Quality factor of components and approximate analysis of high
... usual ω 0 = 1 / LC . We will use these ideas shortly in more complicated resonant circuits. When one uses the inductor and capacitor models of figures 1b and 2b, the circuit models for the parallel- and series-tuned circuits have the configurations of figures За and 3b, respectively. These models ha ...
... usual ω 0 = 1 / LC . We will use these ideas shortly in more complicated resonant circuits. When one uses the inductor and capacitor models of figures 1b and 2b, the circuit models for the parallel- and series-tuned circuits have the configurations of figures За and 3b, respectively. These models ha ...
Homework9
... 12. (2 points) A voltage source of 10 V is connected to a series RC circuit where R = 2.0 × 106 Ω, and C = 3.0 µF. Find the amount of time required for the current in the circuit to decay to 5% of its original value. Hint: This is the same amount of time for the capacitor to reach 95% of its maximum ...
... 12. (2 points) A voltage source of 10 V is connected to a series RC circuit where R = 2.0 × 106 Ω, and C = 3.0 µF. Find the amount of time required for the current in the circuit to decay to 5% of its original value. Hint: This is the same amount of time for the capacitor to reach 95% of its maximum ...
Instrumentation and Resistor Circuits Physics 517/617 Experiment 1
... and compare with the scopes spec sheet. You can use a resistor divider network to measure R, and a capacitor divider to measure C. 5) Design and build a circuit with the following specs: a) four or more resistors (all different) resistors in series and parallel b) circuit draws between 10 and 50 mil ...
... and compare with the scopes spec sheet. You can use a resistor divider network to measure R, and a capacitor divider to measure C. 5) Design and build a circuit with the following specs: a) four or more resistors (all different) resistors in series and parallel b) circuit draws between 10 and 50 mil ...
RLC Circuits Note
... the oscillator frequency to find the half-power frequencies and calculate the Q from the measurements. (Note: At the half-power frequencies the output voltage is smaller than the output at resonance by a factor of 1/√2.) Calculate and measure the ratio of input and output voltages at resonance. You ...
... the oscillator frequency to find the half-power frequencies and calculate the Q from the measurements. (Note: At the half-power frequencies the output voltage is smaller than the output at resonance by a factor of 1/√2.) Calculate and measure the ratio of input and output voltages at resonance. You ...
Electric Circuit`s
... 2 Resistors two and three are connected in parallel to each other. They are then connected in series to resistor four. This combination is in series to resistor one. 3 Resistors two and three are connected in series to each other. They are connected in parallel to resistor four. This combination is ...
... 2 Resistors two and three are connected in parallel to each other. They are then connected in series to resistor four. This combination is in series to resistor one. 3 Resistors two and three are connected in series to each other. They are connected in parallel to resistor four. This combination is ...
Wave, Filters
... • The rate at which energy is converted into another form (i.e. heat, motion) • P=V*I ...
... • The rate at which energy is converted into another form (i.e. heat, motion) • P=V*I ...
Unit 2
... 2. A parallel circuit has two resistors, one is 2 Ω the other is 3Ω what is the total resistance of the circuit? 3. Three resistors are in parallel (three seperate branches) their resitances are 2Ω,2Ω and 1 Ω what is the resistance of the circuit? ...
... 2. A parallel circuit has two resistors, one is 2 Ω the other is 3Ω what is the total resistance of the circuit? 3. Three resistors are in parallel (three seperate branches) their resitances are 2Ω,2Ω and 1 Ω what is the resistance of the circuit? ...
H parameter equivalent circuit
... The input circuit appears as a resistance h11 in series with a voltage generator h12 v2. The output circuit involves two components ; a current generator h21 i1 and shunt resistance h22. ...
... The input circuit appears as a resistance h11 in series with a voltage generator h12 v2. The output circuit involves two components ; a current generator h21 i1 and shunt resistance h22. ...
Circuits and Circuit Diagrams
... Electric current is the same through each device / resistor / bulb. (I = V/Rtotal) Current stays the same across all resistors. ...
... Electric current is the same through each device / resistor / bulb. (I = V/Rtotal) Current stays the same across all resistors. ...
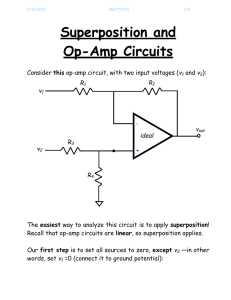
Superposition and
... Likewise, the remainder of the circuit is simply the noninverting amplifier, where: ...
... Likewise, the remainder of the circuit is simply the noninverting amplifier, where: ...
Homework
... 2. The opposition to the flow of electricity in a circuit is called _____________________. 3. If the switch in a circuit is turned 'OFF,' then the circuit is ______________________. 4. Resistance to the flow of electricity is measured in ______________________. 5. If a circuit is open, then there is ...
... 2. The opposition to the flow of electricity in a circuit is called _____________________. 3. If the switch in a circuit is turned 'OFF,' then the circuit is ______________________. 4. Resistance to the flow of electricity is measured in ______________________. 5. If a circuit is open, then there is ...
Capacitor Self
... Equipment Required: • Agilent 54600 - Series Oscilloscope • Agilent 33120A - Function/Arb Generator Purpose: In any series circuit all elements carry the same current, and the circuit voltage is the sum of the individual voltage drops. In an a–c series circuit containing resistance, inductance, and ...
... Equipment Required: • Agilent 54600 - Series Oscilloscope • Agilent 33120A - Function/Arb Generator Purpose: In any series circuit all elements carry the same current, and the circuit voltage is the sum of the individual voltage drops. In an a–c series circuit containing resistance, inductance, and ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.