Physics 4700 HOMEWORK V Due Nov 2
... 1) The following problem is designed to familiarize you with the concept of amplitude modulation (Simpson P118-126). This concept is obviously crucial to the understanding of the AM radio you are about to build. The general expression for an Amplitude Modulated voltage is: V(t) = (1 + acos ω mt)(cos ...
... 1) The following problem is designed to familiarize you with the concept of amplitude modulation (Simpson P118-126). This concept is obviously crucial to the understanding of the AM radio you are about to build. The general expression for an Amplitude Modulated voltage is: V(t) = (1 + acos ω mt)(cos ...
Physics 4700 HOMEWORK V Due March 21
... 1) The following problem is designed to familiarize you with the concept of amplitude modulation (Simpson P118-126). This concept is obviously crucial to the understanding of the AM radio you are about to build. The general expression for an Amplitude Modulated voltage is: V(t) = (1 + acos ω mt)(cos ...
... 1) The following problem is designed to familiarize you with the concept of amplitude modulation (Simpson P118-126). This concept is obviously crucial to the understanding of the AM radio you are about to build. The general expression for an Amplitude Modulated voltage is: V(t) = (1 + acos ω mt)(cos ...
Resistors, Currents and All That Jazz
... The rod in the figure is made of two materials. The figure is not drawn to scale. Each conductor has a square cross section 3.00 mm on a side. The first material has a resistivity of 4.00 × 10–3 Ω · m and is 25.0 cm long, while the second material has a resistivity of 6.00 × 10–3 Ω · m and is 40.0 ...
... The rod in the figure is made of two materials. The figure is not drawn to scale. Each conductor has a square cross section 3.00 mm on a side. The first material has a resistivity of 4.00 × 10–3 Ω · m and is 25.0 cm long, while the second material has a resistivity of 6.00 × 10–3 Ω · m and is 40.0 ...
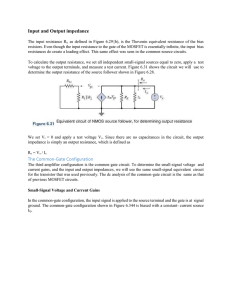
The Common-Gate Configuration
... resistors. Even though the input resistance to the gate of the MOSFET is essentially infinite, the input bias resistances do create a loading effect. This same effect was seen in the common-source circuits. To calculate the output resistance, we set all independent small-signal sources equal to zero ...
... resistors. Even though the input resistance to the gate of the MOSFET is essentially infinite, the input bias resistances do create a loading effect. This same effect was seen in the common-source circuits. To calculate the output resistance, we set all independent small-signal sources equal to zero ...
Experiment 27: AC Circuits: LR, LCR
... record. Set up your multimeter to read the 10 volt AC scale. b) Upon your instructor’s approval, turn ON the power, and adjust the output voltage to between 9.80 and 9.95 volts (or to YOUR maximum voltage if you can’t reach 9.80 V). Record this as VOUT to the accuracy of 0.05 V. c) Measure and recor ...
... record. Set up your multimeter to read the 10 volt AC scale. b) Upon your instructor’s approval, turn ON the power, and adjust the output voltage to between 9.80 and 9.95 volts (or to YOUR maximum voltage if you can’t reach 9.80 V). Record this as VOUT to the accuracy of 0.05 V. c) Measure and recor ...
ETEE3211 Fall 2004
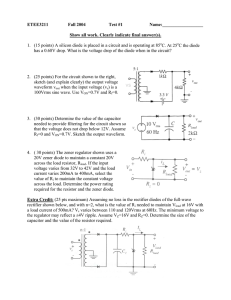
... across the load resistor, Rload. If the input voltage varies from 32V to 42V and the load current varies 200mA to 400mA, select the value of Ri to maintain the constant voltage across the load. Determine the power rating required for the resistor and the zener diode. Extra Credit: (25 pts maximum) A ...
... across the load resistor, Rload. If the input voltage varies from 32V to 42V and the load current varies 200mA to 400mA, select the value of Ri to maintain the constant voltage across the load. Determine the power rating required for the resistor and the zener diode. Extra Credit: (25 pts maximum) A ...
Electricity - Ccphysics.us
... Positive charges collect on the highest point on the ground. Intervening air breaks down and becomes ionized, capable of carrying electricity. Strike starts from the ground and joins the stroke from the cloud at about 30 feet. ...
... Positive charges collect on the highest point on the ground. Intervening air breaks down and becomes ionized, capable of carrying electricity. Strike starts from the ground and joins the stroke from the cloud at about 30 feet. ...
In a series circuit
... Current is the same in the series circuit In a series circuit, the total voltage equals the sum of the voltage across the batteries wired in series in the circuit. In a series circuit, the total resistance (in ohms) equals the sum of the resistance of each device using ...
... Current is the same in the series circuit In a series circuit, the total voltage equals the sum of the voltage across the batteries wired in series in the circuit. In a series circuit, the total resistance (in ohms) equals the sum of the resistance of each device using ...
AIC-6 AC Circuit Tools NI ELVIS
... a 2-D plot as a line along the X axis often called the real component. For a capacitor, the impedance (or more specifically, the reactance) XC is imaginary, depends on frequency and can be represented as a line along the Y axis of a 2-D plot. It is called the imaginary component. Mathematically, the ...
... a 2-D plot as a line along the X axis often called the real component. For a capacitor, the impedance (or more specifically, the reactance) XC is imaginary, depends on frequency and can be represented as a line along the Y axis of a 2-D plot. It is called the imaginary component. Mathematically, the ...
Short Version : 25. Electric Circuits
... A camera flash gets its energy from a 150-F capacitor & requires 170 V to fire. If the capacitor is charged by a 200-V source through an 18-k resistor, how long must the photographer wait between flashes? Assume the capacitor is fully charged at each flash. ...
... A camera flash gets its energy from a 150-F capacitor & requires 170 V to fire. If the capacitor is charged by a 200-V source through an 18-k resistor, how long must the photographer wait between flashes? Assume the capacitor is fully charged at each flash. ...
Circuits - cottonphysics
... • Current is divided in the branches • Resistance of individual resistors determines how much current will flow through it • So – essentially, the currents will be different through each of the resistors. ...
... • Current is divided in the branches • Resistance of individual resistors determines how much current will flow through it • So – essentially, the currents will be different through each of the resistors. ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.