The Rock Cycle - Simpson County Schools
... When hot conditions that caused magma to melt will cool, either because the source of heat subsides or the magma moves into cooler regions of the Earth. When it gets cool enough the minerals that will make up the rock begin to crystallize and form an intergrown mass of crystals. If the crystals begi ...
... When hot conditions that caused magma to melt will cool, either because the source of heat subsides or the magma moves into cooler regions of the Earth. When it gets cool enough the minerals that will make up the rock begin to crystallize and form an intergrown mass of crystals. If the crystals begi ...
Mgr. Petr Schnabl - Dissertation Paleomagnetism and
... Strombolian-type volcanoes, while the Kozákov Formation (5.2 – 4.6 Ma) is represented by effusive products with a crater vent of a single giant volcano. One Pliocene (4.3–3.3 Ma) and two Pleistocene phases (2.6 –2.1 Ma and 1.8 – 1.1 Ma) of volcanic activity Magnetostratigraphy is a very important to ...
... Strombolian-type volcanoes, while the Kozákov Formation (5.2 – 4.6 Ma) is represented by effusive products with a crater vent of a single giant volcano. One Pliocene (4.3–3.3 Ma) and two Pleistocene phases (2.6 –2.1 Ma and 1.8 – 1.1 Ma) of volcanic activity Magnetostratigraphy is a very important to ...
Earth 1
... 2. Sedimentary Rocks a. Form in water from “sediment”, which is grains and bits of rock that were created by erosion or weathering. b. Fact: The sediment builds up over many years and becomes cemented together to form sedimentary rock. c. Characteristics: These rocks are layered. The layers tell th ...
... 2. Sedimentary Rocks a. Form in water from “sediment”, which is grains and bits of rock that were created by erosion or weathering. b. Fact: The sediment builds up over many years and becomes cemented together to form sedimentary rock. c. Characteristics: These rocks are layered. The layers tell th ...
Changes to Texas Land (7
... When carbon dioxide in the air dissolves in rainwater, it acts as a mild acid and degrades the rocks that it contacts. Chemical weathering can weaken rocks and make them more susceptible to physical weathering, but these two processes do not always occur together. If a rock is physically weathered, ...
... When carbon dioxide in the air dissolves in rainwater, it acts as a mild acid and degrades the rocks that it contacts. Chemical weathering can weaken rocks and make them more susceptible to physical weathering, but these two processes do not always occur together. If a rock is physically weathered, ...
Planet Earth - Manasquan Public Schools
... compounds with a definite chemical composition and internal structure. 3500 known minerals in Earth’s crust Rocks and minerals classified by texture, hardness, color, and density. ...
... compounds with a definite chemical composition and internal structure. 3500 known minerals in Earth’s crust Rocks and minerals classified by texture, hardness, color, and density. ...
What is a Rock?
... outermost part of the mantle and glide across the underlying asthenosphere. The continents are located on tectonic plates and move around with them. ...
... outermost part of the mantle and glide across the underlying asthenosphere. The continents are located on tectonic plates and move around with them. ...
Sculpting the Earth`s Surface
... Sediments are the end products of weathering Mechanical – the physical breaking apart of Earth materials Chemical – alters the internal structure of minerals by removing and/or adding elements ...
... Sediments are the end products of weathering Mechanical – the physical breaking apart of Earth materials Chemical – alters the internal structure of minerals by removing and/or adding elements ...
Planet Earth - Manasquan Public Schools
... compounds with a definite chemical composition and internal structure. 3500 known minerals in Earth’s crust Rocks and minerals classified by texture, hardness, color, and density. ...
... compounds with a definite chemical composition and internal structure. 3500 known minerals in Earth’s crust Rocks and minerals classified by texture, hardness, color, and density. ...
An overview of mass movement
... gravity. It is related closely to weathering, which is the breakdown of minerals or rocks at or near Earth's surface through physical, chemical, or biological processes, and to erosion, the transport of material through a variety of agents, most of them flowing media, such as air or water. Varieties ...
... gravity. It is related closely to weathering, which is the breakdown of minerals or rocks at or near Earth's surface through physical, chemical, or biological processes, and to erosion, the transport of material through a variety of agents, most of them flowing media, such as air or water. Varieties ...
Rocks - SchoolWorld an Edline Solution
... Sediments are loose materials such as rock fragments, mineral grains, bits of plants and animals that have been moved by wind, water, ice, or gravity ...
... Sediments are loose materials such as rock fragments, mineral grains, bits of plants and animals that have been moved by wind, water, ice, or gravity ...
Gober Paleoclimatology Presentation.pptx
... Uplift Weathering Hypothesis Uplift is the cause of large-scale climate changes, through both direct physical impacts and indirect biochemical effects ...
... Uplift Weathering Hypothesis Uplift is the cause of large-scale climate changes, through both direct physical impacts and indirect biochemical effects ...
Rocks and the Rock Cycle
... • Rock that forms from magma • Magma –mix of molten rock, gases and water vapor that forms underground • Magma flows from volcanoes as lava and then ...
... • Rock that forms from magma • Magma –mix of molten rock, gases and water vapor that forms underground • Magma flows from volcanoes as lava and then ...
Rocks: Lesson 1 Thinking Map completed
... Rock- a solid mixture dof crystals of one or more minerals. Some types of rock such as coal are made up of organic materials. ...
... Rock- a solid mixture dof crystals of one or more minerals. Some types of rock such as coal are made up of organic materials. ...
Earth Science - Wiki-by
... sources of fuel, (e.g., petroleum, natural gas) or for growing the plants we use as food. Earth materials provide many of the resources that humans use. ...
... sources of fuel, (e.g., petroleum, natural gas) or for growing the plants we use as food. Earth materials provide many of the resources that humans use. ...
Unit 1 Landforms and Water Forms
... Physical Weathering – The disintegration or splitting up of rock by the Physical environment without chemical changes occurring. Chemical Weathering – Processes that involve the action of chemical elements or compounds that change the rock’s chemical composition. ...
... Physical Weathering – The disintegration or splitting up of rock by the Physical environment without chemical changes occurring. Chemical Weathering – Processes that involve the action of chemical elements or compounds that change the rock’s chemical composition. ...
“changed rocks” – can form from: sedimentary, igneous or other
... rock (melted rocks reform into igneous rocks) B. Pressure: from burial at great depths or stress from mountain building (squeezing) activity ...
... rock (melted rocks reform into igneous rocks) B. Pressure: from burial at great depths or stress from mountain building (squeezing) activity ...
2008 EXAM 1 With Answers
... When molten material freezes so quickly that the atoms do not have sufficient time to produce an orderly arrangement, the resulting material is termed a _____ (a) volatile (b) crystal (c) mineral (d) natural glass (e) organic molecule ...
... When molten material freezes so quickly that the atoms do not have sufficient time to produce an orderly arrangement, the resulting material is termed a _____ (a) volatile (b) crystal (c) mineral (d) natural glass (e) organic molecule ...
How old is our Earth
... 36. Humus in a soil is mostly______ A) partially weathered bed rock *B) decomposed plant material C) China clay D) materials leached from the top soil 37 The process of Frost wedging______A) produces sinkholes B) is a type of physical weathering C) cracks open a rock due to freezing of water in a fr ...
... 36. Humus in a soil is mostly______ A) partially weathered bed rock *B) decomposed plant material C) China clay D) materials leached from the top soil 37 The process of Frost wedging______A) produces sinkholes B) is a type of physical weathering C) cracks open a rock due to freezing of water in a fr ...
How The Earth Works
... • Rocks Broken Down Mechanically and Chemically (Weathering) • Components Transported by Erosion • Components Cemented into Sedimentary Rocks • Burial and Heating creates Metamorphic Rocks • Melting Creates Igneous Rocks ...
... • Rocks Broken Down Mechanically and Chemically (Weathering) • Components Transported by Erosion • Components Cemented into Sedimentary Rocks • Burial and Heating creates Metamorphic Rocks • Melting Creates Igneous Rocks ...
REGION II: Southeastern Minnesota
... erosion and weathering by flowing glacial melt water. Rock cycle processes that are occurring today are normal weathering and erosion by precipitation, runoff, and rivers. In Southeast Minnesota there is also weathering and erosion of underground rocks from naturally acidic groundwater. Shale: Durin ...
... erosion and weathering by flowing glacial melt water. Rock cycle processes that are occurring today are normal weathering and erosion by precipitation, runoff, and rivers. In Southeast Minnesota there is also weathering and erosion of underground rocks from naturally acidic groundwater. Shale: Durin ...
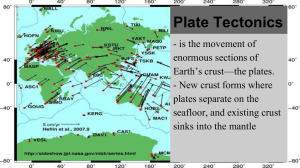
Plate Tectonics
... is a linear feature that exists between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other. ...
... is a linear feature that exists between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other. ...
Quantification of rock mass deterioration process for cut slope
... Road construction in mountainous areas especially in humid tropical climates is often afflicted by slope instability. Road cut slopes are designed to be stable over a certain time span; i.e. the engineering lifetime, however many slopes or parts of slopes fail before the end of the lifetime. The rea ...
... Road construction in mountainous areas especially in humid tropical climates is often afflicted by slope instability. Road cut slopes are designed to be stable over a certain time span; i.e. the engineering lifetime, however many slopes or parts of slopes fail before the end of the lifetime. The rea ...
Changes to Earths surface powerpoint
... Mechanical Weathering • Mechanical weathering is when mechanical energy creates weathering. This mechanical energy could come from: – Moving water/wind (abrasion) – Freezing ice – Burrowing animals – Growing plant roots ...
... Mechanical Weathering • Mechanical weathering is when mechanical energy creates weathering. This mechanical energy could come from: – Moving water/wind (abrasion) – Freezing ice – Burrowing animals – Growing plant roots ...
forces of change
... Process that breaks down rocks on the earth’s surface into smaller pieces. Form of weathering that occurs when large masses of rock are broken down into smaller pieces. Give an example of this process: ...
... Process that breaks down rocks on the earth’s surface into smaller pieces. Form of weathering that occurs when large masses of rock are broken down into smaller pieces. Give an example of this process: ...
Weathering

Weathering is the breaking down of rocks, soil and minerals as well as artificial materials through contact with the Earth's atmosphere, biota and waters. Weathering occurs in situ, roughly translated to: ""with no movement"" , and thus should not be confused with erosion, which involves the movement of rocks and minerals by agents such as water, ice, snow, wind, waves and gravity and then being transported and deposited in other locations.Two important classifications of weathering processes exist – physical and chemical weathering; each sometimes involves a biological component. Mechanical or physical weathering involves the breakdown of rocks and soils through direct contact with atmospheric conditions, such as heat, water, ice and pressure. The second classification, chemical weathering, involves the direct effect of atmospheric chemicals or biologically produced chemicals also known as biological weathering in the breakdown of rocks, soils and minerals. While physical weathering is accentuated in very cold or very dry environments, chemical reactions are most intense where the climate is wet and hot. However, both types of weathering occur together, and each tends to accelerate the other. For example, physical abrasion (rubbing together) decreases the size of particles and therefore increases their surface area, making them more susceptible to rapid chemical reactions. The various agents act in concert to convert primary minerals (feldspars and micas) to secondary minerals (clays and carbonates) and release plant nutrient elements in soluble forms.The materials left over after the rock breaks down combined with organic material creates soil. The mineral content of the soil is determined by the parent material, thus a soil derived from a single rock type can often be deficient in one or more minerals for good fertility, while a soil weathered from a mix of rock types (as in glacial, aeolian or alluvial sediments) often makes more fertile soil. In addition, many of Earth's landforms and landscapes are the result of weathering processes combined with erosion and re-deposition.