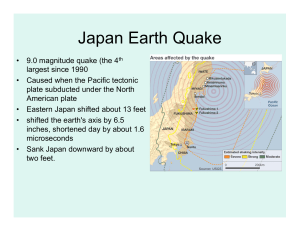
00258 Guide to CH Building Stone
... was experiencing hot arid conditions stricken with flash flooding across this desert. These would rip up clasts from sediments and bedrock they flowed over and it was these large angular pebbles that make up the rock between coarse sandy grains. The matrix and cement that glues the rock together is ...
... was experiencing hot arid conditions stricken with flash flooding across this desert. These would rip up clasts from sediments and bedrock they flowed over and it was these large angular pebbles that make up the rock between coarse sandy grains. The matrix and cement that glues the rock together is ...
File - CBSE FRIENDS OCEAN
... Aventurine Aventurescence (or aventurization) is a reflectance effect like that of glitter. It arises from minute, preferentially oriented mineral platelets within the material. These platelets are so numerous that they also influence the material's body colour. In aventurine quartz, chrome-bearing ...
... Aventurine Aventurescence (or aventurization) is a reflectance effect like that of glitter. It arises from minute, preferentially oriented mineral platelets within the material. These platelets are so numerous that they also influence the material's body colour. In aventurine quartz, chrome-bearing ...
Rock Jeopardy
... Living plants in a swamp are covered with sediment. Eventually this valuable source of energy may form. ...
... Living plants in a swamp are covered with sediment. Eventually this valuable source of energy may form. ...
08_chapter 2
... chelates that have the ability to decompose minerals and rocks by the removal of metallic cations. Complex chemical effects occur as a result of chelation. Chelating molecules are found to increase the dissolution rates of cations by forming strong bonds with cations or with mineral surfaces (Palmer ...
... chelates that have the ability to decompose minerals and rocks by the removal of metallic cations. Complex chemical effects occur as a result of chelation. Chelating molecules are found to increase the dissolution rates of cations by forming strong bonds with cations or with mineral surfaces (Palmer ...
Igneous Rocks and Processes
... into the air before falling to the ground or are carried down the slopes of the volcano as a gascharged surface flow. Settling to the ground while still hot, these materials can become fused or welded together to form a pyroclastic rock. Extrusive rocks with pyroclastic textures usually contain smal ...
... into the air before falling to the ground or are carried down the slopes of the volcano as a gascharged surface flow. Settling to the ground while still hot, these materials can become fused or welded together to form a pyroclastic rock. Extrusive rocks with pyroclastic textures usually contain smal ...
Field Guide Local Geology Review
... small particles of rocks, minerals, and organic material deposited in piles on Earth’s surface. Two lithification processes are: Cementation of sediments usually by watery solutions that percolate through buried sediments and deposit mineral glues that then cement the sediments together). Example: ...
... small particles of rocks, minerals, and organic material deposited in piles on Earth’s surface. Two lithification processes are: Cementation of sediments usually by watery solutions that percolate through buried sediments and deposit mineral glues that then cement the sediments together). Example: ...
geology of vinalhaven island, maine
... concentrated on the stratigraphic variation of a major depositional unit with a gabbroic base which grades upward to hybrid and felsic rocks. His work documents both vertical and lateral compositional variation in an effort to understand the processes responsible for hybridization between mafic and ...
... concentrated on the stratigraphic variation of a major depositional unit with a gabbroic base which grades upward to hybrid and felsic rocks. His work documents both vertical and lateral compositional variation in an effort to understand the processes responsible for hybridization between mafic and ...
Metamorphism
... indicating that preexisting, microscopic, platy minerals were pushed into alignment during metamorphism, we say the rock is slaty, or that it possesses slaty cleavage. If visible platy or needle-shaped minerals have grown essentially parallel to a plane due to differential stress, the rock is schist ...
... indicating that preexisting, microscopic, platy minerals were pushed into alignment during metamorphism, we say the rock is slaty, or that it possesses slaty cleavage. If visible platy or needle-shaped minerals have grown essentially parallel to a plane due to differential stress, the rock is schist ...
PDF file
... In the millenia since then, the area has at times been above sea level and sometimes below it. When it was above sea level, it was subject to erosion. When it was below sea level it was subject to deposition of sediments and thus, over time, to the creation of new rocks. Few traces of those new rock ...
... In the millenia since then, the area has at times been above sea level and sometimes below it. When it was above sea level, it was subject to erosion. When it was below sea level it was subject to deposition of sediments and thus, over time, to the creation of new rocks. Few traces of those new rock ...
Organic sedimentary rocks
... Sometimes evaporites are precipitated on broad coastal salt flats called sabkhas. This specimen is from Tunisia in North Africa, where locals dig them out of the salt flats to sell to tourists. This one cost just 50 pence in 1986! ...
... Sometimes evaporites are precipitated on broad coastal salt flats called sabkhas. This specimen is from Tunisia in North Africa, where locals dig them out of the salt flats to sell to tourists. This one cost just 50 pence in 1986! ...
Geochemistry of the Neoarchaean mafic volcanic rocks of the Geita
... Sukumaland greenstone belt (SGB) of northwestern Tanzania with the aim of constraining their petrogenesis, tectonic setting and to assess a possible genetic link with mafic volcanic rocks from the Rwamagaza area also from the SGB previously reported by [Manya, S., Maboko, M.A.H., 2003. Dating basalt ...
... Sukumaland greenstone belt (SGB) of northwestern Tanzania with the aim of constraining their petrogenesis, tectonic setting and to assess a possible genetic link with mafic volcanic rocks from the Rwamagaza area also from the SGB previously reported by [Manya, S., Maboko, M.A.H., 2003. Dating basalt ...
DES601 - Hour 21
... biological materials, or chemical precipitates • Highway sediments may be a mix of materials, ...
... biological materials, or chemical precipitates • Highway sediments may be a mix of materials, ...
Chapter 8
... • Difficulties in dating the geologic time scale • Not all rocks can be dated by radiometric methods – Grains comprising detrital sedimentary rocks are not the same age as the rock in which they formed – The age of a particular mineral in a metamorphic rock may not necessarily represent the time whe ...
... • Difficulties in dating the geologic time scale • Not all rocks can be dated by radiometric methods – Grains comprising detrital sedimentary rocks are not the same age as the rock in which they formed – The age of a particular mineral in a metamorphic rock may not necessarily represent the time whe ...
THEME 8: The Mokolian Era Namaqualand Metamorphic Complex
... Soutpansberg all represent reactivation of faults, especially the Limpopo Belt, between 2.0 and 1.8 Ga. Might be related to the Eburnean Orogeny, when other cratons were been added to the northern edge of the Zimbabwe Craton. This same timing for orogenic activity is also recorded in other parts of ...
... Soutpansberg all represent reactivation of faults, especially the Limpopo Belt, between 2.0 and 1.8 Ga. Might be related to the Eburnean Orogeny, when other cratons were been added to the northern edge of the Zimbabwe Craton. This same timing for orogenic activity is also recorded in other parts of ...
1. THE COLORADO PLATEAU
... not named after the State of Colorado, but after the Colorado River, which courses from the northeast to the southwest of this region. The varied topography of the Colorado Plateau exposes many easily recognizable, widely distributed and distinctive rock formations. The Plateau is surrounded by majo ...
... not named after the State of Colorado, but after the Colorado River, which courses from the northeast to the southwest of this region. The varied topography of the Colorado Plateau exposes many easily recognizable, widely distributed and distinctive rock formations. The Plateau is surrounded by majo ...
1 - Assets - Cambridge - Cambridge University Press
... deposition by water, wind, or ice. By contrast, igneous and metamorphic rocks form mainly below Earth’s surface where temperatures and pressures may be orders of magnitude higher than those at the surface, although volcanic rocks eventually cool at the surface. These fundamental differences in the o ...
... deposition by water, wind, or ice. By contrast, igneous and metamorphic rocks form mainly below Earth’s surface where temperatures and pressures may be orders of magnitude higher than those at the surface, although volcanic rocks eventually cool at the surface. These fundamental differences in the o ...
STATION #1 Compaction and Cementation
... Rare Earth Elements (REEs): As magmas crystallize, elements that cannot easily fit into crystal structures because of their large size or electron charge (chemical valence) are concentrated in the magma. REEs (i.e., La to Lu, plus Sc & Y) are concentrated this way. When the enriched magma finally cr ...
... Rare Earth Elements (REEs): As magmas crystallize, elements that cannot easily fit into crystal structures because of their large size or electron charge (chemical valence) are concentrated in the magma. REEs (i.e., La to Lu, plus Sc & Y) are concentrated this way. When the enriched magma finally cr ...
Origin of magma (pg.270-273)
... Objectives: the origin of MAGMA 1. Define/describe geothermal gradient and how it applies to rock melting. 2. How does reducing confining pressure change rock’s melting temperature? 3. Decompression melting of rock occurs when rocks (ascend, descend)? Explain. 4. What effect do volatiles (such as wa ...
... Objectives: the origin of MAGMA 1. Define/describe geothermal gradient and how it applies to rock melting. 2. How does reducing confining pressure change rock’s melting temperature? 3. Decompression melting of rock occurs when rocks (ascend, descend)? Explain. 4. What effect do volatiles (such as wa ...
Volcanism and its Contribution to Mudrock Genesis
... contain only small amounts of smectite, whereas younger clays "... have a complex clay-mineral suite with montmorillonite, mixed-layer clay, and kaolinite increasing in importance" (Weaver 1967, p. 2185). Most clays in which smectite is a major constituent are of Mesozoic and Cenozoic ages. Thus, th ...
... contain only small amounts of smectite, whereas younger clays "... have a complex clay-mineral suite with montmorillonite, mixed-layer clay, and kaolinite increasing in importance" (Weaver 1967, p. 2185). Most clays in which smectite is a major constituent are of Mesozoic and Cenozoic ages. Thus, th ...
Chapter 4: Origin and Evolution of Igneous Rocks
... • Igneous rocks are classified based on composition, from ultramafic (silica poor and iron rich) to felsic (silica rich and iron poor). • Igneous rocks are also classified based on texture, from glassy (no crystals) to fine-grained (small crystals) to coarse-grained (large crystals) and porphyritic ...
... • Igneous rocks are classified based on composition, from ultramafic (silica poor and iron rich) to felsic (silica rich and iron poor). • Igneous rocks are also classified based on texture, from glassy (no crystals) to fine-grained (small crystals) to coarse-grained (large crystals) and porphyritic ...
Pdf - Text of NPTEL IIT Video Lectures
... of the minerals that is formed in this manner is the granite group of minerals. ...
... of the minerals that is formed in this manner is the granite group of minerals. ...
Geochronology - The Grand Canyon Association
... • More than 150 individual lava flows built 13 individual lava dams across the Colorado River (~22 km3 of lava spilled into the Canyon) • At least one to five large lakes formed behind the dam, thought to have backed up as far as Moab, Utah • 5 catastrophic dam failures and resulting outburst floods ...
... • More than 150 individual lava flows built 13 individual lava dams across the Colorado River (~22 km3 of lava spilled into the Canyon) • At least one to five large lakes formed behind the dam, thought to have backed up as far as Moab, Utah • 5 catastrophic dam failures and resulting outburst floods ...
PETLAB2-14
... This station contains examples of mafic plutonic rocks. They range from high-level (near surface) porphyritic dykes, whose grain-size is virtually indistinguishable from mafic volcanic rocks in the interiors of flows (seen at station B and C) to coarser-grained cumulate rocks formed in large deep-se ...
... This station contains examples of mafic plutonic rocks. They range from high-level (near surface) porphyritic dykes, whose grain-size is virtually indistinguishable from mafic volcanic rocks in the interiors of flows (seen at station B and C) to coarser-grained cumulate rocks formed in large deep-se ...
Overview of Information about the Broad River watershed
... 2010 (Fig. 3). These intrusions generally have sharp contacts with surrounding metamorphic country rocks indicating that the granites were not derived by local melting, but, instead, were derived from greater depths in the crust. The Elberton Granite is the largest of these late granites exposed in ...
... 2010 (Fig. 3). These intrusions generally have sharp contacts with surrounding metamorphic country rocks indicating that the granites were not derived by local melting, but, instead, were derived from greater depths in the crust. The Elberton Granite is the largest of these late granites exposed in ...
Clastic rock

Clastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus, chunks and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks by physical weathering. Geologists use the term clastic with reference to sedimentary rocks as well as to particles in sediment transport whether in suspension or as bed load, and in sediment deposits.