Ch. 17 From Gene to Protein
... Each end of a pre-mRNA molecule is modified in a particular way The 5 end receives a modified nucleotide cap The 3 end gets a poly-A tail A modified guanine nucleotide added to the 5 end ...
... Each end of a pre-mRNA molecule is modified in a particular way The 5 end receives a modified nucleotide cap The 3 end gets a poly-A tail A modified guanine nucleotide added to the 5 end ...
File
... • Nuclear envelope: double membrane that surrounds nucleus • Ribosomes (80S- EU, 70S-PRO): site of protein synthesis • Smooth ER: lipid (including steroid, hormones)synthesis • Rough ER: contains ribosomes, protein synthesis • Golgi apparatus: modification and packaging of cellular products (esp. pr ...
... • Nuclear envelope: double membrane that surrounds nucleus • Ribosomes (80S- EU, 70S-PRO): site of protein synthesis • Smooth ER: lipid (including steroid, hormones)synthesis • Rough ER: contains ribosomes, protein synthesis • Golgi apparatus: modification and packaging of cellular products (esp. pr ...
Ribosomes
... plants, fungi, protists, and bacteria. Animals have no cell walls. For plants, the cell wall is what gives the plant support and structure. Plants don't have a skeleton like animals, so the cell wall made of tough fibrous cellulose holds up the entire plant structure. Giant redwoods and sequoias sta ...
... plants, fungi, protists, and bacteria. Animals have no cell walls. For plants, the cell wall is what gives the plant support and structure. Plants don't have a skeleton like animals, so the cell wall made of tough fibrous cellulose holds up the entire plant structure. Giant redwoods and sequoias sta ...
File
... codon, the ribosome dissociates into its two subunits and falls off the mRNA (which is recycled). -- the peptide/protein chain is released by the tRNA in the P-site into the lumen of the Rough ER (if for export), or into a transition vesicle bound for the Golgi for modifications (if it is to remain ...
... codon, the ribosome dissociates into its two subunits and falls off the mRNA (which is recycled). -- the peptide/protein chain is released by the tRNA in the P-site into the lumen of the Rough ER (if for export), or into a transition vesicle bound for the Golgi for modifications (if it is to remain ...
Molecular Machines (1MB429) Exam 2011-12-21
... Answer: Initiation factor eIF4F binds to the Cap structure on the 5’ end of mRNA. The 4G subunit of 4F complex binds also to PABP proteins that interact with the 3’ poly-A sequence of mRNA. This leads to the formation of a closed mRNA loop and to a more efficient translation of mRNA. In addition, PA ...
... Answer: Initiation factor eIF4F binds to the Cap structure on the 5’ end of mRNA. The 4G subunit of 4F complex binds also to PABP proteins that interact with the 3’ poly-A sequence of mRNA. This leads to the formation of a closed mRNA loop and to a more efficient translation of mRNA. In addition, PA ...
Slides - University of Sydney
... – Bringing in one tRNA at a time, forming peptide bonds as it goes – Protein gets longer as the ribosome moves down the mRNA ...
... – Bringing in one tRNA at a time, forming peptide bonds as it goes – Protein gets longer as the ribosome moves down the mRNA ...
MIT 2006: Engineering bacteria to smell good
... Regulating the timing of expression osmY: active in stationary phase & under high osmotic pressure conditions ...
... Regulating the timing of expression osmY: active in stationary phase & under high osmotic pressure conditions ...
video slide - Mr. Patrick Wagner's Teacher Web Site
... 3. CYTOPLASMIC ORGANELLES (“tiny organs”) A. Ribosomes=not membrane-bound Are particles made of ribosomal RNA & protein. All cells (pro and eukaryote) must have! The smallest and most numerous organelle. ...
... 3. CYTOPLASMIC ORGANELLES (“tiny organs”) A. Ribosomes=not membrane-bound Are particles made of ribosomal RNA & protein. All cells (pro and eukaryote) must have! The smallest and most numerous organelle. ...
A different PowerPoint that combines the
... order of nucleotides on mRNA and have that tell us the order of amino acids within each protein • As there are 20 amino acids and only 4 different bases each nucleotide on its own cant specify the position of a different amino acid ...
... order of nucleotides on mRNA and have that tell us the order of amino acids within each protein • As there are 20 amino acids and only 4 different bases each nucleotide on its own cant specify the position of a different amino acid ...
DNA Strand 2
... stops. Every time you see three nucleotides together it is called a codon and each codon calls for a specific Amino Acid. There are only 20 amino acids in nature but there are 64 codons. T Translation is the process that occurs between the mRNA and the Ribosome. Translation is the process of transla ...
... stops. Every time you see three nucleotides together it is called a codon and each codon calls for a specific Amino Acid. There are only 20 amino acids in nature but there are 64 codons. T Translation is the process that occurs between the mRNA and the Ribosome. Translation is the process of transla ...
CHNOPS Bubblegram
... C: “Yes, he’s gone. I’ll never be able to hold my head up again. I’ve lost CHNOPS!” Z: “Look, Clifford (Zelda ALWAYS called him by his full name), there’s some big footprints. And gasp, a ransom note telling what they want in order to return CHNOPS. “ C: “Now I know I’m a’goner. How much is it for? ...
... C: “Yes, he’s gone. I’ll never be able to hold my head up again. I’ve lost CHNOPS!” Z: “Look, Clifford (Zelda ALWAYS called him by his full name), there’s some big footprints. And gasp, a ransom note telling what they want in order to return CHNOPS. “ C: “Now I know I’m a’goner. How much is it for? ...
chapter9_Sections 4-6 - (per 3) and wed 4/24 (per 2,6)
... • The protein-building information in mRNA consists of a sequence of three mRNA bases (codon); each is a code for a particular amino acid • The four bases A, C, G, and U can be combined into 64 different codons, which constitute the genetic code • Example: AUG codes for the amino acid methionine (me ...
... • The protein-building information in mRNA consists of a sequence of three mRNA bases (codon); each is a code for a particular amino acid • The four bases A, C, G, and U can be combined into 64 different codons, which constitute the genetic code • Example: AUG codes for the amino acid methionine (me ...
DNA Synthesis (Replication)
... rRNA (Ribosomal RNA) – in nucleolus gives rise to ribosomal precursors; makes Ribosome, and is the central component of the Ribosome’s protein-manufacturing machinery. ...
... rRNA (Ribosomal RNA) – in nucleolus gives rise to ribosomal precursors; makes Ribosome, and is the central component of the Ribosome’s protein-manufacturing machinery. ...
Gene regulation I Biochemistry 302
... Translation regulation in bacteria: feedback control of ribosomal proteins ...
... Translation regulation in bacteria: feedback control of ribosomal proteins ...
Translation Study Guide
... support, processing nutrients, copying a cell’s DNA, and regulating other cellular functions. Proteins are made of long chains of amino acids that fold into complex three-dimensional shapes. Each type protein has a unique amino acid sequence and a specific function in the cell. replication – the pro ...
... support, processing nutrients, copying a cell’s DNA, and regulating other cellular functions. Proteins are made of long chains of amino acids that fold into complex three-dimensional shapes. Each type protein has a unique amino acid sequence and a specific function in the cell. replication – the pro ...
tRNA, rRNA, and RNAi Transfer RNA (tRNA) Characteristics of tRNA
... • Splicing of tRNA introns different from spliceosomal introns. ...
... • Splicing of tRNA introns different from spliceosomal introns. ...
Cell Theory, Cell Structure and Cellular Transport
... They maintain the shape of the cell as well as anchoring organelles, moving the cell and controlling internal movement of structures Microtubules function in cell division and serve as a "temporary scaffolding" for other organelles. Actin filaments are thin threads that function in cell division and ...
... They maintain the shape of the cell as well as anchoring organelles, moving the cell and controlling internal movement of structures Microtubules function in cell division and serve as a "temporary scaffolding" for other organelles. Actin filaments are thin threads that function in cell division and ...
ANTIBIOTICS
... Ampicillin is a penicillin derivative that inhibits crosslinking of peptidoglycan chains in the cell wall of eubacteria. Cells growing in the presence of ampicillin synthesize weak cell walls, causing them to burst due to the high internal osmotic pressure. AmpR encoded by Mu derivatives and pBR pla ...
... Ampicillin is a penicillin derivative that inhibits crosslinking of peptidoglycan chains in the cell wall of eubacteria. Cells growing in the presence of ampicillin synthesize weak cell walls, causing them to burst due to the high internal osmotic pressure. AmpR encoded by Mu derivatives and pBR pla ...
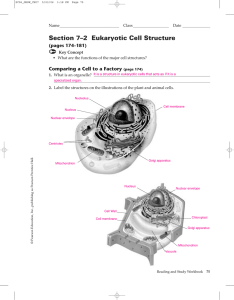
Section 7–2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
... 5. What is the function of the nucleus? It is the control center of the cell. 6. What important molecules does the nucleus contain? It contains DNA. chromatin ...
... 5. What is the function of the nucleus? It is the control center of the cell. 6. What important molecules does the nucleus contain? It contains DNA. chromatin ...
Lecture 18: Powerpoint
... The catalytic site on the large subunit catalyzes the formation of a peptide bond linking the amino acids ...
... The catalytic site on the large subunit catalyzes the formation of a peptide bond linking the amino acids ...
Example of Research Proposal
... by Scott Strobel Hypothesis What is the chirality of the tetrahedral intermediate that occurs during ribosome catalyzed peptide bond formation? How does the ribosome provide transition state stabilization of the tetrahedral intermediate ? Background Information Ribosomes are the macromolecular machi ...
... by Scott Strobel Hypothesis What is the chirality of the tetrahedral intermediate that occurs during ribosome catalyzed peptide bond formation? How does the ribosome provide transition state stabilization of the tetrahedral intermediate ? Background Information Ribosomes are the macromolecular machi ...
bomb squad and movie mania 2012
... (_____________________________). Once the messenger is done he/she will slip out through a secret tunnel in the safe (_________________________) and into the ocean (_________________________). Once in the ocean (_________________) you will need to find the underwater bomb making factory (___________ ...
... (_____________________________). Once the messenger is done he/she will slip out through a secret tunnel in the safe (_________________________) and into the ocean (_________________________). Once in the ocean (_________________) you will need to find the underwater bomb making factory (___________ ...
Protein Translation
... In any mRNA sequence, there are three ways triplet codons can be read. Each way to read the codons is called a "Reading Frame". It is very important for ribosome to find correct reading frame. If the wrong reading frame is used, translation generates a protein with the wrong amino acid sequence ...
... In any mRNA sequence, there are three ways triplet codons can be read. Each way to read the codons is called a "Reading Frame". It is very important for ribosome to find correct reading frame. If the wrong reading frame is used, translation generates a protein with the wrong amino acid sequence ...
Chapter 26
... Organic catalysts had to evolve to restrict reactions to the right time and place. The cell developed a system that would provide energy in a controlled fashion when it is needed. Proteins add speed to the process of catalysis. The first genes may have been abiotically produced RNA, whose base sequ ...
... Organic catalysts had to evolve to restrict reactions to the right time and place. The cell developed a system that would provide energy in a controlled fashion when it is needed. Proteins add speed to the process of catalysis. The first genes may have been abiotically produced RNA, whose base sequ ...
Instructor`s Manual to accompany Principles of Life
... of translation and three different stop codons can be used to halt translation. The other 60 codons code only for particular amino acids. The genetic code is redundant, but is not ambiguous. In many human genetic diseases, a single protein is missing or nonfunctional. Some diseases are caused by mut ...
... of translation and three different stop codons can be used to halt translation. The other 60 codons code only for particular amino acids. The genetic code is redundant, but is not ambiguous. In many human genetic diseases, a single protein is missing or nonfunctional. Some diseases are caused by mut ...
Ribosome

The ribosome (/ˈraɪbɵˌzoʊm/) is a large and complex molecular machine, found within all living cells, that serves as the site of biological protein synthesis (translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small ribosomal subunit, which reads the RNA, and the large subunit, which joins amino acids to form a polypeptide chain. Each subunit is composed of one or more ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules and a variety of proteins. The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the translational apparatus.The sequence of DNA encoding for a protein may be copied many times into RNA chains of a similar sequence. Ribosomes can bind to an RNA chain and use it as a template for determining the correct sequence of amino acids in a particular protein. Amino acids are selected, collected and carried to the ribosome by transfer RNA (tRNA molecules), which enter one part of the ribosome and bind to the messenger RNA chain. The attached amino acids are then linked together by another part of the ribosome. Once the protein is produced, it can then fold to produce a specific functional three-dimensional structure.A ribosome is made from complexes of RNAs and proteins and is therefore a ribonucleoprotein. Each ribosome is divided into two subunits: 1. a smaller subunit which binds to a larger subunit and the mRNA pattern, and 2. a larger subunit which binds to the tRNA, the amino acids, and the smaller subunit. When a ribosome finishes reading an mRNA molecule, these two subunits split apart. Ribosomes are ribozymes, because the catalytic peptidyl transferase activity that links amino acids together is performed by the ribosomal RNA. Ribosomes are often embedded in the intercellular membranes that make up the rough endoplasmic reticulum.Ribosomes from bacteria, archaea and eukaryotes (the three domains of life on Earth) differ in their size, sequence, structure, and the ratio of protein to RNA. The differences in structure allow some antibiotics to kill bacteria by inhibiting their ribosomes, while leaving human ribosomes unaffected. In bacteria and archaea, more than one ribosome may move along a single mRNA chain at one time, each ""reading"" its sequence and producing a corresponding protein molecule. The ribosomes in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells functionally resemble many features of those in bacteria, reflecting the likely evolutionary origin of mitochondria.