Document
... 12. What substance is the usual reference point for the density of other substances? _______________________________________________________________ 13. The ratio of an object’s density to the density of water is called the object’s ______________________ SPECIAL PROPERTIES ...
... 12. What substance is the usual reference point for the density of other substances? _______________________________________________________________ 13. The ratio of an object’s density to the density of water is called the object’s ______________________ SPECIAL PROPERTIES ...
lesson 3: what is the rock cycle
... can be cemented together to make sedimentary rock. In this way, igneous rock can become sedimentary rock. All rock can be heated. But where does the heat come from? Inside Earth there is heat from pressure (push your hands together very hard and feel the heat). There is heat from friction (rub your ...
... can be cemented together to make sedimentary rock. In this way, igneous rock can become sedimentary rock. All rock can be heated. But where does the heat come from? Inside Earth there is heat from pressure (push your hands together very hard and feel the heat). There is heat from friction (rub your ...
The Rock Cycle, Isostasy, and the Dynamics of the
... products of chemical weathering • quartz • clay minerals (e.g. kaolinite) • iron oxides (e.g. hematite) • carbonate (calcite) Common in Sedimentary Rocks ...
... products of chemical weathering • quartz • clay minerals (e.g. kaolinite) • iron oxides (e.g. hematite) • carbonate (calcite) Common in Sedimentary Rocks ...
Earth Science Questions and Answers for Teachers Teaching Grade 4
... streaked on an unglazed porcelain plate, so this can be a diagnostic feature of hematite. Rouge is a powdered form of hematite. Copper – is rare as a mineral and often occurs as pure metal copper, in which case it is called native copper. A blue or green color often results when copper is found with ...
... streaked on an unglazed porcelain plate, so this can be a diagnostic feature of hematite. Rouge is a powdered form of hematite. Copper – is rare as a mineral and often occurs as pure metal copper, in which case it is called native copper. A blue or green color often results when copper is found with ...
Igneous Rocks - Mrs. GM Earth Science 300
... Granite can be used for architectural construction, ornamental stone, flooring, paving, facing stones, worktops, gravestones and monuments. Pumice which can be used as an abrasive material in hand soaps, soaps, cleansers, and dental products, emery board, etc. Basalt is a commonly used in floor ti ...
... Granite can be used for architectural construction, ornamental stone, flooring, paving, facing stones, worktops, gravestones and monuments. Pumice which can be used as an abrasive material in hand soaps, soaps, cleansers, and dental products, emery board, etc. Basalt is a commonly used in floor ti ...
Continuity of Cause and Effect
... Rock layers are tilted at an angle by uplift, faulting, or folding; these layers are eroded and new horizontal layers are created above them. ...
... Rock layers are tilted at an angle by uplift, faulting, or folding; these layers are eroded and new horizontal layers are created above them. ...
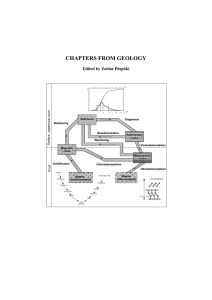
CHAPTERS FROM GEOLOGY
... important minerals of the Earth, we can ignore diamond and ruby and have to focus on silicate structures. To summarize the most common processes of the earth crust we have to know and understand the rock cycle (in the frame of plate tectonics) (figure 1). We have to see that the material in the rock ...
... important minerals of the Earth, we can ignore diamond and ruby and have to focus on silicate structures. To summarize the most common processes of the earth crust we have to know and understand the rock cycle (in the frame of plate tectonics) (figure 1). We have to see that the material in the rock ...
No Slide Title
... depositional environment. E.g. (above) Nearshore - waves crashing on beaches > fairly high energy -> coarse textured deposits (pebbles/sand); offshore -> progressively lower energy environments -> progressively finer textured deposits - medium sand - fine sand - silt/mud - clay - carbonates (beyond ...
... depositional environment. E.g. (above) Nearshore - waves crashing on beaches > fairly high energy -> coarse textured deposits (pebbles/sand); offshore -> progressively lower energy environments -> progressively finer textured deposits - medium sand - fine sand - silt/mud - clay - carbonates (beyond ...
USGS Open-File Report 98-354
... This digital map is based on the 1952−1957 mapping that was released in earlier paper maps (Bonilla, 1965, 1971), modified as described below. The revisions of the 1971 map are of four general types: 1) increase in area of artificial fill near San Francisco Bay shoreline; 2) changes in representatio ...
... This digital map is based on the 1952−1957 mapping that was released in earlier paper maps (Bonilla, 1965, 1971), modified as described below. The revisions of the 1971 map are of four general types: 1) increase in area of artificial fill near San Francisco Bay shoreline; 2) changes in representatio ...
Rocks and Minerals
... cycle involves volcanic activity. Rocks are naturally formed and are made up of one or more minerals. Geologist group rocks into three categories based upon how they form. The three types of rock are Igneous, Sedimentary, and Metamorphic. Igneous rocks are volcanic in origin. When magma rises throug ...
... cycle involves volcanic activity. Rocks are naturally formed and are made up of one or more minerals. Geologist group rocks into three categories based upon how they form. The three types of rock are Igneous, Sedimentary, and Metamorphic. Igneous rocks are volcanic in origin. When magma rises throug ...
Coasts - Mulberry Education Centre
... Beach materials may come from eroded cliffs, river deposits and sediment carried by waves. The composition and size of the materials on the beach vary greatly. − The composition of materials depends on ...
... Beach materials may come from eroded cliffs, river deposits and sediment carried by waves. The composition and size of the materials on the beach vary greatly. − The composition of materials depends on ...
relative age dating summary
... Principle of Original Lateral Continuity – Sedimentary rock layers, and lava flows, extend laterally in all directions until they thin to their termination (pinch out) or reach the edges of their basins of deposition. Principle of Unconformities – An unconformity is a rock surface that represents a ...
... Principle of Original Lateral Continuity – Sedimentary rock layers, and lava flows, extend laterally in all directions until they thin to their termination (pinch out) or reach the edges of their basins of deposition. Principle of Unconformities – An unconformity is a rock surface that represents a ...
Deflation Abrasion
... desert regions, oases sometimes are found in deep blowouts that were formed by deflation. ...
... desert regions, oases sometimes are found in deep blowouts that were formed by deflation. ...
Granitization of the Basic Volcanic Rocks in the Contact Aureole of
... The comparison of the chemical composition of primary basic volcanics of the Vakhtalkinskaya Sequence and their transformation products indicates that metasomatic alteration and magmatic replacement chemically correspond to siliceous–alkaline metasomatism (granitization) and cause sequential and une ...
... The comparison of the chemical composition of primary basic volcanics of the Vakhtalkinskaya Sequence and their transformation products indicates that metasomatic alteration and magmatic replacement chemically correspond to siliceous–alkaline metasomatism (granitization) and cause sequential and une ...
Chapter 5 Igneous Rocks
... • Type of igneous rock that forms depends on the composition of the magma • Magma – often slushy mix of molten rock, dissolved gases, mineral crystals • Common elements present in magma are same major elements that are in Earth’s crust: ...
... • Type of igneous rock that forms depends on the composition of the magma • Magma – often slushy mix of molten rock, dissolved gases, mineral crystals • Common elements present in magma are same major elements that are in Earth’s crust: ...
Igneous Rocks
... that form below the Earth’s surface are called intrusive igneous rocks (or plutonic). ...
... that form below the Earth’s surface are called intrusive igneous rocks (or plutonic). ...
Rocks and Weathering - 6thgrade
... weathering. Water weathers rock by dissolving it. Oxygen – the oxygen gas in air is an important cause of chemical weathering. Ex: rust on a bicycle. Carbon Dioxide – it dissolves in rainwater and in water that sinks through air pockets in the soil. ...
... weathering. Water weathers rock by dissolving it. Oxygen – the oxygen gas in air is an important cause of chemical weathering. Ex: rust on a bicycle. Carbon Dioxide – it dissolves in rainwater and in water that sinks through air pockets in the soil. ...
Springfield Plateau
... The West Gulf Coastal Plain is a south sloping plain of gently rolling hills and can be divided into two areas based on the age of the rocks. The area in orange consists of Tertiary clays, sands and silts with lignite deposits and Quaternary gravels, sands and clays. The area in green consists of Cr ...
... The West Gulf Coastal Plain is a south sloping plain of gently rolling hills and can be divided into two areas based on the age of the rocks. The area in orange consists of Tertiary clays, sands and silts with lignite deposits and Quaternary gravels, sands and clays. The area in green consists of Cr ...
What is rock?
... naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals and organic matter. ROCKS ARE ALWAYS CHANGING! The continual process by which new rocks forms from old rock rock material is called the _______ cycle ________. ...
... naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals and organic matter. ROCKS ARE ALWAYS CHANGING! The continual process by which new rocks forms from old rock rock material is called the _______ cycle ________. ...
Ch 15 note taking worksheet
... 1. When all the atoms in a substance are alike, the substance is an _______________________. 2. A _______________________ is a substance with two or more elements combined in a ...
... 1. When all the atoms in a substance are alike, the substance is an _______________________. 2. A _______________________ is a substance with two or more elements combined in a ...
4. The States of Matter
... • Know the correct words for the changes of state between a solid, a liquid and a gas • Be able to draw the particle pictures for these changes of state • Know what effect the changes of state have on the speed of motion of the particles and how tightly held together they are ...
... • Know the correct words for the changes of state between a solid, a liquid and a gas • Be able to draw the particle pictures for these changes of state • Know what effect the changes of state have on the speed of motion of the particles and how tightly held together they are ...
This is another Regents Review Packet to help you.
... 6. How do INTRUSIVE and EXTRUSIVE igneous rocks differ? 7. Which of the above igneous rock type would have NO CRYSTALS? ___________________ LARGE CRYSTALS?_____________ 8. What are the 2 main categories of sedimentary rocks? (use the ESRTs) 9. How are the clastic (fragmental) sed rocks distinguished ...
... 6. How do INTRUSIVE and EXTRUSIVE igneous rocks differ? 7. Which of the above igneous rock type would have NO CRYSTALS? ___________________ LARGE CRYSTALS?_____________ 8. What are the 2 main categories of sedimentary rocks? (use the ESRTs) 9. How are the clastic (fragmental) sed rocks distinguished ...
Clastic rock

Clastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus, chunks and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks by physical weathering. Geologists use the term clastic with reference to sedimentary rocks as well as to particles in sediment transport whether in suspension or as bed load, and in sediment deposits.