Rebel Academy – Khan Academy Review
... mRNA is translated into ______________________ at the ribosome. Ribosomes are the sites where information is converted into ______________________________. The _______________________________ is a part of the nucleus where _____________________________ . The nucleolus is not a separate _____________ ...
... mRNA is translated into ______________________ at the ribosome. Ribosomes are the sites where information is converted into ______________________________. The _______________________________ is a part of the nucleus where _____________________________ . The nucleolus is not a separate _____________ ...
DNA Transcription
... The genetic code is ______________. (i.e. all organisms use this code and follow it to make proteins) Translation = Translation happens in the ___________________ 1. The strand of mRNA attaches to the ________________. 2. A ___________ molecule brings the first amino acid to the mRNA strand that is ...
... The genetic code is ______________. (i.e. all organisms use this code and follow it to make proteins) Translation = Translation happens in the ___________________ 1. The strand of mRNA attaches to the ________________. 2. A ___________ molecule brings the first amino acid to the mRNA strand that is ...
Genetic Coding in Ce..
... 5. After the DNA finishes “unzipping” and the spare DNA units join up with the rungs on the half ladders, 2 identical molecules are formed. ...
... 5. After the DNA finishes “unzipping” and the spare DNA units join up with the rungs on the half ladders, 2 identical molecules are formed. ...
Translation - Santa Susana High School
... – is "L" shaped with a 3' attachment site for an AA and a loop on the other side that carries the anticodon • each tRNA is specific for the AA it attaches to • 45 different versions in the cytoplasm at all times that correspond to the different AAs – should be 61 for the different codons – a few can ...
... – is "L" shaped with a 3' attachment site for an AA and a loop on the other side that carries the anticodon • each tRNA is specific for the AA it attaches to • 45 different versions in the cytoplasm at all times that correspond to the different AAs – should be 61 for the different codons – a few can ...
Transcription and Translation
... strand moves like an assembly line, releasing the first codon and anticodon. ...
... strand moves like an assembly line, releasing the first codon and anticodon. ...
Translation - Crestwood Local Schools
... the process of matching amino acids to corresponding sets of three bases (codons) and linking them into a protein. ...
... the process of matching amino acids to corresponding sets of three bases (codons) and linking them into a protein. ...
Translation
... mRNA= blueprint for one room of building Protein= actual bricks that make up the building Nucleus = boss’ office Ribosome = job site (where the building is actually built) ...
... mRNA= blueprint for one room of building Protein= actual bricks that make up the building Nucleus = boss’ office Ribosome = job site (where the building is actually built) ...
Protein Synthesis: Transcription
... Just like the alphabet, 26 letters can make more than 26 words Letters of RNA are put together in different ways. Codon: three nucleotide sequence which codes for the insertion of a unique amino acid Language of the genetic code Multiple codons for the same amino acid Anticodon: on one end of ...
... Just like the alphabet, 26 letters can make more than 26 words Letters of RNA are put together in different ways. Codon: three nucleotide sequence which codes for the insertion of a unique amino acid Language of the genetic code Multiple codons for the same amino acid Anticodon: on one end of ...
Chapter 15: PowerPoint
... enzyme and the sigma factor which is required for transcription initiation ...
... enzyme and the sigma factor which is required for transcription initiation ...
BIOL 1107 - Chapter 15
... enzyme and the sigma factor which is required for transcription initiation ...
... enzyme and the sigma factor which is required for transcription initiation ...
The Nature of Genes The Nature of Genes The Nature of Genes The
... component of the ribosome which forms peptide bonds between amino acids ...
... component of the ribosome which forms peptide bonds between amino acids ...
Cells
... • 1. The structural, functional and biological unit of all organisms. • 2. An autonomous self-replicating unit that may exist as functional independent unit of life (as in the case of unicellular organism), or as sub-unit in a multicellular organism (such as in plants and animals) that is specialize ...
... • 1. The structural, functional and biological unit of all organisms. • 2. An autonomous self-replicating unit that may exist as functional independent unit of life (as in the case of unicellular organism), or as sub-unit in a multicellular organism (such as in plants and animals) that is specialize ...
REVIEW SHEET FOR RNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
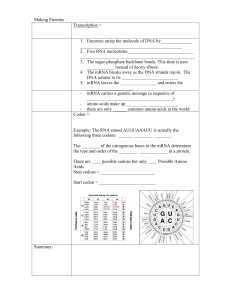
... Codon (including start and stop): Three sequential bases of mRNA (usually codes for an amino acid)- Start=AUGStop=UAA, UAG, UGA- 64 possibilities -Group of 3 nucleotides in mRNA that specifies an amino acid -Group that can be thought of as one of the words of the genetic message -The sequence of 3 n ...
... Codon (including start and stop): Three sequential bases of mRNA (usually codes for an amino acid)- Start=AUGStop=UAA, UAG, UGA- 64 possibilities -Group of 3 nucleotides in mRNA that specifies an amino acid -Group that can be thought of as one of the words of the genetic message -The sequence of 3 n ...
13.2 Ribosomes and Protein Synthesis
... The methionine codon AUG serves as the “start” codon for protein synthesis. There are three “stop” codons. UAA, UAG, and UGA are “stop” codons ...
... The methionine codon AUG serves as the “start” codon for protein synthesis. There are three “stop” codons. UAA, UAG, and UGA are “stop” codons ...
Bio102 Problems
... C. Okazaki fragment D. tRNA E. Amino acids and nucleic acids are never covalently connected. 17. Release Factor is needed to stop A. transcription. B. polyadenylation. C. replication. D. splicing. E. translation. 18. VEGF is a molecule that is secreted into the blood by many human cancer cells and i ...
... C. Okazaki fragment D. tRNA E. Amino acids and nucleic acids are never covalently connected. 17. Release Factor is needed to stop A. transcription. B. polyadenylation. C. replication. D. splicing. E. translation. 18. VEGF is a molecule that is secreted into the blood by many human cancer cells and i ...
Protein Synthesis Overview
... The mRNA then enters the cytoplasm and attaches to a ribosome. Translation begins at AUG, the start codon. Each transfer RNA has an anticodon whose bases are complementary to a codon on the mRNA strand. The ribosome positions the start codon to attract its anticodon, which is part of the tRNA that b ...
... The mRNA then enters the cytoplasm and attaches to a ribosome. Translation begins at AUG, the start codon. Each transfer RNA has an anticodon whose bases are complementary to a codon on the mRNA strand. The ribosome positions the start codon to attract its anticodon, which is part of the tRNA that b ...
Biol 256 SI UNIT 1B_Biochem_Organic Molecules Macromolecules
... Triglycerides are transported in your blood by ____________________. Proteins Proteins and polypeptides are macromolecules composed of _________________ (unit molecule) bond together by _____________________. The difference between proteins and polypeptide is ...
... Triglycerides are transported in your blood by ____________________. Proteins Proteins and polypeptides are macromolecules composed of _________________ (unit molecule) bond together by _____________________. The difference between proteins and polypeptide is ...
Document
... mRNA; transfer RNA (tRNA) assist in polypeptide (protein) construction by bringing in the specific amino acids that string together to create the protein. Protein synthesis begins with the “unzipping” of DNA by the enzyme helicase in the nucleus. As the DNA nucleotides unbind from their partner pair ...
... mRNA; transfer RNA (tRNA) assist in polypeptide (protein) construction by bringing in the specific amino acids that string together to create the protein. Protein synthesis begins with the “unzipping” of DNA by the enzyme helicase in the nucleus. As the DNA nucleotides unbind from their partner pair ...
DNA and RNA
... • Converts/transfers information from mRNA into amino acids • Amino acids are the monomers of proteins • String amino acids together and a protein is made • 3 RNAs needed – mRNA (messenger—from nucleus to ribosome) – rRNA (ribosomal—used in the ribosome) – tRNA (transfer—transfers the codons into am ...
... • Converts/transfers information from mRNA into amino acids • Amino acids are the monomers of proteins • String amino acids together and a protein is made • 3 RNAs needed – mRNA (messenger—from nucleus to ribosome) – rRNA (ribosomal—used in the ribosome) – tRNA (transfer—transfers the codons into am ...
File
... …Then the mRNA code reads like this… UAG-CAU-GCG-UUA-ACG The enzyme RNA polymerase separates two strands of a DNA double helix and builds a strand of RNA using RNA nucleotides. Remember, RNA coding: ...
... …Then the mRNA code reads like this… UAG-CAU-GCG-UUA-ACG The enzyme RNA polymerase separates two strands of a DNA double helix and builds a strand of RNA using RNA nucleotides. Remember, RNA coding: ...
Proteins
... …Then the mRNA code reads like this… UAG-CAU-GCG-UUA-ACG The enzyme RNA polymerase separates two strands of a DNA double helix and builds a strand of RNA using RNA nucleotides. Remember, RNA coding: ...
... …Then the mRNA code reads like this… UAG-CAU-GCG-UUA-ACG The enzyme RNA polymerase separates two strands of a DNA double helix and builds a strand of RNA using RNA nucleotides. Remember, RNA coding: ...
Ribosome

The ribosome (/ˈraɪbɵˌzoʊm/) is a large and complex molecular machine, found within all living cells, that serves as the site of biological protein synthesis (translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small ribosomal subunit, which reads the RNA, and the large subunit, which joins amino acids to form a polypeptide chain. Each subunit is composed of one or more ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules and a variety of proteins. The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the translational apparatus.The sequence of DNA encoding for a protein may be copied many times into RNA chains of a similar sequence. Ribosomes can bind to an RNA chain and use it as a template for determining the correct sequence of amino acids in a particular protein. Amino acids are selected, collected and carried to the ribosome by transfer RNA (tRNA molecules), which enter one part of the ribosome and bind to the messenger RNA chain. The attached amino acids are then linked together by another part of the ribosome. Once the protein is produced, it can then fold to produce a specific functional three-dimensional structure.A ribosome is made from complexes of RNAs and proteins and is therefore a ribonucleoprotein. Each ribosome is divided into two subunits: 1. a smaller subunit which binds to a larger subunit and the mRNA pattern, and 2. a larger subunit which binds to the tRNA, the amino acids, and the smaller subunit. When a ribosome finishes reading an mRNA molecule, these two subunits split apart. Ribosomes are ribozymes, because the catalytic peptidyl transferase activity that links amino acids together is performed by the ribosomal RNA. Ribosomes are often embedded in the intercellular membranes that make up the rough endoplasmic reticulum.Ribosomes from bacteria, archaea and eukaryotes (the three domains of life on Earth) differ in their size, sequence, structure, and the ratio of protein to RNA. The differences in structure allow some antibiotics to kill bacteria by inhibiting their ribosomes, while leaving human ribosomes unaffected. In bacteria and archaea, more than one ribosome may move along a single mRNA chain at one time, each ""reading"" its sequence and producing a corresponding protein molecule. The ribosomes in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells functionally resemble many features of those in bacteria, reflecting the likely evolutionary origin of mitochondria.