obsidian, gabbro, and basalt. Sedimentary rocks take their compositional elements from other sources that have been weathered to sediment, redeposited, and re solidif ...
Study Guide: Earth`s Layer, Pangaea, Plate Tectonics, Minerals and
... 23. Define: A. Igneous Rock: Formed when molten rock cools and becomes a solid B. Sedimentary Rock: Forms when rock, sand, plants and other sediments layer and are cemented together by pressure over time C. Metamorphic Rock: Rocks that form when heat and pressure are applied to an existing parent r ...
... 23. Define: A. Igneous Rock: Formed when molten rock cools and becomes a solid B. Sedimentary Rock: Forms when rock, sand, plants and other sediments layer and are cemented together by pressure over time C. Metamorphic Rock: Rocks that form when heat and pressure are applied to an existing parent r ...
G2S15Lesson1 Introd
... Igneous rocks form from a cooling magma. The composition (mineral makeup) of igneous rocks can be divided into two main groups: 1. Felsic (silicic) rocks: These are lighter colored rocks and include abundant quartz, potassium feldspar – this includes Granite and Rhyolite 2. Mafic Rocks: These are da ...
... Igneous rocks form from a cooling magma. The composition (mineral makeup) of igneous rocks can be divided into two main groups: 1. Felsic (silicic) rocks: These are lighter colored rocks and include abundant quartz, potassium feldspar – this includes Granite and Rhyolite 2. Mafic Rocks: These are da ...
Document
... If the magma is intruded along vertical joints, it forms dykes whereas if it moves along horizontal bedding planes, it cools to form sills. If the overlying rocks are eroded away, these features may be exposed at the surface. Sometimes, large areas of intrusive granite (called batholiths) are expose ...
... If the magma is intruded along vertical joints, it forms dykes whereas if it moves along horizontal bedding planes, it cools to form sills. If the overlying rocks are eroded away, these features may be exposed at the surface. Sometimes, large areas of intrusive granite (called batholiths) are expose ...
Classifying Rocks
... Become more familiar with and practice criteria for distinguishing among sedimentary, metamorphic, igneous plutonic, and igneous volcanic rocks. Become more familiar with several common rock types within each of the classifications above. ...
... Become more familiar with and practice criteria for distinguishing among sedimentary, metamorphic, igneous plutonic, and igneous volcanic rocks. Become more familiar with several common rock types within each of the classifications above. ...
Sulfur in weathering and sedimentary processes
... removed via sulfate reduction and evaporite deposition. The reduction of sulfate in marine sediments leads to the formation of pyrite and organic compounds containing sulfur. This process is mediated by sulfate-reducing bacteria that oxidize organic matter. Sulfate is also extracted from seawater by ...
... removed via sulfate reduction and evaporite deposition. The reduction of sulfate in marine sediments leads to the formation of pyrite and organic compounds containing sulfur. This process is mediated by sulfate-reducing bacteria that oxidize organic matter. Sulfate is also extracted from seawater by ...
Science 7 Unit 4 Earth`s Crust and Resources
... 2. Why do you think there is such a distinct pattern to where the earthquakes occur on the map on page 264? ...
... 2. Why do you think there is such a distinct pattern to where the earthquakes occur on the map on page 264? ...
Vocabulary Chapter 14
... Plants, animals and bacteria can form fossils, but only organisms that are buried rapidly in sediment are readily preserved. Most organisms decompose before they have a chance to become fossilized. ...
... Plants, animals and bacteria can form fossils, but only organisms that are buried rapidly in sediment are readily preserved. Most organisms decompose before they have a chance to become fossilized. ...
Minerals and Rocks
... chemical alteration most easily. Charged particles, that is, ions, that form part of a molecule in a mineral may leave or be traded for other substances, generally weakening the mineral structure and forming the chemical basis of rock weathering. Minerals can be categorized into groups based on thei ...
... chemical alteration most easily. Charged particles, that is, ions, that form part of a molecule in a mineral may leave or be traded for other substances, generally weakening the mineral structure and forming the chemical basis of rock weathering. Minerals can be categorized into groups based on thei ...
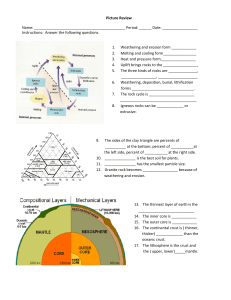
Picture Review Name
... The sides of the clay triangle are percents of __________ at the bottom, percent of ___________at the left side, percent of ___________ at the right side. 10. _______________ is the best soil for plants. 11. _______________ has the smallest particle size. 12. Granite rock becomes _________________ b ...
... The sides of the clay triangle are percents of __________ at the bottom, percent of ___________at the left side, percent of ___________ at the right side. 10. _______________ is the best soil for plants. 11. _______________ has the smallest particle size. 12. Granite rock becomes _________________ b ...
Chapter 8 Notes
... 1. The roots push into cracks on the rock 2. The roots produce weak acids that slowly dissolve rock ii. Lichens—plantlike organisms that grow on rocks—produce acids too 9. Acid Rain i. Burning fuels such as coal, oil, and gas can pollute air with sulfur, carbon, and nitrogen 1. When they react with ...
... 1. The roots push into cracks on the rock 2. The roots produce weak acids that slowly dissolve rock ii. Lichens—plantlike organisms that grow on rocks—produce acids too 9. Acid Rain i. Burning fuels such as coal, oil, and gas can pollute air with sulfur, carbon, and nitrogen 1. When they react with ...
The Rock Cycle
... • My friend from the dike turned into an organic sedimentary rock • He contains materials generated by living organisms and includes carbonate minerals created by organisms such as coral ...
... • My friend from the dike turned into an organic sedimentary rock • He contains materials generated by living organisms and includes carbonate minerals created by organisms such as coral ...
Metamorphic Rock Lab
... undergo metamorphism, or changes in structure and mineral content. Elevated temperatures and pressures within the Earth’s crust may cause some or all of the minerals in a pre-existing rock to become unstable and change. Chemically active fluids such as water help to promote changes by adding or subt ...
... undergo metamorphism, or changes in structure and mineral content. Elevated temperatures and pressures within the Earth’s crust may cause some or all of the minerals in a pre-existing rock to become unstable and change. Chemically active fluids such as water help to promote changes by adding or subt ...
Rocks and the Rock Cycle - Johnston County Schools
... Sedimentary rocks form from particles deposited by water and wind If you have ever walked along a beach (which I am sure you have) you may have noticed tiny sand grains, mud, and pebbles. These are some sediments that eventually form into sedimentary rocks Sedimentary Rocks formation usually invol ...
... Sedimentary rocks form from particles deposited by water and wind If you have ever walked along a beach (which I am sure you have) you may have noticed tiny sand grains, mud, and pebbles. These are some sediments that eventually form into sedimentary rocks Sedimentary Rocks formation usually invol ...
I Can
... I can safely and appropriately use equipment, materials, organisms, and models. SC.O.E. 1.2 I can collect observations, data, and other evidence from a scientific investigation. I can use evidence collected from an experiment to explain what happened in the investigation. SC.O.E. 1.3 I can design an ...
... I can safely and appropriately use equipment, materials, organisms, and models. SC.O.E. 1.2 I can collect observations, data, and other evidence from a scientific investigation. I can use evidence collected from an experiment to explain what happened in the investigation. SC.O.E. 1.3 I can design an ...
G2S15Lesson1 Introd
... Igneous rocks form from a cooling magma. The composition (mineral makeup) of igneous rocks can be divided into two main groups: 1. Felsic (silicic) rocks: These are lighter colored rocks and include abundant quartz, potassium feldspar – this includes Granite and Rhyolite 2. Mafic Rocks: These are da ...
... Igneous rocks form from a cooling magma. The composition (mineral makeup) of igneous rocks can be divided into two main groups: 1. Felsic (silicic) rocks: These are lighter colored rocks and include abundant quartz, potassium feldspar – this includes Granite and Rhyolite 2. Mafic Rocks: These are da ...
micro-analysis of inclusion-bearing albite and garnet porphyroblasts
... define them. Petrologic analysis has shown the presence of an early foliation as well as a later, more predominate, foliation. Certain garnet porphyroblasts indicate two, or perhaps three, growth stages. Analysis is underway to determine absolute age relations of metamorphism and the P-T-t-D path of ...
... define them. Petrologic analysis has shown the presence of an early foliation as well as a later, more predominate, foliation. Certain garnet porphyroblasts indicate two, or perhaps three, growth stages. Analysis is underway to determine absolute age relations of metamorphism and the P-T-t-D path of ...
green ch9 lesson4
... form large crystals. 8. Magma that reaches the earth's surface is f::l . 9. MJ is a sedimentary rock made of mud and clay sediments. 10. How is sandstone formed? 11. The bones and shells from dead organisms form part of the sedimentary rock called %t. 12. Heat and pressure inside the earth can chang ...
... form large crystals. 8. Magma that reaches the earth's surface is f::l . 9. MJ is a sedimentary rock made of mud and clay sediments. 10. How is sandstone formed? 11. The bones and shells from dead organisms form part of the sedimentary rock called %t. 12. Heat and pressure inside the earth can chang ...
Chapter 10 Section 4
... The angle of repose is the steepest angle, or slope, at which loose material no longer moves downslope. ...
... The angle of repose is the steepest angle, or slope, at which loose material no longer moves downslope. ...
The role of calcium and magnesium in agriculture
... For healthy plants, an adequate supply of calcium compounds in the soil is required. This is because calcium is an essential constituent of plants. Not only are they a principle factor in controlling the pH of the soil but also they affect the plants ability to absorb nutrients through the roots. Ma ...
... For healthy plants, an adequate supply of calcium compounds in the soil is required. This is because calcium is an essential constituent of plants. Not only are they a principle factor in controlling the pH of the soil but also they affect the plants ability to absorb nutrients through the roots. Ma ...
Weathering

Weathering is the breaking down of rocks, soil and minerals as well as artificial materials through contact with the Earth's atmosphere, biota and waters. Weathering occurs in situ, roughly translated to: ""with no movement"" , and thus should not be confused with erosion, which involves the movement of rocks and minerals by agents such as water, ice, snow, wind, waves and gravity and then being transported and deposited in other locations.Two important classifications of weathering processes exist – physical and chemical weathering; each sometimes involves a biological component. Mechanical or physical weathering involves the breakdown of rocks and soils through direct contact with atmospheric conditions, such as heat, water, ice and pressure. The second classification, chemical weathering, involves the direct effect of atmospheric chemicals or biologically produced chemicals also known as biological weathering in the breakdown of rocks, soils and minerals. While physical weathering is accentuated in very cold or very dry environments, chemical reactions are most intense where the climate is wet and hot. However, both types of weathering occur together, and each tends to accelerate the other. For example, physical abrasion (rubbing together) decreases the size of particles and therefore increases their surface area, making them more susceptible to rapid chemical reactions. The various agents act in concert to convert primary minerals (feldspars and micas) to secondary minerals (clays and carbonates) and release plant nutrient elements in soluble forms.The materials left over after the rock breaks down combined with organic material creates soil. The mineral content of the soil is determined by the parent material, thus a soil derived from a single rock type can often be deficient in one or more minerals for good fertility, while a soil weathered from a mix of rock types (as in glacial, aeolian or alluvial sediments) often makes more fertile soil. In addition, many of Earth's landforms and landscapes are the result of weathering processes combined with erosion and re-deposition.