File
... _______________________ is when minerals split along the flat surfaces of the crystals Fracture is when minerals break along uneven surfaces Mica has cleavage because it breaks in smooth flat sheets Chemical Properties Some minerals will react with substances like ____________________ Calc ...
... _______________________ is when minerals split along the flat surfaces of the crystals Fracture is when minerals break along uneven surfaces Mica has cleavage because it breaks in smooth flat sheets Chemical Properties Some minerals will react with substances like ____________________ Calc ...
GLOSSARY MINERAL – a naturally occurring inorganic element or
... GLOSSARY MINERAL – a naturally occurring inorganic element or compound having an orderly internal structure and characteristic chemical composition, crystal form, and physical properties (hardness, luster, streak, etc.). Examples of minerals include quartz, calcite, gypsum, biotite and galena. ROCK ...
... GLOSSARY MINERAL – a naturally occurring inorganic element or compound having an orderly internal structure and characteristic chemical composition, crystal form, and physical properties (hardness, luster, streak, etc.). Examples of minerals include quartz, calcite, gypsum, biotite and galena. ROCK ...
Oceanography Worksheet #1
... 10. When the seafloor moves as a result of an underwater earthquake and a large tsunami develops, what will most likely occur? 1 Deep-ocean sediments will be transported over great distances. 2 No destruction will occur near the origin of the earthquake. 3 The direction of the tsunami will be determ ...
... 10. When the seafloor moves as a result of an underwater earthquake and a large tsunami develops, what will most likely occur? 1 Deep-ocean sediments will be transported over great distances. 2 No destruction will occur near the origin of the earthquake. 3 The direction of the tsunami will be determ ...
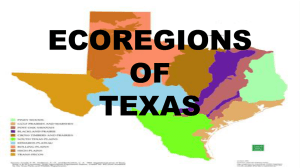
Texas eco regions 2016
... The shape of the hills in this region is rounded due to increased precipitation and chemical weathering. Central Texas' Flash Flood Alley is one of the most flood-prone areas nationwide. When rocks and soil can absorb no more rainfall, it gets carried off into a stream or at the bottom of a lake ...
... The shape of the hills in this region is rounded due to increased precipitation and chemical weathering. Central Texas' Flash Flood Alley is one of the most flood-prone areas nationwide. When rocks and soil can absorb no more rainfall, it gets carried off into a stream or at the bottom of a lake ...
Weathering
... physical and chemical phenomena is collectively called soil degradation. The three general types of soil degradation are erosion, chemical deterioration, and physical deterioration, each with seperate but related processes. Soil Erosion: Wind and running water are responsible for most soil erosin. W ...
... physical and chemical phenomena is collectively called soil degradation. The three general types of soil degradation are erosion, chemical deterioration, and physical deterioration, each with seperate but related processes. Soil Erosion: Wind and running water are responsible for most soil erosin. W ...
Regents Earth Science
... I. Igneous Rocks A. James Hutton (1795) began concept of uniformitarianism, which states that: 1. The same geologic processes have always been at work. 2. These processes formed the Earth as it is today over a long period of time. B. Rock (def'n) - a group of minerals bound together in some way. C. ...
... I. Igneous Rocks A. James Hutton (1795) began concept of uniformitarianism, which states that: 1. The same geologic processes have always been at work. 2. These processes formed the Earth as it is today over a long period of time. B. Rock (def'n) - a group of minerals bound together in some way. C. ...
The Rock Cycle
... and/or physical mechanisms into smaller particles. There are three types of weathering Physical weathering: physical action which breaks up rocks. An example of this is freethaw weathering Chemical Weathering: when the rock is attacked by chemicals. An example of this is how acid rain breaks down li ...
... and/or physical mechanisms into smaller particles. There are three types of weathering Physical weathering: physical action which breaks up rocks. An example of this is freethaw weathering Chemical Weathering: when the rock is attacked by chemicals. An example of this is how acid rain breaks down li ...
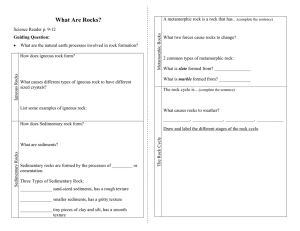
What Are Rocks - Lewiston School District
... Sedimentary rocks are formed by the processes of _________ or cementation. Three Types of Sedimentary Rock: ______________ sand-sized sediments, has a rough texture ______________ smaller sediments, has a gritty texture ______________ tiny pieces of clay and silt, has a smooth ...
... Sedimentary rocks are formed by the processes of _________ or cementation. Three Types of Sedimentary Rock: ______________ sand-sized sediments, has a rough texture ______________ smaller sediments, has a gritty texture ______________ tiny pieces of clay and silt, has a smooth ...
Social Studies
... 4. Mountain formation a. tectonic plates push together b. two plates collide and one moves up over the other ...
... 4. Mountain formation a. tectonic plates push together b. two plates collide and one moves up over the other ...
2nd 6 week test review 2015-2016 ppt
... • A substance that cannot be broken into simpler substances by chemical means • All atoms are the same type • Example: Mg / C / H ...
... • A substance that cannot be broken into simpler substances by chemical means • All atoms are the same type • Example: Mg / C / H ...
Study Guide for Science SOL 2
... Land surfaces are affected by weathering and erosion. Land surfaces that are no covered with or protected by plants are more likely to lose soil by wind and water. Vocabulary: 1. Dormancy-A time of rest for plants and animals 2. Camouflage-Something that protects an animal from attack by making it ...
... Land surfaces are affected by weathering and erosion. Land surfaces that are no covered with or protected by plants are more likely to lose soil by wind and water. Vocabulary: 1. Dormancy-A time of rest for plants and animals 2. Camouflage-Something that protects an animal from attack by making it ...
The Rock Cycle (1).
... and/or physical mechanisms into smaller particles. There are three types of weathering Physical weathering: physical action which breaks up rocks. An example of this is freethaw weathering Chemical Weathering: when the rock is attacked by chemicals. An example of this is how acid rain breaks down li ...
... and/or physical mechanisms into smaller particles. There are three types of weathering Physical weathering: physical action which breaks up rocks. An example of this is freethaw weathering Chemical Weathering: when the rock is attacked by chemicals. An example of this is how acid rain breaks down li ...
Section 4: Sedimentary Rocks
... Rocks can have same mineral composition, but different texture. Texture depends on size and shape of its mineral crystals. Intrusive rocks have larger grains (slow cooling) Extrusive rocks have smaller grains (rapid cooling) *Porphyry is a type of rock that cools slowly and then quickly, which resul ...
... Rocks can have same mineral composition, but different texture. Texture depends on size and shape of its mineral crystals. Intrusive rocks have larger grains (slow cooling) Extrusive rocks have smaller grains (rapid cooling) *Porphyry is a type of rock that cools slowly and then quickly, which resul ...
George Cuvier (1769 – 1832) Introduced the concept of
... Neptunism: rocks form from crystallization in the early earth’s oceans James Hutton (1726 – 1797) “present is the key to the past” – Uniformitariansim Uniformitariansim: geologic process creates and destroys rock. Studied rock exposures, showed how rocks could form by slow geologic process Recognize ...
... Neptunism: rocks form from crystallization in the early earth’s oceans James Hutton (1726 – 1797) “present is the key to the past” – Uniformitariansim Uniformitariansim: geologic process creates and destroys rock. Studied rock exposures, showed how rocks could form by slow geologic process Recognize ...
Rock Cycle
... 11. Define these terms: WeatheringErosionCompactionCementation12. Provide two examples of organic rocks: 1. ...
... 11. Define these terms: WeatheringErosionCompactionCementation12. Provide two examples of organic rocks: 1. ...
Mid Term Review Sample Questions
... 4. What is the colored powder resulting from rubbing a mineral against a harder surface? _____________ 5. What is the most useful property in identifying an unknown rock? __________________________ 6. What mineral, when in the form of sand, can be used to manufacture glass? ___________________ 7. Wh ...
... 4. What is the colored powder resulting from rubbing a mineral against a harder surface? _____________ 5. What is the most useful property in identifying an unknown rock? __________________________ 6. What mineral, when in the form of sand, can be used to manufacture glass? ___________________ 7. Wh ...
Mineral Resources
... crystallization of magma (melted rock). Sedimentary Rocks – form by deposition and consolidation of sediments (e.g., sand, mud, etc.) or by evaporation of water and crystallization of dissolved materials. Metamorphic Rocks – form by the action of heat and pressure on some other rock. ...
... crystallization of magma (melted rock). Sedimentary Rocks – form by deposition and consolidation of sediments (e.g., sand, mud, etc.) or by evaporation of water and crystallization of dissolved materials. Metamorphic Rocks – form by the action of heat and pressure on some other rock. ...
No Slide Title
... The small Canadian vegetation region that has the greatest chance of disappearing due to pressures of urbanization ...
... The small Canadian vegetation region that has the greatest chance of disappearing due to pressures of urbanization ...
Earth systems Notes - Leon County Schools
... The process of dissolving breaks up the minerals in the rock into small pieces. The small pieces mix with water to form a solution and are washed away from the rock. Acids are also agents of chemical weathering and cause more chemical weathering than pure water does. Oxidation combines the element o ...
... The process of dissolving breaks up the minerals in the rock into small pieces. The small pieces mix with water to form a solution and are washed away from the rock. Acids are also agents of chemical weathering and cause more chemical weathering than pure water does. Oxidation combines the element o ...
Napoleon - Kawameeh Middle School
... conditions, along with short-term changes, of a certain place at a certain time. ...
... conditions, along with short-term changes, of a certain place at a certain time. ...
Rocks and the Rock Cycle
... Metamorphic Rocks are created under the Earth’s surface when extremely high pressure and heat cause the rock to “change form” Slate and Marble are two examples of metamorphic rocks ...
... Metamorphic Rocks are created under the Earth’s surface when extremely high pressure and heat cause the rock to “change form” Slate and Marble are two examples of metamorphic rocks ...
Key Points to Review for Science
... Rocks are made from a combination of different minerals. All rocks are minerals, but not all minerals are rocks. There are three different types of rocks. (sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic) Sedimentary rocks are formed form layers, igneous rocks are formed from melted rock that has cooled and h ...
... Rocks are made from a combination of different minerals. All rocks are minerals, but not all minerals are rocks. There are three different types of rocks. (sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic) Sedimentary rocks are formed form layers, igneous rocks are formed from melted rock that has cooled and h ...
Constructive and Destructive Forces Study Guide
... Sand Spit and Barrier Island – land, narrow piles of sand that are formed by watering moving sand. They help protect the mainland from wave erosion. (water erosion and deposition) Delta – a area of new land at the mouth of a ___________. It is formed when a river slows and deposits sediment. (de ...
... Sand Spit and Barrier Island – land, narrow piles of sand that are formed by watering moving sand. They help protect the mainland from wave erosion. (water erosion and deposition) Delta – a area of new land at the mouth of a ___________. It is formed when a river slows and deposits sediment. (de ...
Weathering

Weathering is the breaking down of rocks, soil and minerals as well as artificial materials through contact with the Earth's atmosphere, biota and waters. Weathering occurs in situ, roughly translated to: ""with no movement"" , and thus should not be confused with erosion, which involves the movement of rocks and minerals by agents such as water, ice, snow, wind, waves and gravity and then being transported and deposited in other locations.Two important classifications of weathering processes exist – physical and chemical weathering; each sometimes involves a biological component. Mechanical or physical weathering involves the breakdown of rocks and soils through direct contact with atmospheric conditions, such as heat, water, ice and pressure. The second classification, chemical weathering, involves the direct effect of atmospheric chemicals or biologically produced chemicals also known as biological weathering in the breakdown of rocks, soils and minerals. While physical weathering is accentuated in very cold or very dry environments, chemical reactions are most intense where the climate is wet and hot. However, both types of weathering occur together, and each tends to accelerate the other. For example, physical abrasion (rubbing together) decreases the size of particles and therefore increases their surface area, making them more susceptible to rapid chemical reactions. The various agents act in concert to convert primary minerals (feldspars and micas) to secondary minerals (clays and carbonates) and release plant nutrient elements in soluble forms.The materials left over after the rock breaks down combined with organic material creates soil. The mineral content of the soil is determined by the parent material, thus a soil derived from a single rock type can often be deficient in one or more minerals for good fertility, while a soil weathered from a mix of rock types (as in glacial, aeolian or alluvial sediments) often makes more fertile soil. In addition, many of Earth's landforms and landscapes are the result of weathering processes combined with erosion and re-deposition.