Circuit Simulations Activity
... 4. Construct a circuit with a switch, 2 light bulbs in series, a voltmeter, an ammeter and a battery and then short circuit the resistors so the closed loop with the battery is complete without any resistance. Place the ammeter in different locations and measure the various currents. Press visualize ...
... 4. Construct a circuit with a switch, 2 light bulbs in series, a voltmeter, an ammeter and a battery and then short circuit the resistors so the closed loop with the battery is complete without any resistance. Place the ammeter in different locations and measure the various currents. Press visualize ...
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENT
... 3. Power factor of an ac circuit is 0.5. What will be the phase difference between voltage and current in the circuit? 4. Which device will you use to step up/ step down a.c voltage? 5. The e.m.f of ac source is given by the expression E = 300 sin 314 t volts. Write the values of an peak voltage and ...
... 3. Power factor of an ac circuit is 0.5. What will be the phase difference between voltage and current in the circuit? 4. Which device will you use to step up/ step down a.c voltage? 5. The e.m.f of ac source is given by the expression E = 300 sin 314 t volts. Write the values of an peak voltage and ...
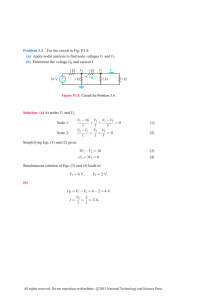
Problem 3.4 For the circuit in Fig. P3.4: (a) Apply nodal analysis to
... Problem 3.4 For the circuit in Fig. P3.4: (a) Apply nodal analysis to find node voltages V1 and V2 . (b) Determine the voltage VR and current I. V1 ...
... Problem 3.4 For the circuit in Fig. P3.4: (a) Apply nodal analysis to find node voltages V1 and V2 . (b) Determine the voltage VR and current I. V1 ...
... 1) Calculate the two break frequencies using the given values. Measure the two break frequencies by finding the points where v0 / vi = 0.7 . Section 5.6 of GIL provides further instructions if needed. Although any amplitude input signal can be used a good recommended signal is 10 V (p-p). The measur ...
Review Test #6: Electric Circuits
... and that a battery gives charge a voltage while voltage is lost when a charge passes through an electronic component like a bulb or resistor. Know why a light bulb lights immediately when connected in a circuit. Know current (I) is the rate of charge flow measured in Amps (A) and be able to calculat ...
... and that a battery gives charge a voltage while voltage is lost when a charge passes through an electronic component like a bulb or resistor. Know why a light bulb lights immediately when connected in a circuit. Know current (I) is the rate of charge flow measured in Amps (A) and be able to calculat ...
MONOLITHIC PHASE LOCKED LOOPS (PLL IC 565)
... output voltage in order to stabilize the VCO frequency. ...
... output voltage in order to stabilize the VCO frequency. ...
here
... If one load is broken or missing, charges will still run through the other branches. So, the loads on those branches will keep working. ...
... If one load is broken or missing, charges will still run through the other branches. So, the loads on those branches will keep working. ...
university of oslo faculty of mathematics and natural sciences
... Figure 4 shows a typical transistor amplifier. To secure the circuit against wrongful wiring of the battery, we have inserted a silicon diode D1 (1N4002) in the supply line. The transistor has a current gain β = 200. All questions in task 4 are based on the circuit shown in Figure 4. The following v ...
... Figure 4 shows a typical transistor amplifier. To secure the circuit against wrongful wiring of the battery, we have inserted a silicon diode D1 (1N4002) in the supply line. The transistor has a current gain β = 200. All questions in task 4 are based on the circuit shown in Figure 4. The following v ...
RLC Circuit SP222
... on one plate of the capacitor will flow to the other, through the resistor and the inductor. If the resistance in the circuit is not too large, the capacitor will become charged again as a result of this flow, but the magnitude of the charge on each plate will be smaller than it was originally, and ...
... on one plate of the capacitor will flow to the other, through the resistor and the inductor. If the resistance in the circuit is not too large, the capacitor will become charged again as a result of this flow, but the magnitude of the charge on each plate will be smaller than it was originally, and ...
9 - Series and Parallel Circuits
... • A parallel circuit is when the elements in a circuit are connected in such a way that there is more than one pathway for the current to flow. • The cells are connected side by side, or in parallel, to increase the electric charge. • The electrons flow through only one cell before passing through t ...
... • A parallel circuit is when the elements in a circuit are connected in such a way that there is more than one pathway for the current to flow. • The cells are connected side by side, or in parallel, to increase the electric charge. • The electrons flow through only one cell before passing through t ...
1 1 1 1
... entering any point will equal the sum of all currents leaving that point. IT= I1+I2+I3+IN ...
... entering any point will equal the sum of all currents leaving that point. IT= I1+I2+I3+IN ...
MCQs from here
... S1: At the resonant frequency the impedance of a series R-L-C circuit is zero S2: In a parallel G-L-C circuit, increasing the conductance G results in increase in its Q ...
... S1: At the resonant frequency the impedance of a series R-L-C circuit is zero S2: In a parallel G-L-C circuit, increasing the conductance G results in increase in its Q ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.