In prokaryotes, replication, transcription, and translation take place
... During translation, the completed peptide chain exits the ribosome through the A ...
... During translation, the completed peptide chain exits the ribosome through the A ...
Ch. 17 DNA to Protein (Transcription and Translation)
... these travel from the nucleus to the ribosome to direct the synthesis of a specific protein Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – help form ribosomes in the cytoplasm (remember, ribosomes help with protein synthesis); reads and decodes RNA Transfer RNA (tRNA) – transport amino acids (building blocks of protein ...
... these travel from the nucleus to the ribosome to direct the synthesis of a specific protein Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – help form ribosomes in the cytoplasm (remember, ribosomes help with protein synthesis); reads and decodes RNA Transfer RNA (tRNA) – transport amino acids (building blocks of protein ...
13 Transcription and translation
... 1. Describe how genetic information is transcribed into sequences of bases in RNA molecules and is finally translated into sequences of amino acids in proteins 2. Explain how restriction enzymes cut DNA molecules into smaller fragments and how ligases reassemble them 3. perform simulations to demons ...
... 1. Describe how genetic information is transcribed into sequences of bases in RNA molecules and is finally translated into sequences of amino acids in proteins 2. Explain how restriction enzymes cut DNA molecules into smaller fragments and how ligases reassemble them 3. perform simulations to demons ...
File
... » When the ribosome reaches a termination codon on the mRNA (UAA, UAG or UGA) it will stop the translation process » The chain of amino acids, called a polypeptide, will be released. It then undergoes some posttranslational processing in the golgi bodies and is transported via the endoplasmic retic ...
... » When the ribosome reaches a termination codon on the mRNA (UAA, UAG or UGA) it will stop the translation process » The chain of amino acids, called a polypeptide, will be released. It then undergoes some posttranslational processing in the golgi bodies and is transported via the endoplasmic retic ...
Document
... resistance of adverse conditions such as high temperature, radiation, toxic chemicals. Volutin is granular intracellular structure, made of inorganic polymetaphosphates. ...
... resistance of adverse conditions such as high temperature, radiation, toxic chemicals. Volutin is granular intracellular structure, made of inorganic polymetaphosphates. ...
Genes - University of Arizona | Ecology and Evolutionary Biology
... (Small and large subunits also have S names: 16S, 18S, 23S, etc. S is for Svedberg units describing how fast something moves in a centrifugal field.) ...
... (Small and large subunits also have S names: 16S, 18S, 23S, etc. S is for Svedberg units describing how fast something moves in a centrifugal field.) ...
Eubacteria
... Cell Wall: The rigid outermost cell layer found in plants and certain algae, and bacteria. Provides structure to eubacteria cell. Cell Membrane: The cell membrane is a selectively permeable outer layer of the cell. This means that the cell wall will only let certain substances in or out of the cell. ...
... Cell Wall: The rigid outermost cell layer found in plants and certain algae, and bacteria. Provides structure to eubacteria cell. Cell Membrane: The cell membrane is a selectively permeable outer layer of the cell. This means that the cell wall will only let certain substances in or out of the cell. ...
Stem Cells, Cancer, and Human Health
... A. Occur when part of a chromosome is missing B. Occur when one base is changed to another C. Don’t change the structure of the protein D. Include insertion and deletion mutants ...
... A. Occur when part of a chromosome is missing B. Occur when one base is changed to another C. Don’t change the structure of the protein D. Include insertion and deletion mutants ...
Protein Synthesis
... What is the name of the enzyme that unwinds DNA? What is the process where a secret message goes ACROSS the nuclear membrane? What carries the sequence from the DNA out of the nucleus? How many strands are copied on the original DNA molecule? What happens to the DNA once the ...
... What is the name of the enzyme that unwinds DNA? What is the process where a secret message goes ACROSS the nuclear membrane? What carries the sequence from the DNA out of the nucleus? How many strands are copied on the original DNA molecule? What happens to the DNA once the ...
File - Mrs. LeCompte
... Those polypeptides that are for secretion are then fed into the lumen of the ER, where they are folded and modified by the addition of sugars, phosphates, or lipids o Since prokaryotes do not have ER, this is a limitation on their use in genetic engineering of eukaryotic proteins ...
... Those polypeptides that are for secretion are then fed into the lumen of the ER, where they are folded and modified by the addition of sugars, phosphates, or lipids o Since prokaryotes do not have ER, this is a limitation on their use in genetic engineering of eukaryotic proteins ...
DNA RNA Proteins - Aurora City Schools
... P site tRNA, moves to the E site and leaves the ribosome. The ribosome then translocates (moves) the tRNA in the A site, with its attached polypeptide, to the P site. Codon and anticodon remain bonded, and the mRNA and tRNA move as a unit Movement brings into the A site the next mRNA codon t ...
... P site tRNA, moves to the E site and leaves the ribosome. The ribosome then translocates (moves) the tRNA in the A site, with its attached polypeptide, to the P site. Codon and anticodon remain bonded, and the mRNA and tRNA move as a unit Movement brings into the A site the next mRNA codon t ...
CHEM 642-09 Powerpoint
... The standard one-letter abbreviation for each amino acid is presented below its three-letter abbreviation (see Panel 3–1, pp. 132–133, for the full name of each amino acid and its structure). By convention, codons are always written with the 5'- terminal nucleotide to the left. Note that most amino ...
... The standard one-letter abbreviation for each amino acid is presented below its three-letter abbreviation (see Panel 3–1, pp. 132–133, for the full name of each amino acid and its structure). By convention, codons are always written with the 5'- terminal nucleotide to the left. Note that most amino ...
The Mechanism of Translation II
... represent the 20 amino acids in proteins • Nonoverlapping codons - Each base is part of at most one codon in nonoverlapping codons - In an overlapping code - one base may be part of two or even three codons ...
... represent the 20 amino acids in proteins • Nonoverlapping codons - Each base is part of at most one codon in nonoverlapping codons - In an overlapping code - one base may be part of two or even three codons ...
Chapter 17 * from gene to protein
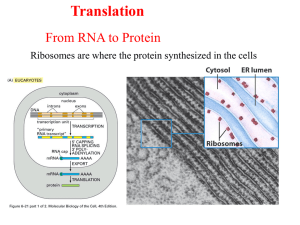
... SITES OF TRANSLATION Ribosomes consist of 2 subunits, large and small; they are composed of rRNA and proteins ...
... SITES OF TRANSLATION Ribosomes consist of 2 subunits, large and small; they are composed of rRNA and proteins ...
Genes chapt15
... ribosome for incorporation into a polypeptide – aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases add amino acids to the acceptor arm of tRNA – the anticodon loop contains 3 nucleotides complementary to mRNA codons ...
... ribosome for incorporation into a polypeptide – aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases add amino acids to the acceptor arm of tRNA – the anticodon loop contains 3 nucleotides complementary to mRNA codons ...
DNA Transcription - Kayla snyder`s biology world
... temporarily. What is the first mRNA codon? _AUG_ Anticodon = region if tRNA that is complementary (or reverse) to the codon of the mRNA. This is where attaches. ...
... temporarily. What is the first mRNA codon? _AUG_ Anticodon = region if tRNA that is complementary (or reverse) to the codon of the mRNA. This is where attaches. ...
Document
... transferred onto it, displacing the AMP. The aminoacyl-tRNA is released from the enzyme. ...
... transferred onto it, displacing the AMP. The aminoacyl-tRNA is released from the enzyme. ...
Practice Questions
... A really bad doctor took X-Rays of a patient’s leg. The doctor didn’t give the patient a protective lead apron to wear over the genital region and the patient’s gametes (sperm or egg cells) were severely mutated as a result of the high powered rays. Will this mutation be passed down the offspring? T ...
... A really bad doctor took X-Rays of a patient’s leg. The doctor didn’t give the patient a protective lead apron to wear over the genital region and the patient’s gametes (sperm or egg cells) were severely mutated as a result of the high powered rays. Will this mutation be passed down the offspring? T ...
PPT NOTES_AP Biology Chapter 17 Notes
... • Enzymes in the eukaryotic nucleus _________________ pre-mRNA before the genetic messages are dispatched to the cytoplasm • During RNA processing, both ___________ of the primary transcript are usually altered • Also, usually some interior parts of the molecule are ________________, and the other p ...
... • Enzymes in the eukaryotic nucleus _________________ pre-mRNA before the genetic messages are dispatched to the cytoplasm • During RNA processing, both ___________ of the primary transcript are usually altered • Also, usually some interior parts of the molecule are ________________, and the other p ...
Q. No. 1. How can RNA be distinguished from DNA?
... into a specific amino acid chain, which consists of two subunits. These subunits are made up of ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and together contain up to eighty-two specific proteins assembled in a precise sequence. This assembled ribosome displays a series of small groves, tunnels, and platforms, where the ...
... into a specific amino acid chain, which consists of two subunits. These subunits are made up of ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and together contain up to eighty-two specific proteins assembled in a precise sequence. This assembled ribosome displays a series of small groves, tunnels, and platforms, where the ...
Biol 115 DNA, the Thread of Life
... Translation Begins After the Assembly of a Complex Structure When translation begins, the small subunit of the ribosome and an initiator tRNA molecule assemble on the mRNA transcript. The small subunit of the ribosome has three binding sites: an amino acid site (A), a polypeptide site (P), and an e ...
... Translation Begins After the Assembly of a Complex Structure When translation begins, the small subunit of the ribosome and an initiator tRNA molecule assemble on the mRNA transcript. The small subunit of the ribosome has three binding sites: an amino acid site (A), a polypeptide site (P), and an e ...
Document
... Amino acid in P site is transferred to amino acid in A site. Translocation requires GTP and EF-G. EF-G enters A site, shifting tRNAs. When EF-G leaves, A site is open for a new ternary complex. A new ternary complex associates with A site, and deacylated tRNA leaves from E site. ...
... Amino acid in P site is transferred to amino acid in A site. Translocation requires GTP and EF-G. EF-G enters A site, shifting tRNAs. When EF-G leaves, A site is open for a new ternary complex. A new ternary complex associates with A site, and deacylated tRNA leaves from E site. ...
Slide 1
... In vitro incubation of a known number of nucleotides In vitro incubation of three components of protein synthesis Recognition of the RNA complex with radioactivity ...
... In vitro incubation of a known number of nucleotides In vitro incubation of three components of protein synthesis Recognition of the RNA complex with radioactivity ...
Chapter 12
... • RNA can base-pair with single-stranded DNA (adenine pairs with uracil instead of thymine) and also can fold over and base-pair with itself. ...
... • RNA can base-pair with single-stranded DNA (adenine pairs with uracil instead of thymine) and also can fold over and base-pair with itself. ...
walk the dogma notes - Nutley Public Schools
... - Structure- Linear single strand - Function- Carries genetic info from the DNA in the nucleus to the cytoplasm 2) Transfer RNA (tRNA) - Structure: Hairpin Loop - Function: Binds and carries specific amino acids 3) Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) - Structure: Globular - Function: Combines with proteins to form ...
... - Structure- Linear single strand - Function- Carries genetic info from the DNA in the nucleus to the cytoplasm 2) Transfer RNA (tRNA) - Structure: Hairpin Loop - Function: Binds and carries specific amino acids 3) Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) - Structure: Globular - Function: Combines with proteins to form ...
Ribosome

The ribosome (/ˈraɪbɵˌzoʊm/) is a large and complex molecular machine, found within all living cells, that serves as the site of biological protein synthesis (translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small ribosomal subunit, which reads the RNA, and the large subunit, which joins amino acids to form a polypeptide chain. Each subunit is composed of one or more ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules and a variety of proteins. The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the translational apparatus.The sequence of DNA encoding for a protein may be copied many times into RNA chains of a similar sequence. Ribosomes can bind to an RNA chain and use it as a template for determining the correct sequence of amino acids in a particular protein. Amino acids are selected, collected and carried to the ribosome by transfer RNA (tRNA molecules), which enter one part of the ribosome and bind to the messenger RNA chain. The attached amino acids are then linked together by another part of the ribosome. Once the protein is produced, it can then fold to produce a specific functional three-dimensional structure.A ribosome is made from complexes of RNAs and proteins and is therefore a ribonucleoprotein. Each ribosome is divided into two subunits: 1. a smaller subunit which binds to a larger subunit and the mRNA pattern, and 2. a larger subunit which binds to the tRNA, the amino acids, and the smaller subunit. When a ribosome finishes reading an mRNA molecule, these two subunits split apart. Ribosomes are ribozymes, because the catalytic peptidyl transferase activity that links amino acids together is performed by the ribosomal RNA. Ribosomes are often embedded in the intercellular membranes that make up the rough endoplasmic reticulum.Ribosomes from bacteria, archaea and eukaryotes (the three domains of life on Earth) differ in their size, sequence, structure, and the ratio of protein to RNA. The differences in structure allow some antibiotics to kill bacteria by inhibiting their ribosomes, while leaving human ribosomes unaffected. In bacteria and archaea, more than one ribosome may move along a single mRNA chain at one time, each ""reading"" its sequence and producing a corresponding protein molecule. The ribosomes in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells functionally resemble many features of those in bacteria, reflecting the likely evolutionary origin of mitochondria.