A connected circuit that consists of e elements connected to each
... We can measure the current of any circuit element by adding an ammeter in series with that element. An ideal ammeter is equivalent to a short circuit and does not change the value of the current. ...
... We can measure the current of any circuit element by adding an ammeter in series with that element. An ideal ammeter is equivalent to a short circuit and does not change the value of the current. ...
Electrical Circuits
... called resistance. The resistor may also be called the load and is the part of the circuit that converts the electrical energy into another form. (Such as light bulbs). Resistance is measured in ohms. An ohm is equivalent to one volt per ampere. The source of current is also the voltage. The switch ...
... called resistance. The resistor may also be called the load and is the part of the circuit that converts the electrical energy into another form. (Such as light bulbs). Resistance is measured in ohms. An ohm is equivalent to one volt per ampere. The source of current is also the voltage. The switch ...
PSpiceAssignments1
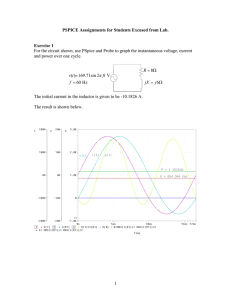
... In probe, select Plot control and Add Plot to create two graphs on the screen. Select Xaxis and set the range to change the frequency axis scale to 350 450 Hz. Using Add Trace plot P and Q with the trace expressions given by (2) and (3). Use Plot Control, select plot and down key to switch to the lo ...
... In probe, select Plot control and Add Plot to create two graphs on the screen. Select Xaxis and set the range to change the frequency axis scale to 350 450 Hz. Using Add Trace plot P and Q with the trace expressions given by (2) and (3). Use Plot Control, select plot and down key to switch to the lo ...
Lec #10 ppt
... 3. Be sure to put your discussion section leader’s name on your homework to facilitate its return to you. 4. HW 5 is due at 12:00 noon Tuesday Oct. 4 in 42/100 boxes in 240 Cory. Solutions will be put on top of the boxes at 1 pm that day. 5. Midterm 1 will not include a problem on 2nd-order transien ...
... 3. Be sure to put your discussion section leader’s name on your homework to facilitate its return to you. 4. HW 5 is due at 12:00 noon Tuesday Oct. 4 in 42/100 boxes in 240 Cory. Solutions will be put on top of the boxes at 1 pm that day. 5. Midterm 1 will not include a problem on 2nd-order transien ...
Electrical Circuits
... one after another • Example: old christmas tree lights • If one light goes out All go out • One load effects the current in the loads after it. (example– lights will get dimmer one after another) ...
... one after another • Example: old christmas tree lights • If one light goes out All go out • One load effects the current in the loads after it. (example– lights will get dimmer one after another) ...
Problem 3.67 For the circuit in Fig. P3.66, find the Thévenin
... Problem 3.67 For the circuit in Fig. P3.66, find the Thévenin equivalent circuit as seen by the 6-Ω resistor connected between terminals (c, d) as if the 6-Ω resistor is a load resistor connected to (but external to) the circuit. Determine the current flowing through that resistor. 4A ...
... Problem 3.67 For the circuit in Fig. P3.66, find the Thévenin equivalent circuit as seen by the 6-Ω resistor connected between terminals (c, d) as if the 6-Ω resistor is a load resistor connected to (but external to) the circuit. Determine the current flowing through that resistor. 4A ...
Slide 1
... Capacitors Capacitors are components that are used to store an electrical charge and are used in timer circuits. A capacitor may be used with a resistor to produce a timer. Sometimes capacitors are used to smooth a current in a circuit as they can prevent false triggering of other components such as ...
... Capacitors Capacitors are components that are used to store an electrical charge and are used in timer circuits. A capacitor may be used with a resistor to produce a timer. Sometimes capacitors are used to smooth a current in a circuit as they can prevent false triggering of other components such as ...
Kit 7. 3V FM TRANSMITTER
... microphone from the base voltage of the transistor and only allows alternating current (AC) signals to pass. The tank (LC) circuit: every Tx needs an oscillator to generate the radio Frequency (RF) carrier waves. The tank (LC) circuit, the BC547 and the feedback 5pF capacitor are the oscillator in t ...
... microphone from the base voltage of the transistor and only allows alternating current (AC) signals to pass. The tank (LC) circuit: every Tx needs an oscillator to generate the radio Frequency (RF) carrier waves. The tank (LC) circuit, the BC547 and the feedback 5pF capacitor are the oscillator in t ...
Activity 1.2.4 Circuit Calculations Introduction
... Regardless of circuit complexity, circuit designers as well as users need to be able to apply basic electrical theories to circuits in order to verify safe operation and troubleshoot unexpected circuit failure. In this activity you will gain experience applying Ohm’s law and Kirchhoff’s voltage and ...
... Regardless of circuit complexity, circuit designers as well as users need to be able to apply basic electrical theories to circuits in order to verify safe operation and troubleshoot unexpected circuit failure. In this activity you will gain experience applying Ohm’s law and Kirchhoff’s voltage and ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.