Genetics and the Human Influence on Genes
... Describe the importance of DNA Develop a scientific explanation for how chromosomes pass genetic information onto the next generation Justify an explanation for the link between genes and disease Observe similar traits in parents and offspring Understand that genes determine specific characteristics ...
... Describe the importance of DNA Develop a scientific explanation for how chromosomes pass genetic information onto the next generation Justify an explanation for the link between genes and disease Observe similar traits in parents and offspring Understand that genes determine specific characteristics ...
here - Population Genetics Group
... either directly onto the computer in the lecture theatre or into the correct Dropbox folder well before each session. Please name your files with your surname followed by the time of your talk (eg. Smith_1015.pdf). All computers are PCs. If you want to use your own computer please speak to a confere ...
... either directly onto the computer in the lecture theatre or into the correct Dropbox folder well before each session. Please name your files with your surname followed by the time of your talk (eg. Smith_1015.pdf). All computers are PCs. If you want to use your own computer please speak to a confere ...
Landscapes in Mind - The Prehistoric Society
... Mussi (Chapter 15) analyses Gravettian female figurines to assess degree of variability in formal qualities, anatomical traits, and decorative motifs Although these statues are often considered to be a homogenous group, and her data suggest the presence of a broad uniformity in production style and ...
... Mussi (Chapter 15) analyses Gravettian female figurines to assess degree of variability in formal qualities, anatomical traits, and decorative motifs Although these statues are often considered to be a homogenous group, and her data suggest the presence of a broad uniformity in production style and ...
Chapter 21~The Evolution of Populations
... Evolution Natural selection acts on trait variation, and trait variation is determined by genes. Whether or not a trait gives an advantage depends on the environment. Thus genes, traits, environment, and natural selection are all involved in microevolution. Microevolution occurs when allele fre ...
... Evolution Natural selection acts on trait variation, and trait variation is determined by genes. Whether or not a trait gives an advantage depends on the environment. Thus genes, traits, environment, and natural selection are all involved in microevolution. Microevolution occurs when allele fre ...
What is multiculturalism_definition
... What is multiculturalism? The term multiculturalism generally refers to a state of racial, cultural and ethnic diversity within the demographics of a specified place, usually at the scale of an organization such as a school, business, neighbourhood, city or nation. Some countries have official, or d ...
... What is multiculturalism? The term multiculturalism generally refers to a state of racial, cultural and ethnic diversity within the demographics of a specified place, usually at the scale of an organization such as a school, business, neighbourhood, city or nation. Some countries have official, or d ...
Reproduction - Net Start Class
... offspring, using the blueprint provided by the combination of the two individual parents. Heredity is not merely observed within single species, however. Mapping the human genome, as well as that of other species, has provided insight into how different species are related to each other. Not only ha ...
... offspring, using the blueprint provided by the combination of the two individual parents. Heredity is not merely observed within single species, however. Mapping the human genome, as well as that of other species, has provided insight into how different species are related to each other. Not only ha ...
News Network Archaeology - University of Leicester
... others who also display the trait. The similarity discrimination effect does not depend on any fixed trait: individuals cooperate selectively with others who are genetically similar to themselves, whatever traits they may display. Research has shown that the greenbeard effect can drive the evolutio ...
... others who also display the trait. The similarity discrimination effect does not depend on any fixed trait: individuals cooperate selectively with others who are genetically similar to themselves, whatever traits they may display. Research has shown that the greenbeard effect can drive the evolutio ...
Motoo Kimura
... determined by random genetic drift • Theory: Genetic variation accounts for a large fraction of observed genetic diversity • Genetic variation that does not result in fitness difference means selection cannot directly affect the frequency of the variation. Genetic variation at those sites will be hi ...
... determined by random genetic drift • Theory: Genetic variation accounts for a large fraction of observed genetic diversity • Genetic variation that does not result in fitness difference means selection cannot directly affect the frequency of the variation. Genetic variation at those sites will be hi ...
CHS H Bio Final Exam Review Sheet:
... gametes can each parent produce & what are the expected phenotypes of the offspring? What are the 3 alleles for human blood? Which of the two are codominant to each other and which is recessive? What are linked genes? What is more likely to occur the farther genes are position from one another on th ...
... gametes can each parent produce & what are the expected phenotypes of the offspring? What are the 3 alleles for human blood? Which of the two are codominant to each other and which is recessive? What are linked genes? What is more likely to occur the farther genes are position from one another on th ...
Assembly, Comparison, and Annotation of Mammalian Genomes
... Ancestral retrotransposons • Retrotransposon relics from our common ancestor with mouse and other placental mammals ...
... Ancestral retrotransposons • Retrotransposon relics from our common ancestor with mouse and other placental mammals ...
Evolution
... Individuals of all populations have the capacity to produce more offspring than the environment is able to support, so individuals must compete for resources. Individuals of a population vary in size, form, and other traits. The variant forms of a trait may be more or less adaptive under prevailing ...
... Individuals of all populations have the capacity to produce more offspring than the environment is able to support, so individuals must compete for resources. Individuals of a population vary in size, form, and other traits. The variant forms of a trait may be more or less adaptive under prevailing ...
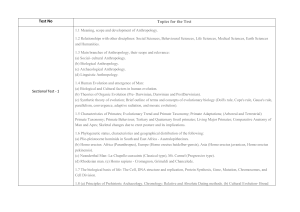
Test No Topics for the Test
... methodology (c) Tools of data collection: observation, interview, schedules, questionnaire, Case study, genealogy, life-history, oral history, secondary sources of information, participatory methods. (d) Analysis, interpretation and presentation of data. ...
... methodology (c) Tools of data collection: observation, interview, schedules, questionnaire, Case study, genealogy, life-history, oral history, secondary sources of information, participatory methods. (d) Analysis, interpretation and presentation of data. ...
Exam Format
... individuals with CF did not survive to a reproductive age, however this mutation is still maintained within the population. What is the cause of this? A) Heterozygote superiority B) Genetic drift C) Heterozygote inferiority D) Inbreeding E) Migration 18. Which of the following will not result in vio ...
... individuals with CF did not survive to a reproductive age, however this mutation is still maintained within the population. What is the cause of this? A) Heterozygote superiority B) Genetic drift C) Heterozygote inferiority D) Inbreeding E) Migration 18. Which of the following will not result in vio ...
The Genetic Engine
... “Truisms” about natural selection • Natural selection can “happen” if the trait undergoing selective pressure is genetically determined • Natural selection can only work toward traits' that increase fitness for survival and reproduction • Natural selection acts by changing the frequency of alleles ...
... “Truisms” about natural selection • Natural selection can “happen” if the trait undergoing selective pressure is genetically determined • Natural selection can only work toward traits' that increase fitness for survival and reproduction • Natural selection acts by changing the frequency of alleles ...
NATURAL SELECTION
... • When one group has more viable offspring than another. If two populations are similar but one has a variation that leads to fewer births and more deaths, you will see differential reproductive success between the populations. ...
... • When one group has more viable offspring than another. If two populations are similar but one has a variation that leads to fewer births and more deaths, you will see differential reproductive success between the populations. ...
Are humans still evolving?
... intergenerational genetic change—only two reproductive generations have passed since the discovery of the structure of DNA. Clearly, we need a different approach to study evolution within our species. Second, much of the genetic variation that we see in human populations today developed within the ...
... intergenerational genetic change—only two reproductive generations have passed since the discovery of the structure of DNA. Clearly, we need a different approach to study evolution within our species. Second, much of the genetic variation that we see in human populations today developed within the ...
Traditionally, evolutionary psychology has been focussing on expl
... sample. Despite the lack of evidence, Nettle argues that the high extraverts are more likely to change partners which increases the risk for step parenting and could therefore have negative effects on children well-being. In general, effect sizes range from small to medium. Strengths and weaknesses: ...
... sample. Despite the lack of evidence, Nettle argues that the high extraverts are more likely to change partners which increases the risk for step parenting and could therefore have negative effects on children well-being. In general, effect sizes range from small to medium. Strengths and weaknesses: ...
Molecular Evolution and Population Genetics
... Random Genetic Drift • Some changes in allele frequency are random due to genetic drift • Random genetic drift comes about because populations are not infinitely large • Only relatively few of the gametes participate in fertilization = sampling • With random genetic drift, the probability of fixati ...
... Random Genetic Drift • Some changes in allele frequency are random due to genetic drift • Random genetic drift comes about because populations are not infinitely large • Only relatively few of the gametes participate in fertilization = sampling • With random genetic drift, the probability of fixati ...
HSP3M
... Polynesian society (ie: Samoa)? Why are rites of passage meaningful? What are the usual steps for rites of passage? How does culture help to shape identity? What is the significance of the tattoo to Samoan identity? Describe the ritual. How have perspectives on tattooing changed? What is the role of ...
... Polynesian society (ie: Samoa)? Why are rites of passage meaningful? What are the usual steps for rites of passage? How does culture help to shape identity? What is the significance of the tattoo to Samoan identity? Describe the ritual. How have perspectives on tattooing changed? What is the role of ...